《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Malaria(疟疾)

Malaria Yuan Zhe MD Dept.Infectious Disease 1st Affiliated Hospital Chongqing Medical University
Malaria Yuan Zhe MD Dept. Infectious Disease 1st Affiliated Hospital Chongqing Medical University

Definition *Malaria is a parasitosis caused by plasmodia. It is transmitted to human by the bite of mosquito. Clinical feature:cyclic chill,high fever profuse sweating.In chronic illness,there are anemia splenomegaly
Definition ❖Malaria is a parasitosis caused by plasmodia. ❖It is transmitted to human by the bite of mosquito. ❖Clinical feature: cyclic chill, high fever & profuse sweating. In chronic illness, there are anemia & splenomegaly

Etiology Causative organism:Plasmodia P.Vivax:tertian malaria >P.Malariae:quartan malaria >P.Falciparum:malignant malaria >P.Ovale:tertian malaria Pathogenicity:merozoite,malarial pigment products of metabolism
Etiology ❖Causative organism: Plasmodia ➢ P. Vivax: tertian malaria ➢ P. Malariae: quartan malaria ➢ P. Falciparum: malignant malaria ➢P. Ovale: tertian malaria ❖Pathogenicity: merozoite, malarial pigment & products of metabolism

Etiology Tachysporozoite *Bradysporozoite *Merozoite *Sporozoite *Parasitemia
Etiology ❖Tachysporozoite ❖Bradysporozoite ❖Merozoite ❖Sporozoite ❖Parasitemia

Etiology Tow period: >human-whole asexual reproduction >mosquito sexual parasitic stage Two host: >human-intermediate host >mosquito-final host *notes: >clinical symptoms:erythrocytic stage >relapse:exerythrocytic stage >infectivity:sporozoite
Etiology ❖Tow period: ➢human - whole asexual reproduction ➢mosquito - sexual parasitic stage ❖Two host: ➢human - intermediate host ➢mosquito - final host ❖notes: ➢clinical symptoms: erythrocytic stage ➢relapse: exerythrocytic stage ➢infectivity: sporozoite
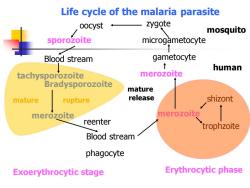
Life cycle of the malaria parasite oocyst zygote mosquito sporozoite microgametocyte Blood stream gametocyte human tachysporozoite merozoite Bradysporozoite mature mature rupture release shizont merozoite merozoite reenter trophzoite Blood stream phagocyte Exoerythrocytic stage Erythrocytic phase
Life cycle of the malaria parasite mosquito microgametocyte oocyst zygote sporozoite Blood stream tachysporozoite merozoite mature rupture Bradysporozoite Blood stream reenter phagocyte merozoite trophzoite shizont mature release merozoite gametocyte Exoerythrocytic stage Erythrocytic phase human

Epidemiology *Source of infection Patient,parasite carrier Route of transmission >female mosquito biting person blood transfusion Susceptibility: >universal susceptibility no-cross-immunity >re-infection Epidemic features: >sporadic or endemic,tropic or subtropic
Epidemiology ❖Source of infection Patient, parasite carrier ❖Route of transmission ➢female mosquito biting person ➢blood transfusion ❖Susceptibility: ➢universal susceptibility ➢no-cross-immunity ➢re-infection ❖Epidemic features: ➢sporadic or endemic, tropic or subtropic

Pathogenesis Mechanism of attack merozoite RBC rupture→l malaria pigment products of metabolism blood stream-allergy P.Faciparam:produce microvascular disease magnitude of the parasitemia age of patient no specific Ab or cell -mediated response
Pathogenesis ❖Mechanism of attack merozoite RBC rupture malaria pigment products of metabolism blood stream allergy ❖P. Faciparam: produce microvascular disease ❖magnitude of the parasitemia & age of patient ❖no specific Ab or cell -mediated response

Pathology Anemia: >P.Vivax-retiform RBC >P.Malariae -mature RBC >P.Falciparum every RBC Prolifeation of mononuclear phagocyte >hepatomegaly >splenomegaly Cerebral edema congestion
Pathology ❖Anemia: ➢P. Vivax - retiform RBC ➢P. Malariae - mature RBC ➢P. Falciparum - every RBC ❖Prolifeation of mononuclear phagocyte ➢hepatomegaly ➢splenomegaly ❖Cerebral edema & congestion

Clinical manifestation Incubation period: quartan malaria:24-30 day tertian malaria:13~15 day malignant malaria:7~12 day
Clinical manifestation Incubation period: quartan malaria: 24-30 day tertian malaria: 13~15 day malignant malaria: 7~12 day
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)General Principles of Infectious Diseases(总论).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Epidemic Cerebrospinal Meningitis(流脑).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Cholera(霍乱).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Bacillary dysentery(菌痢).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)AIDS(艾滋病).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)严重急性呼吸综合征、人禽流感病、人猪链球菌(重庆医科大学:邹启园).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)霍乱 Cholera(重庆医科大学:朱卫民).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)败血症 septicemia.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)病毒性肝炎 viral hepatitis(重庆医科大学:卢萍).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)流行性脑脊髓膜炎 meningococcal meningitis.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)传染病总论(重庆医科大学:袁喆).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)伤寒与副伤寒 Typhoid Fever and Paratyphoid Fever.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)艾滋病 Acquired Immune deficiency Syndrome.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)流行性出血热.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)人禽流感 human avian influenza(重庆医科大学:邓蕙).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)严重急性呼吸综合征(severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)艾滋病(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)课后习题(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)霍乱(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)流行性乙型脑炎(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Typhoid Fever and Paratyphoid Fever(伤寒与副伤寒).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Viral Hepatitis(肝炎).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学大纲(供5年制及7年制使用).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)出血热.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)钩端螺旋体病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)败血症.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)伤寒.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)病毒性肝炎.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)总论.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)阿米巴肝脓肿.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)伤寒(感染病科:石小枫).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)败血症 septicemia.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)钩端螺旋体病 Leptospirosis.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)传染病总论(主讲:赵有蓉).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流行性出血热 epidemic hemorrhagic fever(EHF)hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome(HFRS).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)阿米巴肝脓肿 amebic liver abscess.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)病毒性肝炎 Viral Hepatitis(主讲:张大志).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《儿童保健学》课程教学大纲(供临床医学五年制儿科方向使用).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿童保健学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论(主讲:李廷玉).ppt
