《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 09 The Analysis of Competitive Markets

Chapter 9 The Analysis of Competitive Markets Chapter Outline Evaluating the Gains and Losses from Government Policies -Consumer and Producer Surplus The Efficiency of a Competitive Market ·Minimum Prices Price Supports and Production Quotas Import Quotas and Tariffs The Impact of a Tax or Subsidy
Chapter 9 The Analysis of Competitive Markets Chapter Outline • Evaluating the Gains and Losses from Government Policies —Consumer and Producer Surplus • The Efficiency of a Competitive Market • Minimum Prices • Price Supports and Production Quotas • Import Quotas and Tariffs • The Impact of a Tax or Subsidy
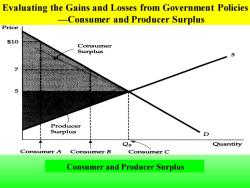
Evaluating the Gains and Losses from Government Policies -Consumer and Producer Surplus Price $10 Consumer Surplus 5 Producer Surplus o Quantity Consumer A Consumer B Consumer C Consumer and Producer Surplus
Evaluating the Gains and Losses from Government Policies —Consumer and Producer Surplus Consumer and Producer Surplus

Consumer A would pay $10 for a good whose market price is $5 and therefore enjoys a benefit of $5.Consumer B enjoys a benefit of $2,and Consumer C,who values the good at exactly the market price,enjoys no benefit.Consumer surplus,which measures the total benefit to all consumers,is the shaded area between the demand curve and the market price
Consumer A would pay $10 for a good whose market price is $5 and therefore enjoys a benefit of $5. Consumer B enjoys a benefit of $2, and Consumer C, who values the good at exactly the market price, enjoys no benefit. Consumer surplus, which measures the total benefit to all consumers, is the shaded area between the demand curve and the market price

Producer surplus is the shaded area between the supply curve and the market price.Together consumer and producer surplus measure the welfare benefit of a competitive market. >Welfare effects-Gains and losses caused by government intervention in the market
Producer surplus is the shaded area between the supply curve and the market price. Together consumer and producer surplus measure the welfare benefit of a competitive market. ➢ Welfare effects-Gains and losses caused by government intervention in the market
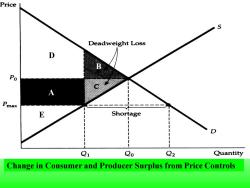
Price S Deadweight Loss D Po Pma以 E Shortage Q1 Qo Q2 Quantity Change in Consumer and Producer Surplus from Price Controls
Change in Consumer and Producer Surplus from Price Controls B A D E

●Deadweight loss(无谓损失)-Net loss of total(consumer plus producer)surplus. The price of a good has been regulated to be no higher than Pmax,Which is below the market-clearing price Po. The gain to consumers is the difference between rectangle A and triangle B(A-B). The loss to producers is the sum of rectangle A and triangle C (A+C).Triangles B and C together measure the deadweight loss from price controls(B+C)
⚫ Deadweight loss (无谓损失) - Net loss of total (consumer plus producer)surplus. ◆The price of a good has been regulated to be no higher than Pmax, which is below the market-clearing price P0 . The gain to consumers is the difference between rectangle A and triangle B (A-B). The loss to producers is the sum of rectangle A and triangle C (A+C). Triangles B and C together measure the deadweight loss from price controls (B+C)
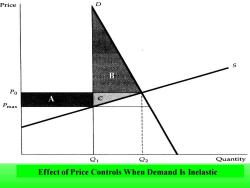
Price D S Po Pmax Q1 Q2 Quantity Effect of Price Controls When Demand Is Inelastic
Effect of Price Controls When Demand Is Inelastic B A

If demand is sufficiently inelastic,triangle B can be larger than rectangle A.In this case,consumers suffer a net loss from price controls
If demand is sufficiently inelastic, triangle B can be larger than rectangle A. In this case, consumers suffer a net loss from price controls
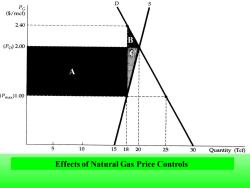
D PG ($/mcf) 2.40 B (Po)2.00 (Pmax)1.00 10 151820 25 30 Quantity (Tcf) Effects of Natural Gas Price Controls
Effects of Natural Gas Price Controls A A B C

The market-clearing price of natural gas is $2 per mef,and the maximum allowable price is $1.A shortage of 25-18=7 Tcf results.The gain to consumers is rectangle A minus triangle B, and the loss to producers is rectangle A plus triangle C
The market-clearing price of natural gas is $2 per mcf, and the maximum allowable price is $1. A shortage of 25-18 = 7 Tcf results. The gain to consumers is rectangle A minus triangle B, and the loss to producers is rectangle A plus triangle C
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 08 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 07 The Cost of Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 06 Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 05 Choice under Uncertainty.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 04 Individual and Market Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 03 Consumer Behavior.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 02 The Basics of Supply and Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 01 Preliminaries.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 19 Advances in Business Cycle theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 17 Investment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 18 Money supply and monetary Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 16 Consumption.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 15Government Debt and Budget Deficits.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 14 Stabilization Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 13 Aggregate supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 12 Aggregate demand in open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 11 Application of IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 10 The IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 09 Introduction to AS-AD model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 07 Economic growth(1/2).ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 10 Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 11 Pricing with Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 12 Monopolistic Competition.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 13 Game Theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 14 Markets for Factor Inputs.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 15 Investment, Time, and Capital.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 16 General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Markets with Asymmetric Information.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 18 Externalities.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Microeconomics.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程课程教学大纲 COST ACCOUNTING.pdf
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第一章 总论.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三章 成本汇集与分配.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二章 成本核算方法体系.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第五章 分步成本计算.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第六章 分类法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第四章 单步骤成本计算方法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第七章 作业成本计算.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第九章 标准成本法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十章 成本报表与成本分析.doc
