《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 01 The Science of Macroeconomics

CHAPTER ONE The Science of Macroeconomics macroeconomics N.Gregory Mankiw College of Management,HUST
macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw CHAPTER ONE The Science of Macroeconomics macro College of Management, HUST

Learning objectives This chapter introduces you to the issues macroeconomists study the tools macroeconomists use some important concepts in macroeconomic analysis CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 1
CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 1 Learning objectives This chapter introduces you to ▪ the issues macroeconomists study ▪ the tools macroeconomists use ▪ some important concepts in macroeconomic analysis

Content 1.Important issues in macroeconomics 2.Why Learn Macroeconomics 3.Economic Models 4.Price:Flexible Versus Sticky 5.Chapter Summary CHAPTER1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 2
CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 2 Content 1. Important issues in macroeconomics 2. Why Learn Macroeconomics 3. Economic Models 4. Price: Flexible Versus Sticky 5. Chapter Summary

Important issues in macroeconomics Why does the cost of living keep rising? Why are millions of people unemployed,even when the economy is booming? Why are there recessions? Can the government do anything to combat recessions? Should it?? CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 3
CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 3 Important issues in macroeconomics ▪ Why does the cost of living keep rising? ▪ Why are millions of people unemployed, even when the economy is booming? ▪ Why are there recessions? Can the government do anything to combat recessions? Should it?? 1

Important issues in macroeconomics What is the government budget deficit?How does it affect the economy? Why does the U.S.have such a huge trade deficit? Why are so many countries poor? What policies might help them grow out of poverty? CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 4
CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 4 Important issues in macroeconomics ▪ What is the government budget deficit? How does it affect the economy? ▪ Why does the U.S. have such a huge trade deficit? ▪ Why are so many countries poor? What policies might help them grow out of poverty? 1
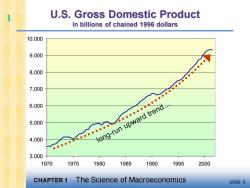
U.S.Gross Domestic Product in billions of chained 1996 dollars 10,000 9,000 8,000 7,000 6.000 6'or0· 5,000 leng-run upward trend. 4,000 C.o 3,000 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 5
CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 5 U.S. Gross Domestic Product in billions of chained 1996 dollars 3,000 4,000 5,000 6,000 7,000 8,000 9,000 10,000 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 1
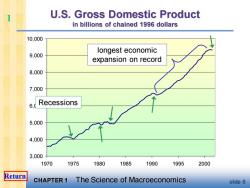
U.S.Gross Domestic Product in billions of chained 1996 dollars 10,000 longest economic 9,000 expansion on record 8,000 7,000 6.(Recessions 5,000 4,000 3,000 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 Return CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 6
CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 6 U.S. Gross Domestic Product in billions of chained 1996 dollars 3,000 4,000 5,000 6,000 7,000 8,000 9,000 10,000 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 Recessions longest economic expansion on record 1 Return

2 Why learn macroeconomics? 1.The macroeconomy affects society's well-being. ■example. Unemployment and social problems CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 7
CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 7 Why learn macroeconomics? 1. The macroeconomy affects society’s well-being. ▪ example: ▪ Unemployment and social problems 2

Unemployment and social problems Each one-point increase in the unemployment rate is associated with: 920 more suicides ·650 more homicides 4000 more people admitted to state mental institutions 3300 more people sent to state prisons ·37,000 more deaths increases in domestic violence and homelessness CHAPTER1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 8
CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 8 Unemployment and social problems Each one-point increase in the unemployment rate is associated with: ▪ 920 more suicides ▪ 650 more homicides ▪ 4000 more people admitted to state mental institutions ▪ 3300 more people sent to state prisons ▪ 37,000 more deaths ▪ increases in domestic violence and homelessness 2

2 Why learn macroeconomics? 1.The macroeconomy affects society's well-being. example: Unemployment and social problems 2.The macroeconomy affects your well-being. ■example1: Unemployment and earnings growth 。example2: Interest rates and mortgage payments CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 9
CHAPTER 1 The Science of Macroeconomics slide 9 Why learn macroeconomics? 1. The macroeconomy affects society’s well-being. ▪ example: Unemployment and social problems 2. The macroeconomy affects your well-being. ▪ example 1: Unemployment and earnings growth ▪ example 2: Interest rates and mortgage payments 2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007微观经济学(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007微观经济学(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)名词解释(英文).doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009微观经济学期终考试(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009微观经济学期终考试(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2007-2008微观经济学期终考试(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2007-2008微观经济学期终考试(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2007-2008微观经济学期终考试(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2007-2008微观经济学期终考试(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(宏观经济学)2008-2009宏观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(宏观经济学)2008-2009宏观经济学(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(宏观经济学)2008-2009宏观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 02 The Data of Macroeconomics.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 03 Where NI comes from and goes.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 04 Money and inflation.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 05 The open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 06 Unemployment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 08 Economic growth(2/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 07 Economic growth(1/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 09 Introduction to AS-AD model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 10 The IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 11 Application of IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 12 Aggregate demand in open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 13 Aggregate supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 14 Stabilization Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 15Government Debt and Budget Deficits.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 16 Consumption.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 18 Money supply and monetary Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 17 Investment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 19 Advances in Business Cycle theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 01 Preliminaries.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 02 The Basics of Supply and Demand.ppt
