《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Epidemic Cerebrospinal Meningitis(流脑)

Epidemic Cerebrospinal Meningitis Yuan Zhe MD Dept.Of Infectious Disease The First Affiliated Hospital Chongqing Medical University
Epidemic Cerebrospinal Meningitis Yuan Zhe MD Dept. Of Infectious Disease The First Affiliated Hospital Chongqing Medical University

DEFINITION 1.Epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis is acute infectious disease caused by meningococcus. 2.characteristics of ECM are fever, ■headache,vomiting, petechiae or ecchymosis and meningeal irritation signs.CSF is purulent
DEFINITION ◼ 1. Epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis is acute infectious disease caused by ◼ meningococcus. ◼ 2.characteristics of ECM are fever, ◼ headache, vomiting , petechiae or ecchymosis , and meningeal irritation signs. CSF is purulent

ETIOLOGY 1.Pathogen is Neisseria meningitidis (meningococcus);G diplococcus 2.Biological features: 2.1.The organism grow by incubation on blood,chocolate or trypticase soy agar in 5≈10%CO2,PH7.4~7.6; 2.2.The organism is susceptible to dry, heat chill and disinfectant;
ETIOLOGY ◼ 1.Pathogen is Neisseria meningitidis (meningococcus); G- diplococcus. ◼ 2.Biological features: ◼ 2.1.The organism grow by incubation ◼ on blood,chocolate or trypticase soy agar in 5~10%CO2,PH 7.4~7.6; ◼ 2.2.The organism is susceptible to dry, ◼ heat , chill and disinfectant;

ETIOLOGY 2.3.autolysis by autolysin in vitro; 3.The organism can be detected in patient's nasopharynx,blood,CSF, petechiae in skin; 4.Pathogenic factor:endotoxin
◼ 2.3. autolysis by autolysin in vitro; ◼ 3.The organism can be detected in patient’s nasopharynx, blood, CSF, petechiae in skin; ◼ 4.Pathogenic factor: endotoxin. ETIOLOGY

ETIOLOGY 5.Serogroups of meningoccus; ■13 serogroups and more than 20 serotypes found in the world; ■ most common serogroups: A B C group Group A is the most common in china
◼ 5.Serogroups of meningoccus; ◼ 13 serogroups and more than 20 serotypes found in the world; ◼ most common serogroups: ◼ A B C group ◼ Group A is the most common in china. ETIOLOGY

EPIDEMIOLOGY 1.Source of infection: patients and carriers; 2.The routes of transmission ■1)air borne 2)closed contact transmission 3.Susceptibility of population:universal susceptible ■ stable and persistent immunity
EPIDEMIOLOGY ◼ 1.Source of infection: ◼ patients and carriers; ◼ 2.The routes of transmission : ◼ 1) air borne ◼ 2) closed contact transmission : ◼ 3.Susceptibility of population: universal susceptible ◼ stable and persistent immunity

EPIDEMIOLOGY 4.Epidemiologic feature: (1).Season:November May high peak:March April (2).age:6 months to 2 years old
◼ 4.Epidemiologic feature: ◼ (1). Season: November - May ◼ high peak: March - April ◼ (2).age: 6 months to 2 years old EPIDEMIOLOGY

PATHOGENESIS meningococci extinguished nasopharynx carriers 60-700 upprespiratoract infection 20-30% period
PATHOGENESIS ◼ meningococci ◼ extinguished ◼ nasopharynx carriers 60 - 70% ◼ upper respiratory tract ◼ infection 20 -30% ◼ meningococcemia period septicemia
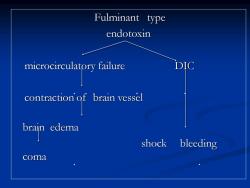
Fulminant type endotoxin microcirculatory failure DIC brain edema shock bleeding coma
Fulminant type endotoxin microcirculatory failure DIC contraction of brain vessel brain edema shock bleeding coma
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Cholera(霍乱).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Bacillary dysentery(菌痢).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)AIDS(艾滋病).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)严重急性呼吸综合征、人禽流感病、人猪链球菌(重庆医科大学:邹启园).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)霍乱 Cholera(重庆医科大学:朱卫民).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)败血症 septicemia.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)病毒性肝炎 viral hepatitis(重庆医科大学:卢萍).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)流行性脑脊髓膜炎 meningococcal meningitis.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)传染病总论(重庆医科大学:袁喆).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)伤寒与副伤寒 Typhoid Fever and Paratyphoid Fever.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)艾滋病 Acquired Immune deficiency Syndrome.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)流行性出血热.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)人禽流感 human avian influenza(重庆医科大学:邓蕙).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)严重急性呼吸综合征(severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)艾滋病(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)课后习题(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)霍乱(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)流行性乙型脑炎(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)伤寒、副伤寒(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)败血症(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)General Principles of Infectious Diseases(总论).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Malaria(疟疾).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Typhoid Fever and Paratyphoid Fever(伤寒与副伤寒).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Viral Hepatitis(肝炎).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学大纲(供5年制及7年制使用).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)出血热.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)钩端螺旋体病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)败血症.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)伤寒.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)病毒性肝炎.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)总论.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)阿米巴肝脓肿.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)伤寒(感染病科:石小枫).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)败血症 septicemia.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)钩端螺旋体病 Leptospirosis.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)传染病总论(主讲:赵有蓉).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流行性出血热 epidemic hemorrhagic fever(EHF)hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome(HFRS).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)阿米巴肝脓肿 amebic liver abscess.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)病毒性肝炎 Viral Hepatitis(主讲:张大志).ppt
