《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 03 Where NI comes from and goes

CHAPTER THREE National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes macroeconomics N.Gregory Mankiw College of Management,HUST
macroeconomics N. Gregory Mankiw macro College of Management, HUST CHAPTER THREE National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes

Learning objectives what determines the economy's total output/income how the prices of the factors of production are determined how total income is distributed what determines the demand for goods and services how equilibrium in the goods market is achieved CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 1
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 1 Learning objectives ▪ what determines the economy’s total output/income ▪ how the prices of the factors of production are determined ▪ how total income is distributed ▪ what determines the demand for goods and services ▪ how equilibrium in the goods market is achieved

Content 1.Factors determine the total output/income 2.Distribution of national income 3.Goods market equilibrium 4.Loanable funds market equilibrium 5.General equilibrium and changing of S,I 6.Chapter summary CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 2
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 2 Content 1. Factors determine the total output/income 2. Distribution of national income 3. Goods market equilibrium 4. Loanable funds market equilibrium 5. General equilibrium and changing of S, I 6. Chapter summary

Total Output Is Determined By Factors of production: K =capital L =labor the economy's level of technology, expressed by production function, denoted Y=F(K,L) CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 3
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 3 Total Output Is Determined By ▪ Factors of production: K =capital L = labor ▪ the economy’s level of technology, expressed by production function, denoted Y = F (K,L) 1

Returns to scale:a review Initially Y=F(K,L) Scale all inputs by the same factor z: K2=zK and L2=L (If 1.25,then all inputs are increased by 25%) What happens to output,Y2=F(K2,L2)? If constant returns to scale,Y2=Y If increasing returns to scale,Y2>Y If decreasing returns to scale,Y2<Y CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 4
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 4 Returns to scale: a review Initially Y1 = F (K1 ,L1 ) Scale all inputs by the same factor z: K2 = zK1 and L2 = zL1 (If z = 1.25, then all inputs are increased by 25%) What happens to output, Y2 = F (K2 ,L2 ) ? ▪ If constant returns to scale, Y2 = zY1 ▪ If increasing returns to scale, Y2 > zY1 ▪ If decreasing returns to scale, Y2 < zY1 1
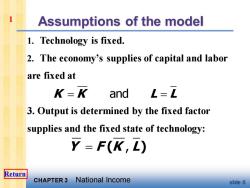
Assumptions of the model 1.Technology is fixed. 2.The economy's supplies of capital and labor are fixed at K=K and L=L 3.Output is determined by the fixed factor supplies and the fixed state of technology: Y=F(K,L) Return CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 6
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 6 Assumptions of the model 1. Technology is fixed. 2. The economy’s supplies of capital and labor are fixed at 3. Output is determined by the fixed factor supplies and the fixed state of technology: K K L L = = and 1 Y F K L = ( ) , Return

The distribution of national income -The distribution of the total income is determined by factor prices,the prices per unit that firms pay for the factors of production. -The wage is the price of L,the rental rate is the price of K. CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 7
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 7 The distribution of national income ▪ The distribution of the total income is determined by factor prices, the prices per unit that firms pay for the factors of production. ▪ The wage is the price of L, the rental rate is the price of K. 2

2 Notation W nominal wage R nominal rental rate P price of output WIP real wage (measured in units of output) R/P real rental rate CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 8
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 8 Notation W = nominal wage R = nominal rental rate P = price of output W/P = real wage (measured in units of output) R/P = real rental rate 2
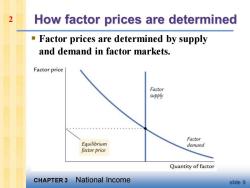
2 How factor prices are determined Factor prices are determined by supply and demand in factor markets. Factor price Factor supply Factor Equilibrium demand factor price Quantity of factor CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 9
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 9 How factor prices are determined ▪ Factor prices are determined by supply and demand in factor markets. 2

2 Demand for labor Assume markets are competitive: each firm takes W,R,and P as given -Basic idea: A firm hires each unit of labor if the cost does not exceed the benefit. cost real wage benefit marginal product of labor MPL F(K,L+1)-F(K,L) CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 10
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 10 Demand for labor ▪Assume markets are competitive: each firm takes W, R, and P as given ▪Basic idea: A firm hires each unit of labor if the cost does not exceed the benefit. cost = real wage benefit = marginal product of labor ▪ MPL = F (K,L +1) – F (K,L) 2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 02 The Data of Macroeconomics.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 01 The Science of Macroeconomics.ppt
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007学年度第1学期微观经济学(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007微观经济学(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2006-2007微观经济学(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)名词解释(英文).doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2009-2010微观经济学(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009微观经济学期终考试(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2008-2009微观经济学期终考试(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2007-2008微观经济学期终考试(B)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2007-2008微观经济学期终考试(A)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2007-2008微观经济学期终考试(A)试卷.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(微观经济学)2007-2008微观经济学期终考试(B)答案.doc
- 海南大学:《西方经济学》课程试卷解答(宏观经济学)2008-2009宏观经济学(B)试卷.doc
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 04 Money and inflation.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 05 The open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 06 Unemployment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 08 Economic growth(2/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 07 Economic growth(1/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 09 Introduction to AS-AD model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 10 The IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 11 Application of IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 12 Aggregate demand in open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 13 Aggregate supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 14 Stabilization Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 15Government Debt and Budget Deficits.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 16 Consumption.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 18 Money supply and monetary Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 17 Investment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 19 Advances in Business Cycle theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 01 Preliminaries.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 02 The Basics of Supply and Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 03 Consumer Behavior.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 04 Individual and Market Demand.ppt
