《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 10 The IS-LM model

CHAPTER TEN The IS-LM Model macroeconomics N.Gregory Mankiw College of Management,HUST
macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER TEN The IS-LM Model macro College of Management, HUST

In this chapter you will learn the IS curve,and its relation to the Keynesian Cross the Loanable Funds model the LM curve,and its relation to the Theory of Liquidity Preference how the IS-LM model determines income and the interest rate in the short run when P is fixed CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 1
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 1 In this chapter you will learn ▪ the IS curve, and its relation to – the Keynesian Cross – the Loanable Funds model ▪ the LM curve, and its relation to – the Theory of Liquidity Preference ▪ how the IS-LM model determines income and the interest rate in the short run when P is fixed

Content 1.The Keynesian Cross 2.Fiscal policy and the multiplier 3.The IS curve 4.The Theory of Liquidity Preference 5.The LM curve 6.IS-LM model 7.Chapter summary CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 2
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 2 Content 1. The Keynesian Cross 2. Fiscal policy and the multiplier 3. The IS curve 4. The Theory of Liquidity Preference 5. The LM curve 6. IS-LM model 7. Chapter summary

1 Introduction Chapter 9 introduced the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply. ■Long run prices flexible 一 output determined by factors of production technology 一 unemployment rate equals its natural rate ▣Short run -prices fixed output determined by aggregate demand unemployment is negatively related to output CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 3
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 3 Introduction ▪ Chapter 9 introduced the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply. ▪ Long run – prices flexible – output determined by factors of production & technology – unemployment rate equals its natural rate ▪ Short run – prices fixed – output determined by aggregate demand – unemployment is negatively related to output 1

Introduction This chapter develops the IS-LM model,the theory that yields the aggregate demand curve. We focus on the short run and assume the price level is fixed. CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 4
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 4 Introduction ▪ This chapter develops the IS-LM model, the theory that yields the aggregate demand curve. ▪ We focus on the short run and assume the price level is fixed. 1

1 The Keynesian Cross A simple closed economy model in which income is determined by expenditure.(due to J.M.Keynes) ▣Notation: I planned investment E=C+I+G planned expenditure Y=real GDP=actual expenditure Difference between actual planned expenditure: unplanned inventory investment CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 5
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 5 The Keynesian Cross ▪ A simple closed economy model in which income is determined by expenditure. (due to J.M. Keynes) ▪ Notation: I = planned investment E = C + I + G = planned expenditure Y = real GDP = actual expenditure ▪ Difference between actual & planned expenditure: unplanned inventory investment 1
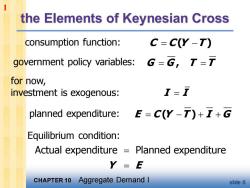
1 the Elements of Keynesian Cross consumption function: C=C(Y-T) government policy variables:G=G,T= for now, investment is exogenous: T-T planned expenditure:E=C(Y-T)++G Equilibrium condition: Actual expenditure =Planned expenditure Y=E CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 6
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 6 the Elements of Keynesian Cross C C Y T = − ( ) I I = G G T T = = , E C Y T I G = − + + ( ) Actual expenditure Planned expenditure Y E = = consumption function: for now, investment is exogenous: planned expenditure: Equilibrium condition: government policy variables: 1
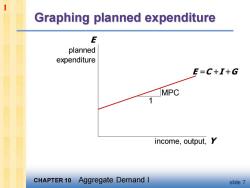
1 Graphing planned expenditure E planned expenditure E=C+I+G MPC income,output,Y CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 7
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 7 Graphing planned expenditure income, output, Y E planned expenditure E =C +I +G MPC 1 1
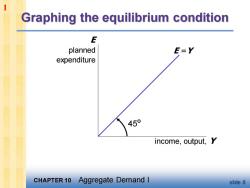
1 Graphing the equilibrium condition E planned E=Y expenditure 450 income,output,Y CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 8
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 8 Graphing the equilibrium condition income, output, Y E planned expenditure E =Y 45º 1

1 The equilibrium value of income E planned E=Y expenditure E=C+I+G income,output,Y Equilibrium income Return CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 9
CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Demand I slide 9 The equilibrium value of income income, output, Y E planned expenditure E =Y E =C +I +G Equilibrium income 1 Return
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 09 Introduction to AS-AD model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 07 Economic growth(1/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 08 Economic growth(2/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 06 Unemployment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 05 The open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 04 Money and inflation.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 03 Where NI comes from and goes.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 02 The Data of Macroeconomics.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 01 The Science of Macroeconomics.ppt
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007微观经济学(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007微观经济学(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)名词解释(英文).doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(A)答案.doc
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 11 Application of IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 12 Aggregate demand in open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 13 Aggregate supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 14 Stabilization Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 15Government Debt and Budget Deficits.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 16 Consumption.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 18 Money supply and monetary Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 17 Investment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 19 Advances in Business Cycle theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 01 Preliminaries.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 02 The Basics of Supply and Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 03 Consumer Behavior.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 04 Individual and Market Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 05 Choice under Uncertainty.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 06 Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 07 The Cost of Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 08 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 09 The Analysis of Competitive Markets.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 10 Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 11 Pricing with Market Power.ppt
