《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 13 Game Theory

Chapter 13 Game Theory and Competitive Strategy Chapter Outline >Gaming and Strategic Decision Dominant Strategies The Nash Equilibrium Revisited Repeated Games Sequential Games Threats,Commitments,and Credibility Entry Deterrence Bargaining Strategy
Chapter 13 Game Theory and Competitive Strategy Chapter Outline ➢ Gaming and Strategic Decision ➢ Dominant Strategies ➢ The Nash Equilibrium Revisited ➢ Repeated Games ➢ Sequential Games ➢ Threats, Commitments, and Credibility ➢ Entry Deterrence ➢ Bargaining Strategy

13.1 Gaming and Strategic Decisions Game-Situation in which players (participants)make strategic decisions that take into account each other's actions and responses. Payoff-Value associated with a possible outcome of a game that generates rewards or benefits for the player. Strategy-Rule or plan of action for playing a game
13.1 Gaming and Strategic Decisions Game - Situation in which players (participants) make strategic decisions that take into account each other’s actions and responses. Payoff -Value associated with a possible outcome of a game that generates rewards or benefits for the player. Strategy - Rule or plan of action for playing a game

Optimal strategy-Strategy that maximizes player's expected payoff. Cooperative game-Game in which participants can negotiate binding contracts that allow them to plan joint strategies. Noncooperative game-Game in which negotiation and enforcement of binding contracts between players are not possible
Optimal strategy - Strategy that maximizes player’s expected payoff. Cooperative game - Game in which participants can negotiate binding contracts that allow them to plan joint strategies. Noncooperative game - Game in which negotiation and enforcement of binding contracts between players are not possible

13.2 Dominant Strategies Dominant strategy-Strategy that is optimal no matter what an opponent does. Equilibrium in dominant strategies-Outcome of a game in which each firm is doing the best it can regardless of what its competitors are doing
13.2 Dominant Strategies Dominant strategy - Strategy that is optimal no matter what an opponent does. Equilibrium in dominant strategies - Outcome of a game in which each firm is doing the best it can regardless of what its competitors are doing

Payoff Matrix for Advertising Game Firm B Advertise Don't advertise Advertise 10,5 15,0 FirmA Don't advertise 6,8 10,2
10, 5 15, 0 6, 8 10, 2 Firm B Advertise Don’t advertise Firm A Advertise Don’t advertise Payoff Matrix for Advertising Game

Modified Advertising Game Firm B Advertise Don't advertise Advertise 10,5 15,0 FirmA Don't advertise 6,8 20,2
10, 5 15, 0 6, 8 20, 2 Firm B Advertise Don’t advertise Firm A Advertise Don’t advertise Modified Advertising Game

13.3 The Nash Equilibrium Revisited Nash equilibrium-Set of strategies or actions in which each firm does the best it can given its competitors'actions. Each firm has no incentive to change its decision. Comparison of Nash equilibrium with an equilibrium in dominant strategies Equilibrium in I'm doing the best I can no matter what you do. Dominant Strategies You're doing the best you can no matter what I do. Nash equilibrium I'm doing the best I can given what you are doing. You're doing the best you can given what I am doing
13.3 The Nash Equilibrium Revisited Nash equilibrium - Set of strategies or actions in which each firm does the best it can given its competitors’ actions. Each firm has no incentive to change its decision. Comparison of Nash equilibrium with an equilibrium in dominant strategies Equilibrium in Dominant Strategies I’m doing the best I can no matter what you do. You’re doing the best you can no matter what I do. Nash equilibrium I’m doing the best I can given what you are doing. You’re doing the best you can given what I am doing
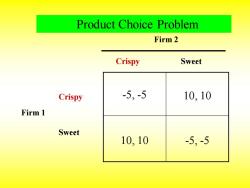
Product Choice Problem Firm 2 Crispy Sweet Crispy -5,-5 10,10 Firm 1 Sweet 10,10 -5,-5
-5, -5 10, 10 10, 10 -5, -5 Firm 2 Crispy Sweet Firm 1 Crispy Sweet Product Choice Problem

The Beach Location Game You (Y)and a competitor (C)plan to sell soft drinks on a beach. if sunbathers are spread evenly across the beach and will walk to the closest vendor,the two of you will locate next to each other at the center of the beach.This is the only Nash equilibrium
The Beach Location Game You (Y) and a competitor (C) plan to sell soft drinks on a beach. if sunbathers are spread evenly across the beach and will walk to the closest vendor, the two of you will locate next to each other at the center of the beach. This is the only Nash equilibrium

If your competitor located at point A,you would want to move until you were just to her left,where you could capture three-fourths of all sales. but your competitor would then want to move back to the center,and you would do the same
If your competitor located at point A, you would want to move until you were just to her left, where you could capture three-fourths of all sales. but your competitor would then want to move back to the center, and you would do the same
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 12 Monopolistic Competition.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 11 Pricing with Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 10 Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 09 The Analysis of Competitive Markets.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 08 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 07 The Cost of Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 06 Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 05 Choice under Uncertainty.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 04 Individual and Market Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 03 Consumer Behavior.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 02 The Basics of Supply and Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 01 Preliminaries.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 19 Advances in Business Cycle theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 17 Investment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 18 Money supply and monetary Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 16 Consumption.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 15Government Debt and Budget Deficits.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 14 Stabilization Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 13 Aggregate supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 12 Aggregate demand in open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 14 Markets for Factor Inputs.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 15 Investment, Time, and Capital.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 16 General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Markets with Asymmetric Information.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 18 Externalities.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Microeconomics.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程课程教学大纲 COST ACCOUNTING.pdf
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第一章 总论.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三章 成本汇集与分配.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二章 成本核算方法体系.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第五章 分步成本计算.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第六章 分类法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第四章 单步骤成本计算方法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第七章 作业成本计算.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第九章 标准成本法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十章 成本报表与成本分析.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(试卷习题)各章题库(含参考答案).doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 01 成本的涵义、分类和作用(主讲:董建华).ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 02 产品成本核算概述.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 03 要素费用的归集与分配.ppt
