《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 03 Consumer Behavior

Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior Chapter Outline Consumer Preferences ·Budget Constraints 。Consumer Choice Marginal Utility and Consumer Choice Microeconomics (fitth edition) Author:Robert S.Pindyc,Daniel L.Rubinfeld
Chapter 3 Consumer Behavior Chapter Outline • Consumer Preferences • Budget Constraints • Consumer Choice • Marginal Utility and Consumer Choice • Microeconomics (fitth edition) • Author: Robert S. Pindyc, Daniel L. Rubinfeld

>Theory of consumer behavior-Description of how consumers allocate incomes among different goods and services to maximize their well-being(福利). >Consumer behavior is best understood in the following three distinct steps: Consumer Preferences √Budget Constraints √Consumer choices
➢ Theory of consumer behavior-Description of how consumers allocate incomes among different goods and services to maximize their well-being (福利). ➢ Consumer behavior is best understood in the following three distinct steps: ✓ Consumer Preferences ✓ Budget Constraints ✓ Consumer choices

3.1 Consumer Preferences >Market basket(购物篮)(or bundle)List with specific quantities of one or more goods. 3.1.1 Some Basic Assumptions about Preferences √Completeness(完备性):Preferences are assumed to be complete.In other words,consumers can compare and rank all possible baskets
3.1 Consumer Preferences ➢ Market basket (购物篮) (or bundle) List with specific quantities of one or more goods. 3.1.1 Some Basic Assumptions about Preferences ✓ Completeness (完备性): Preferences are assumed to be complete. In other words, consumers can compare and rank all possible baskets

√Transitivity(传递性):Preferences are transitive.Transitivity means that if a consumer prefers basket A to basket B and basket B to basket C,then the consumer also prefers A to C. √Nonsatiation(贪得无厌):Consumers always prefer more of any good to less
✓ Transitivity (传递性): Preferences are transitive. Transitivity means that if a consumer prefers basket A to basket B and basket B to basket C, then the consumer also prefers A to C. ✓ Nonsatiation (贪得无厌) : Consumers always prefer more of any good to less

▣The theory of consumer choice rests on(取决于)the assumption that people behave rationally in an attempt to maximize the satisfaction that they can obtain by purchasing a particular combination of goods and services
❑ The theory of consumer choice rests on (取决于) the assumption that people behave rationally in an attempt to maximize the satisfaction that they can obtain by purchasing a particular combination of goods and services
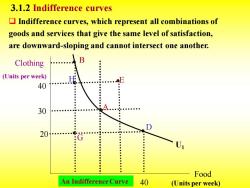
3.1.2 Indifference curves Indifference curves,which represent all combinations of goods and services that give the same level of satisfaction, are downward-sloping and cannot intersect one another. Clothing B : (Units per week) 40 ◆ : ·: : 30 : 20 : : Food An Indifference Curve 40 (Units per week)
3.1.2 Indifference curves ❑ Indifference curves, which represent all combinations of goods and services that give the same level of satisfaction, are downward-sloping and cannot intersect one another. Clothing Food (Units per week) (Units per week) U1 A D H E G B 40 20 30 40 An Indifference Curve

The indifference curve U that passes through market basket A shows all baskets that give the consumer the same level of satisfaction as does market basket A;these include baskets B and D. Our consumer prefers basket E,which lies above U1,to A,but prefers A to H or G,which lie below U1
The indifference curve U1 that passes through market basket A shows all baskets that give the consumer the same level of satisfaction as does market basket A; these include baskets B and D. Our consumer prefers basket E, which lies above U1 , to A, but prefers A to H or G, which lie below U1

3.1.3 Indifference Maps Consumer preferences can be completely described by a set of indifference curves known as an indifference map. An indifference map provides an ordinal ranking(序数排列) of all choices that the consumer might make
➢ Consumer preferences can be completely described by a set of indifference curves known as an indifference map. An indifference map provides an ordinal ranking (序数排列) of all choices that the consumer might make. 3.1.3 Indifference Maps
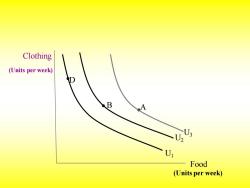
Clothing (Units per week) D B 02 U Food (Units per week)
D B A U1 U2 U3 Food (Units per week) Clothing (Units per week)

>An indifference map is a set of indifference curves that describes a person's preferences. Any market basket on indifference curve U3,such as basket A, is preferred to any basket on curve U2(e.g.,basket B),which in turn(依次,轮流)is preferred to any basket on U,such as basket D
➢ An indifference map is a set of indifference curves that describes a person’s preferences. Any market basket on indifference curve U3 , such as basket A, is preferred to any basket on curve U2 (e.g., basket B), which in turn(依次,轮流) is preferred to any basket on U1 , such as basket D
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 02 The Basics of Supply and Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 01 Preliminaries.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 19 Advances in Business Cycle theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 17 Investment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 18 Money supply and monetary Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 16 Consumption.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 15Government Debt and Budget Deficits.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 14 Stabilization Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 13 Aggregate supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 12 Aggregate demand in open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 11 Application of IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 10 The IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 09 Introduction to AS-AD model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 07 Economic growth(1/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 08 Economic growth(2/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 06 Unemployment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 05 The open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 04 Money and inflation.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 03 Where NI comes from and goes.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 02 The Data of Macroeconomics.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 04 Individual and Market Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 05 Choice under Uncertainty.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 06 Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 07 The Cost of Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 08 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 09 The Analysis of Competitive Markets.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 10 Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 11 Pricing with Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 12 Monopolistic Competition.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 13 Game Theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 14 Markets for Factor Inputs.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 15 Investment, Time, and Capital.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 16 General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Markets with Asymmetric Information.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 18 Externalities.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Microeconomics.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程课程教学大纲 COST ACCOUNTING.pdf
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第一章 总论.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三章 成本汇集与分配.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二章 成本核算方法体系.doc
