《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 12 Monopolistic Competition

Chapter 12 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Chapter Outline Monopolistic Competition ·Oligopoly(寡头垄断) ·Price Competition Competition versus Collusion:The Prisoners' Dilemma for Oligopolistic Pricing 。Cartels
Chapter 12 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Chapter Outline • Monopolistic Competition • Oligopoly (寡头垄断) • Price Competition • Competition versus Collusion: The Prisoners’ Dilemma for Oligopolistic Pricing • Cartels

12.1 Monopolistic Competition Monopolistic competition-Market in which firms can enter freely,each producing its own brand or version of a differentiated product. Oligopoly-Market in which only a few firms compete with one another,and entry by new firms is impeded. Cartel-Market in which some or all firms explicitly collude, coordinating prices and output levels to maximize joint profits
12.1 Monopolistic Competition Monopolistic competition - Market in which firms can enter freely, each producing its own brand or version of a differentiated product. Oligopoly - Market in which only a few firms compete with one another, and entry by new firms is impeded. Cartel - Market in which some or all firms explicitly collude, coordinating prices and output levels to maximize joint profits
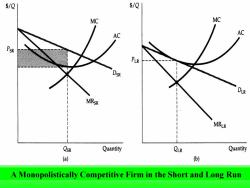
$/Q $/Q MC MC AC AC PsR P DSR 08 MRsR MRLR QSR Quantity QLR Quantity (a) 6) A Monopolistically Competitive Firm in the Short and Long Run
A Monopolistically Competitive Firm in the Short and Long Run

Because the firm is the only producer of its brand,it faces a downward-sloping demand curve: Price exceeds marginal cost and the firm has monopoly power. In the short run described in part (a),price also exceeds average cost,and the firm earns profits shown by the shaded rectangle
Because the firm is the only producer of its brand, it faces a downward-sloping demand curve: Price exceeds marginal cost and the firm has monopoly power. In the short run described in part (a), price also exceeds average cost, and the firm earns profits shown by the shaded rectangle

In the long run,these profits attract new firms with competing brands.The firm's market share falls,and its demand curve shifts downward. In long-run equilibrium,described in part (b),price equals average cost,so the firm earns zero profit,even though it has monopoly power
In the long run, these profits attract new firms with competing brands. The firm's market share falls, and its demand curve shifts downward. In long-run equilibrium, described in part (b), price equals average cost, so the firm earns zero profit, even though it has monopoly power
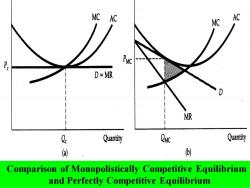
MC AC MC AC Pe PMC D=MR MR Q. Quantity Cvc Quantity (a) ) Comparison of Monopolistically Competitive Equilibrium and Perfectly Competitive Equilibrium
Comparison of Monopolistically Competitive Equilibrium and Perfectly Competitive Equilibrium

Under perfect competition,as in (a),price equals marginal cost, but under monopolistic competition,price exceeds marginal cost, so there is a deadweight loss as shown by the shaded area in (b). In both type of markets,entry occurs until profits are driven to zero
Under perfect competition, as in (a), price equals marginal cost, but under monopolistic competition, price exceeds marginal cost, so there is a deadweight loss as shown by the shaded area in (b). In both type of markets, entry occurs until profits are driven to zero

Under perfect competition,the demand curve facing the firm is horizontal,so the zero-profit point occurs at the point of minimum average cost. Under monopolistic competition the demand curve is downward sloping,so the zero-profit point is to the left of the point of minimum average cost. In evaluating monopolistic competition,these inefficiencies must be balanced (against the gains to consumers from product diversity
Under perfect competition, the demand curve facing the firm is horizontal, so the zero-profit point occurs at the point of minimum average cost. Under monopolistic competition the demand curve is downward sloping, so the zero-profit point is to the left of the point of minimum average cost. In evaluating monopolistic competition, these inefficiencies must be balanced (抵消) against the gains to consumers from product diversity

12.2 Oligopoly Nash equilibrium-Set of strategies or actions in which each firm does the best it can given its competitors'actions. Duopoly-Market in which two firms compete with each other. Cournot model-Oligopoly model in which firms produce a homogeneous good,each firm treats the output of its competitors as fixed,and all firms decide simultaneously how much to produce
12.2 Oligopoly Nash equilibrium - Set of strategies or actions in which each firm does the best it can given its competitors’ actions. Duopoly - Market in which two firms compete with each other. Cournot model - Oligopoly model in which firms produce a homogeneous good, each firm treats the output of its competitors as fixed, and all firms decide simultaneously how much to produce
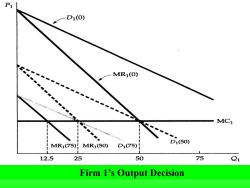
Pi D1(0) MR1(0) MC1 MR1(75) MR1(50)D1(75) p50 12.5 25 50 75 Q1 Firm 1's Output Decision
Firm 1’s Output Decision
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 11 Pricing with Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 10 Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 09 The Analysis of Competitive Markets.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 08 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 07 The Cost of Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 06 Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 05 Choice under Uncertainty.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 04 Individual and Market Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 03 Consumer Behavior.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 02 The Basics of Supply and Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 01 Preliminaries.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 19 Advances in Business Cycle theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 17 Investment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 18 Money supply and monetary Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 16 Consumption.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 15Government Debt and Budget Deficits.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 14 Stabilization Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 13 Aggregate supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 12 Aggregate demand in open economy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 11 Application of IS-LM model.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 13 Game Theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 14 Markets for Factor Inputs.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 15 Investment, Time, and Capital.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 16 General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Markets with Asymmetric Information.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 18 Externalities.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Microeconomics.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程课程教学大纲 COST ACCOUNTING.pdf
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第一章 总论.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三章 成本汇集与分配.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二章 成本核算方法体系.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第五章 分步成本计算.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第六章 分类法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第四章 单步骤成本计算方法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第七章 作业成本计算.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第九章 标准成本法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十章 成本报表与成本分析.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(试卷习题)各章题库(含参考答案).doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 01 成本的涵义、分类和作用(主讲:董建华).ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 02 产品成本核算概述.ppt
