《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 12 Aggregate demand in open economy

CHAPTER TWELVE Aggregate Demand in the Open Economy macroeconomics N.Gregory Mankiw College of Management,HUST
macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw m a c r o College of Management, HUST CHAPTER TWELVE Aggregate Demand in the Open Economy

Learning objectives ■ The Mundell-Fleming model: IS-LM for the small open economy Causes and effects of interest rate differentials Arguments for fixed vs.floating exchange rates The aggregate demand curve for the small open economy CHAPTER 12 Aggregate Demand in the Open Economy slide 1
slide 1 § The Mundell-Fleming model: IS-LM for the small open economy § Causes and effects of interest rate differentials § Arguments for fixed vs. floating exchange rates § The aggregate demand curve for the small open economy

Content 1.The Mundell-Fleming model 2.Policy analysis under floating exchange rates 3.Policy analysis under fixed exchange rates 4.Interest rate differentials 5.Mundell-Fleming model as an AD theory 6.Case study 7.Chapter summary CHAPTER 12 Aggregate Demand in the Open Economy slide 2
slide 2 1. The Mundell-Fleming model 2. Policy analysis under floating exchange rates 3. Policy analysis under fixed exchange rates 4. Interest rate differentials 5. Mundell-Fleming model as an AD theory 6. Case study 7. Chapter summary
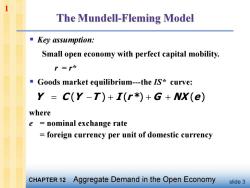
1 The Mundell-Fleming Model ■Key assumption: Small open economy with perfect capital mobility. P=r必 ■( Goods market equilibrium-the IS*curve: Y =C(Y-T)+I(r*)+G+NX(e) where e nominal exchange rate foreign currency per unit of domestic currency CHAPTER 12 Aggregate Demand in the Open Economy slide 3
slide 3 § Key assumption: Small open economy with perfect capital mobility. r = r* § Goods market equilibrium-the IS* curve: Y C (Y T ) I (r *) G NX (e) where e = nominal exchange rate = foreign currency per unit of domestic currency 1
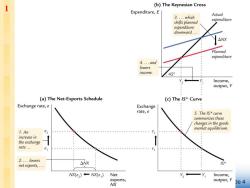
1 (b)The Keynesian Cross Expenditure,E 3.which Actual expenditure shifts planned expenditure downward. △NX Planned expenditure 4.and lowers income. 45° Income, output,Y (a)The Net-Exports Schedule (c)The /S*Curve Exchange rate,e Exchange rate,e 5.The IS*curve summarizes these changes in the goods market equilibrium. 1.An e2 increase in the exchange rate. e e 2.lowers net exports,. : △NX 5* NX(e2)+-NX(e;) Net Y+ 一Y Income, exports, output,y 1e4 NX
slide 4 1
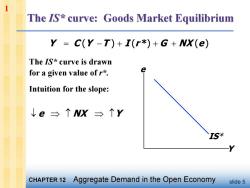
1 The IS*curve:Goods Market Equilibrium Y C(Y-T)+I(r*)+G+NX(e) The IS*curve is drawn for a given value of r*. Intuition for the slope: ↓e三↑NX三个Y IS* CHAPTER 12 Aggregate Demand in the Open Economy slide 5
slide 5 The IS* curve is drawn for a given value of r*. Intuition for the slope: Y e IS* Y C (Y T ) I (r *) G NX (e) e NX Y 1
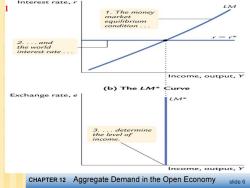
Interest rate,r 1 LA 1.The money market equilibrium condition,·- 2.·and the world interest rate . Income,output,Y (b)The LM米Curve Exchange rate,e 3.determine the level of income. Income,output,y CHAPTER 12 Aggregate Demand in the Open Economy slide 6
slide 6 1
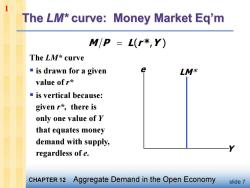
The LM*curve:Money Market Eq'm M/P L(r*,Y) The LM*curve ■is drawn for a given LM* value of r* ■is vertical because: given r*,there is only one value of r that equates money demand with supply, regardless of e. CHAPTER 12 Aggregate Demand in the Open Economy slide 7
slide 7 The LM* curve § is drawn for a given value of r* § is vertical because: given r* , there is only one value of Y that equates money demand with supply, regardless of e. Y e LM* M P L(r * ,Y ) 1
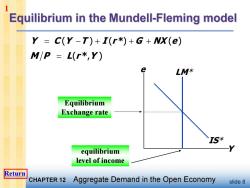
1 Equilibrium in the Mundell-Fleming model Y =C(Y-T)+I(r*)+G+NX(e) M/P L(r*,Y) e LM* Equilibrium Exchange rate TS* equilibrium level of income Return CHAPTER 12 Aggregate Demand in the Open Economy slide 8
slide 8 Y e LM* M P L(r * ,Y ) IS* Y C (Y T ) I (r *) G NX (e) Equilibrium Exchange rate equilibrium level of income 1 Return

2 Floating fixed exchange rates In a system of floating exchange rates,e is allowed to fluctuate in response to changing economic conditions. In contrast,under fixed exchange rates,the central bank trades domestic for foreign currency at a predetermined price(trades A for B用A换B). We now consider fiscal,monetary,and trade policy: first in a floating exchange rate system,then in a fixed exchange rate system. CHAPTER 12 Aggregate Demand in the Open Economy slide 9
slide 9 § In a system of floating exchange rates, e is allowed to fluctuate in response to changing economic conditions. § In contrast, under fixed exchange rates, the central bank trades domestic for foreign currency at a predetermined price (trades A for B 用A换B). § We now consider fiscal, monetary, and trade policy: first in a floating exchange rate system, then in a fixed exchange rate system. 2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 11 Application of IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 10 The IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 09 Introduction to AS-AD model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 07 Economic growth(1/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 08 Economic growth(2/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 06 Unemployment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 05 The open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 04 Money and inflation.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 03 Where NI comes from and goes.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 02 The Data of Macroeconomics.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 01 The Science of Macroeconomics.ppt
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007微观经济学(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007微观经济学(A)答案.doc
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 13 Aggregate supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 14 Stabilization Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 15Government Debt and Budget Deficits.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 16 Consumption.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 18 Money supply and monetary Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 17 Investment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 19 Advances in Business Cycle theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 01 Preliminaries.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 02 The Basics of Supply and Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 03 Consumer Behavior.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 04 Individual and Market Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 05 Choice under Uncertainty.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 06 Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 07 The Cost of Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 08 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 09 The Analysis of Competitive Markets.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 10 Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 11 Pricing with Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 12 Monopolistic Competition.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 13 Game Theory.ppt
