《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy

Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry,and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2006,Prentice Hall
Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2006, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Definitions Conjugated double bonds are separated by one single bond.Example:1,3-pentadiene. Isolated double bonds are separated by two or more single bonds.Example:1,4- pentadiene. Cumulated double bonds are on adjacent carbons.Example:1,2-pentadiene. => Chaper 15
Chaper 15 2 Definitions • Conjugated double bonds are separated by one single bond. Example: 1,3-pentadiene. • Isolated double bonds are separated by two or more single bonds. Example: 1,4- pentadiene. • Cumulated double bonds are on adjacent carbons. Example: 1,2-pentadiene. =>

Stabilities of Dienes Heat of hydrogenation for 1,4-pentadiene is -252 kJ/mol,about twice that of 1-pentene. ·△Hfor1-pentene is-126 kJ/mol and for trans-2-pentene is -116 kJ/mol,so expect -242 kJ/mol for trans-1,3-pentadiene. ·Actual△His-225kJ/mol,so the conjugated diene is more stable. Difference,-242 kJ(-225 kJ)=17 kJ/mol,is the resonance energy. => Chaper 15 3
Chaper 15 3 Stabilities of Dienes • Heat of hydrogenation for 1,4-pentadiene is –252 kJ/mol, about twice that of 1-pentene. • H for 1-pentene is -126 kJ/mol and for trans-2-pentene is -116 kJ/mol, so expect -242 kJ/mol for trans-1,3-pentadiene. • Actual H is -225 kJ/mol, so the conjugated diene is more stable. • Difference, -242 kJ (-225 kJ) = 17 kJ/mol, is the resonance energy. =>
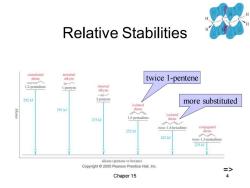
Relative Stabilities cumulated terminal diene alkyne twice 1-pentene 1.2-pentadiene I-pentyne internal alkyne 292 2-pentyne more substituted isolated 291J dlene 入 isolated 275kJ 1.4-pentadiene diene 入 trans-1.4-hexadiene conjugated 252k diene 242k」 trans-1,3-pentadicne 225kJ alkane (pentane or hexane) Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. => Chaper 15 4
Chaper 15 4 Relative Stabilities twice 1-pentene more substituted =>
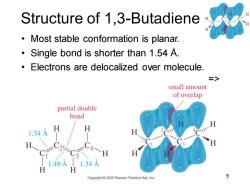
Structure of 1,3-Butadiene Most stable conformation is planar. Single bond is shorter than 1.54 A. Electrons are delocalized over molecule. => small amount of overlap partial double bond 1.34A H 1.34A Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Chaper 15 5 Structure of 1,3-Butadiene • Most stable conformation is planar. • Single bond is shorter than 1.54 Å. • Electrons are delocalized over molecule. =>

Constructing Molecular Orbitals Pi molecular orbitals are the sideways overlap of p orbitals. p orbitals have 2 lobes.Plus (+and minus (-)indicate the opposite phases of the wave function,not electrical charge. When lobes overlap constructively,(and +or-and -)a bonding MO is formed. When and-lobes overlap,waves cancel out and a node forms;antibonding MO.= Chaper 15 6
Chaper 15 6 Constructing Molecular Orbitals • Pi molecular orbitals are the sideways overlap of p orbitals. • p orbitals have 2 lobes. Plus (+) and minus (-) indicate the opposite phases of the wave function, not electrical charge. • When lobes overlap constructively, (+ and +, or - and -) a bonding MO is formed. • When + and - lobes overlap, waves cancel out and a node forms; antibonding MO. =>
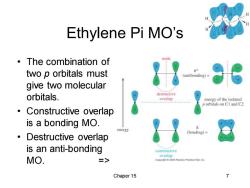
Ethylene Pi MO's ·The combination of node two p orbitals must π* (antibonding)= give two molecular orbitals. destructive overlap energy of the isolated p orbitals on CI and C2 ● Constructive overlap is a bonding MO. energy (bonding)= 。Destructive overlap is an anti-bonding constructive overlap MO. => Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc Chaper 15
Chaper 15 7 Ethylene Pi MO’s • The combination of two p orbitals must give two molecular orbitals. • Constructive overlap is a bonding MO. • Destructive overlap is an anti-bonding MO. =>
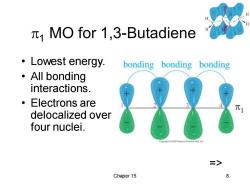
MO for 1,3-Butadiene ·Lowest energy, bonding bonding bonding ·All bonding interactions. ● Electrons are delocalized over four nuclei. Copyright2005 Peerson Prentce Hall,ine > Chaper 15 8
Chaper 15 8 1 MO for 1,3-Butadiene • Lowest energy. • All bonding interactions. • Electrons are delocalized over four nuclei. =>
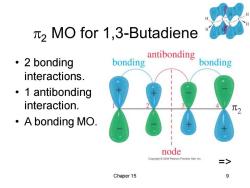
2 MO for 1,3-Butadiene 。2 bonding bonding antibonding bonding interactions. 。1 antibonding interaction. ·A bonding MO. node Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc. > Chaper 15 9
Chaper 15 9 2 MO for 1,3-Butadiene • 2 bonding interactions. • 1 antibonding interaction. • A bonding MO. =>
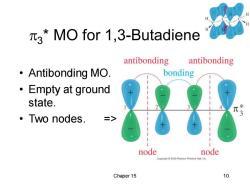
3*MO for 1,3-Butadiene antibonding antibonding ·Antibonding MO. bonding ·Empty at ground state. ·Two nodes. node node Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc Chaper 15 10
Chaper 15 10 3 * MO for 1,3-Butadiene • Antibonding MO. • Empty at ground state. • Two nodes. =>
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 08 Alkenes - Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 10 Alkyl Halides.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 09 Stereochemistry.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 08 Alkynes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 07 Alkenes - Reactions and Synthesis.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 06 Haluros de Alquilo - Substitución Nucleofílica y Eliminación.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review(西北农林科技大学,2010).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules(西北农林科技大学,2010).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
