《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 08 Economic growth(2/2)

CHAPTER Eight Economic Growth Technological progress macroeconomics N.Gregory Mankiw College of Management,HUST
macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw macro College of Management, HUST CHAPTER Eight Economic Growth : Technological progress

Learning objectives Technological progress in the Solow model Policies to promote growth Endogenous growth: Two simple models in which the rate of technological progress is endogenous CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth Il slide 1
CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth II slide 1 Learning objectives ▪ Technological progress in the Solow model ▪ Policies to promote growth ▪ Endogenous growth: Two simple models in which the rate of technological progress is endogenous

Content 1.Technological progress in Solow model 2.Policies to promote growth 2.1 Evaluating the saving rate 2.2 Policies to promote saving rate 2.3 Allocating the economy's investment 2.4 Encouraging technological progress 3.Endogenous growth theory 3.1 Basic model 3.2 Two sector model 4.Chapter summary CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth ll slide 2
CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth II slide 2 Content 1. Technological progress in Solow model 2. Policies to promote growth 2.1 Evaluating the saving rate 2.2 Policies to promote saving rate 2.3 Allocating the economy’s investment 2.4 Encouraging technological progress 3. Endogenous growth theory 3.1 Basic model 3.2 Two sector model 4. Chapter summary

Introduction In the Solow model of Chapter 4, the production technology is held constant income per capita is constant in the steady state. Neither point is true in the real world: 1929-2001:U.S.real GDP per person grew by a factor of 4.8,or 2.2%per year. examples of technological progress abound (see next slide) CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth ll slide 3
CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth II slide 3 Introduction In the Solow model of Chapter 4, ▪ the production technology is held constant ▪ income per capita is constant in the steady state. Neither point is true in the real world: ▪ 1929-2001: U.S. real GDP per person grew by a factor of 4.8, or 2.2% per year. ▪ examples of technological progress abound (see next slide) 1

Examples of technological progress ■ 1970:50,000 computers in the world 2000:51%of U.S.households have 1 or more computers -The real price of computer power has fallen an average of 30%per year over the past three decades. The average car built in 1996 contained more computer processing power than the first lunar landing craft in 1969. Modems are 22 times faster today than two decades ago. 1981:213 computers connected to the Internet 2000:60 million computers connected to the Internet CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth Il slide 4
CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth II slide 4 Examples of technological progress ▪ 1970: 50,000 computers in the world 2000: 51% of U.S. households have 1 or more computers ▪ The real price of computer power has fallen an average of 30% per year over the past three decades. ▪ The average car built in 1996 contained more computer processing power than the first lunar landing craft in 1969. ▪ Modems are 22 times faster today than two decades ago. ▪ 1981: 213 computers connected to the Internet 2000: 60 million computers connected to the Internet 1

Tech.progress in the Solow model A new variable:E=labor efficiency Assume: Technological progress is labor-augmenting: it increases labor efficiency at the exogenous rate g. △E E CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth ll slide 5
CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth II slide 5 Tech. progress in the Solow model ▪ A new variable: E = labor efficiency ▪ Assume: Technological progress is labor-augmenting: it increases labor efficiency at the exogenous rate g: E g E = 1
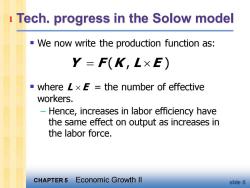
1 Tech.progress in the Solow model -We now write the production function as: Y=F(K,L×E) where LxE the number of effective workers. Hence,increases in labor efficiency have the same effect on output as increases in the labor force. CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth ll slide 6
CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth II slide 6 Tech. progress in the Solow model ▪ We now write the production function as: ▪ where L E = the number of effective workers. – Hence, increases in labor efficiency have the same effect on output as increases in the labor force. Y F K L E = ( , ) 1
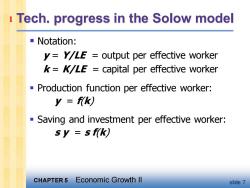
1 Tech.progress in the Solow model ■Notation: y=YLE output per effective worker k=KLE capital per effective worker Production function per effective worker: y=f(k) -Saving and investment per effective worker: sy=sf(k) CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth Il slide 7
CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth II slide 7 Tech. progress in the Solow model ▪ Notation: y = Y/LE = output per effective worker k = K/LE = capital per effective worker ▪ Production function per effective worker: y = f(k) ▪ Saving and investment per effective worker: s y = s f(k) 1

1 Tech.progress in the Solow model (+n+g)k break-even investment: the amount of investment necessary to keep k constant. Consists of: k to replace depreciating capital n to provide capital for new workers gk to provide capital for the new "effective"workers created by technological progress CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth ll slide 8
CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth II slide 8 Tech. progress in the Solow model ( + n + g)k = break-even investment: the amount of investment necessary to keep k constant. Consists of: k to replace depreciating capital n k to provide capital for new workers gk to provide capital for the new “effective” workers created by technological progress 1
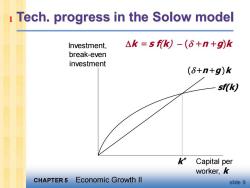
i Tech.progress in the Solow model Investment, △k=sfk)-(6+n+g)k break-even investment (6+n+g)k sf(k) K* Capital per worker,k CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth ll slide 9
CHAPTER 5 Economic Growth II slide 9 Tech. progress in the Solow model Investment, break-even investment Capital per worker, k sf(k) ( +n +g)k k * k = s f(k) − ( +n +g)k 1
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 06 Unemployment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 05 The open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 04 Money and inflation.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 03 Where NI comes from and goes.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 02 The Data of Macroeconomics.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 01 The Science of Macroeconomics.ppt
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007微观经济学(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007微观经济学(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)名词解释(英文).doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009微观经济学期终考试(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009微观经济学期终考试(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2007-2008微观经济学期终考试(B)试卷.doc
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 07 Economic growth(1/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 09 Introduction to AS-AD model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 10 The IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 11 Application of IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 12 Aggregate demand in open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 13 Aggregate supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 14 Stabilization Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 15Government Debt and Budget Deficits.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 16 Consumption.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 18 Money supply and monetary Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 17 Investment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 19 Advances in Business Cycle theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 01 Preliminaries.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 02 The Basics of Supply and Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 03 Consumer Behavior.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 04 Individual and Market Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 05 Choice under Uncertainty.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 06 Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 07 The Cost of Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 08 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply.ppt
