《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 14 Markets for Factor Inputs

Chapter 14 Markets for Factor Inputs Chapter Outline Competitive Factor Markets Equilibrium in a Competitive Factor Market ▣Factor Markets with Monopsony(买方垄断)Power Factor Markets with Monopoly Power
Chapter 14 Markets for Factor Inputs Chapter Outline Competitive Factor Markets Equilibrium in a Competitive Factor Market Factor Markets with Monopsony(买方垄断)Power Factor Markets with Monopoly Power

14.1 Competitive Factor Markets Derived demand-Demand for an input that depends on, and is derived from,both the firm's level of output and the cost of inputs. ▣Marginal revenue product(边际收益产出)-Additional revenue resulting from the sale of output created by the use of one additional unit of an input
14.1 Competitive Factor Markets Derived demand - Demand for an input that depends on, and is derived from, both the firm’s level of output and the cost of inputs. Marginal revenue product(边际收益产出)-Additional revenue resulting from the sale of output created by the use of one additional unit of an input

MRPL is measured by the additional output obtained from the additional unit of this labor,multiplied by the additional revenue from an extra unit of output. Because△R/△L=(△R/△Q)(△Q/△L),it follows that MRPL=(MPL)(MR) In a competitive output market,the marginal revenue from the sale of an additional unit of output is then equal to P. MRPL=P(MPL)
MRPL is measured by the additional output obtained from the additional unit of this labor, multiplied by the additional revenue from an extra unit of output. Because R/L= (R/Q) (Q/L), it follows that MRPL = (MPL) (MR) In a competitive output market, the marginal revenue from the sale of an additional unit of output is then equal to P. MRPL = P (MPL)
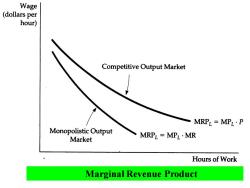
Wage (dollars per hour) Competitive Output Market MRPL=MPL·P Monopolistic Output Market MRPL=MPL·MR Hours of Work Marginal Revenue Product
Marginal Revenue Product

In a competitive factor market in which the producer is a price taker,the buyer's demand for an input is given by the marginal revenue product curve. The MRP curve falls because the marginal product of labor falls as hours of work increase.When the producer of the product has monopoly power,the demand for the input is also given by the MRP curve.In this case,however,the MRP curve falls because both the marginal product of labor and marginal revenue fall
In a competitive factor market in which the producer is a price taker, the buyer's demand for an input is given by the marginal revenue product curve. The MRP curve falls because the marginal product of labor falls as hours of work increase. When the producer of the product has monopoly power, the demand for the input is also given by the MRP curve. In this case, however, the MRP curve falls because both the marginal product of labor and marginal revenue fall

Only when the marginal revenue product is equal to the wage rate will the firm have hired the profit-maximizing amount of labor.This profit-maximizing condition is therefore MRPL=0
Only when the marginal revenue product is equal to the wage rate will the firm have hired the profit-maximizing amount of labor. This profit-maximizing condition is therefore MRPL =

The factor market profit-maximizing condition that the marginal revenue product be equal to the wage rate (MRPL=(MP)MR=o)is analogical to(偻似于)the output market condition that marginal revenue be equal to marginal cost. MR=0/MPL
The factor market profit-maximizing condition that the marginal revenue product be equal to the wage rate ( MRPL =(MPL) MR = ) is analogical to (类似于) the output market condition that marginal revenue be equal to marginal cost. MR = /MPL

The equation shows that both the hiring and output choices of the firm follow the same rule:inputs or output are chosen so that marginal revenue(from the sale of output)is equal to marginal cost(from the purchase of inputs).This principle holds (in both competitive and noncompetitive markets
The equation shows that both the hiring and output choices of the firm follow the same rule: inputs or output are chosen so that marginal revenue (from the sale of output) is equal to marginal cost (from the purchase of inputs).This principle holds (适用) in both competitive and noncompetitive markets
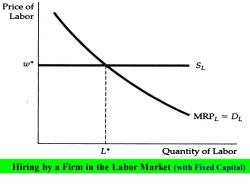
Price of Labor 0¥ SL MRPL=DL L* Quantity of Labor Hiring by a Firm in the Labor Market (with Fixed Capital)
Hiring by a Firm in the Labor Market (with Fixed Capital)

In a competitive labor market,a firm faces a perfectly elastic supply of labor SL and can hire as many workers as it wants at a wage rate w*. The firm's demand for labor D is given by its marginal revenue product of labor MRPL.The profit-maximizing firm will hire L* units of labor at the point where the marginal revenue product of labor is equal to the wage rate
In a competitive labor market, a firm faces a perfectly elastic supply of labor SL and can hire as many workers as it wants at a wage rate w*. The firm's demand for labor DL is given by its marginal revenue product of labor MRPL . The profit-maximizing firm will hire L* units of labor at the point where the marginal revenue product of labor is equal to the wage rate
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 13 Game Theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 12 Monopolistic Competition.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 11 Pricing with Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 10 Market Power.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 09 The Analysis of Competitive Markets.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 08 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 07 The Cost of Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 06 Production.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 05 Choice under Uncertainty.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 04 Individual and Market Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 03 Consumer Behavior.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 02 The Basics of Supply and Demand.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 01 Preliminaries.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 19 Advances in Business Cycle theory.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 17 Investment.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 18 Money supply and monetary Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 16 Consumption.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 15Government Debt and Budget Deficits.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 14 Stabilization Policy.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(宏观经济学)Chapter 13 Aggregate supply.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 15 Investment, Time, and Capital.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 16 General Equilibrium and Economic Efficiency.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Markets with Asymmetric Information.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 18 Externalities.ppt
- 《西方经济学》课程PPT教学课件(微观经济学)Chapter 17 Microeconomics.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程课程教学大纲 COST ACCOUNTING.pdf
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第一章 总论.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三章 成本汇集与分配.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二章 成本核算方法体系.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第五章 分步成本计算.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第六章 分类法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第四章 单步骤成本计算方法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第七章 作业成本计算.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第九章 标准成本法.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十章 成本报表与成本分析.doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(试卷习题)各章题库(含参考答案).doc
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 01 成本的涵义、分类和作用(主讲:董建华).ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 02 产品成本核算概述.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 03 要素费用的归集与分配.ppt
- 海南大学:《成本会计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 04 辅助生产成本与制造费用的核算.ppt
