《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 18 Externalities

Chapter 18 Externalities and Public Goods Chapter Outline ▣Externalities Ways of Correcting Market Failure Externalities and Property Rights Common Property Resources ▣Public Goods Private Preferences for Public Goods
Chapter 18 Externalities and Public Goods Chapter Outline ❑ Externalities ❑ Ways of Correcting Market Failure ❑ Externalities and Property Rights ❑ Common Property Resources ❑ Public Goods ❑ Private Preferences for Public Goods

18.1 Externality Externality-Action taken by either a producer or a consumer which affects other producers or consumers but is not accounted for by the market price. Externalities can arise between producers,between customers, or between consumers and producers. They can be negative-when the action of one party imposes costs -or positive-when the action of one party benefits another party
18.1 Externality Externality-Action taken by either a producer or a consumer which affects other producers or consumers but is not accounted for by the market price. Externalities can arise between producers, between customers, or between consumers and producers. They can be negative- when the action of one party imposes costs —or positive– when the action of one party benefits another party

A negative externality occurs,for example,when a steel plant dumps its waste in a river that fishermen downstream depend on for their daily catch.The more waste the steel plant dumps in the river,the fewer fish will be supported
A negative externality occurs, for example, when a steel plant dumps its waste in a river that fishermen downstream depend on for their daily catch. The more waste the steel plant dumps in the river, the fewer fish will be supported

The firm,however,has no incentive to account for() the external costs that it imposes on fishermen when making its production decision. Furthermore,there is no market in which these external costs can be transmitted into the price of steel
The firm, however, has no incentive to account for(考虑) the external costs that it imposes on fishermen when making its production decision. Furthermore, there is no market in which these external costs can be transmitted into the price of steel

A positive externality occurs when a home owner repaints her house and plants (an attractive garden. ▣All the neighbors benefit from(受益于)this activity,yet the home owner's decision to repaint and landscape(从事自然美化工作) probably did not take these benefits into account,because his neighbors would not pay for the benefit ()
A positive externality occurs when a home owner repaints her house and plants (建立) an attractive garden. All the neighbors benefit from (受益于) this activity, yet the home owner’s decision to repaint and landscape(从事自然美化工作) probably did not take these benefits into account, because his neighbors would not pay for the benefit (好处)

Marginal external cost Increase in cost imposed externally as one or more firms increase output by one unit. ▣Marginal social cost Sum of the marginal cost of production and the marginal external cost
Marginal external cost Increase in cost imposed externally as one or more firms increase output by one unit. Marginal social cost Sum of the marginal cost of production and the marginal external cost
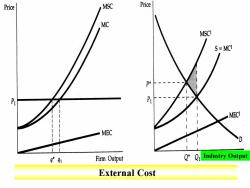
Price MSC Price MC MSCI S=MCI MECI MEC q*91 Firm Output 2*Qi Industry Output External Cost
Industry Output External Cost

When there are negative externalities,the marginal social cost MSC is higher than the marginal cost MC.The difference is the marginal external cost MEC. In (a),a profit-maximizing firm produces at qu,where price is equal to MC.Because externalities are not reflected in market prices,they can be a source of economic inefficiency. The efficient output is q*,at which price equals MSC
When there are negative externalities, the marginal social cost MSC is higher than the marginal cost MC. The difference is the marginal external cost MEC. In (a), a profit-maximizing firm produces at q1 , where price is equal to MC. Because externalities are not reflected in market prices, they can be a source of economic inefficiency. The efficient output is q*, at which price equals MSC
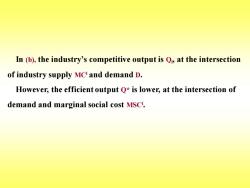
In(b),the industry's competitive output is Qp,at the intersection of industry supply MC and demand D. However,the efficient output Q*is lower,at the intersection of demand and marginal social cost MSC
In (b), the industry’s competitive output is Ql , at the intersection of industry supply MCl and demand D. However, the efficient output Q* is lower, at the intersection of demand and marginal social cost MSCl

Marginal external benefit-Increased benefit that accrues (自然增长)to other parties as a firm increases output by one unit. Marginal social benefit-Sum of the marginal private benefit plus the marginal external benefit
Marginal external benefit-Increased benefit that accrues (自然增长)to other parties as a firm increases output by one unit. Marginal social benefit -Sum of the marginal private benefit plus the marginal external benefit
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Markets with Asymmetric Information.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 16 General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 15 Investment, Time, and Capital.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 14 Markets for Factor Inputs.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 13 Game Theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 12 Monopolistic Competition.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 11 Pricing with Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 10 Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 09 The Analysis of Competitive Markets.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 08 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 07 The Cost of Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 06 Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 05 Choice under Uncertainty.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 04 Individual and Market Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 03 Consumer Behavior.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 02 The Basics of Supply and Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 01 Preliminaries.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 19 Advances in Business Cycle theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 17 Investment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 18 Money supply and monetary Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Microeconomics.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程课程教学大纲 COST ACCOUNTING.pdf
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第一章 总论.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三章 成本汇集与分配.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二章 成本核算方法体系.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第五章 分步成本计算.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第六章 分类法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第四章 单步骤成本计算方法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第七章 作业成本计算.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第九章 标准成本法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十章 成本报表与成本分析.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(试卷习题)各章题库(含参考答案).doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 01 成本的涵义、分类和作用(主讲:董建华).ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 02 产品成本核算概述.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 03 要素费用的归集与分配.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 04 辅助生产成本与制造费用的核算.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 05 成本计算品种法.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 06 产品计算分批法.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 07 废品、返工品和残料 Spoilage, Rework and Scrap.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 08 产品计算分步法.ppt
