《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes

Organic Chemistry,5th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 7 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2003,Prentice Hall
Chapter 7 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2003, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Functional Group Pi bond is the functional group. More reactive than sigma bond. Bond dissociation energies: >C=C BDE 146 kcal/mol >C-C BDE -83 kcal/mol >Pi bond 63 kcal/mol => Chapter 7 2
Chapter 7 2 Functional Group • Pi bond is the functional group. • More reactive than sigma bond. • Bond dissociation energies: ➢C=C BDE 146 kcal/mol ➢C-C BDE -83 kcal/mol ➢Pi bond 63 kcal/mol =>

Orbital Description Sigma bonds around C are sp2 hybridized. Angles are approximately 120 degrees. No nonbonding electrons. Molecule is planar around the double bond. Pi bond is formed by the sideways overlap of parallel p orbitals perpendicular to the plane of the molecule. => Chapter 7 3
Chapter 7 3 Orbital Description • Sigma bonds around C are sp2 hybridized. • Angles are approximately 120 degrees. • No nonbonding electrons. • Molecule is planar around the double bond. • Pi bond is formed by the sideways overlap of parallel p orbitals perpendicular to the plane of the molecule. =>

Bond Lengths and Angles 1.33A H 1.54A H 116.6° 121.7° ethylene ethane Hybrid orbitals have more s character. Pi overlap brings carbon atoms closer. Bond angle with pi orbitals increases. >Angle C=C-His121.7° >Angle H-C-His116.6° Chapter 7 4
Chapter 7 4 Bond Lengths and Angles • Hybrid orbitals have more s character. • Pi overlap brings carbon atoms closer. • Bond angle with pi orbitals increases. ➢Angle C=C-H is 121.7 ➢Angle H-C-H is 116. 6 =>
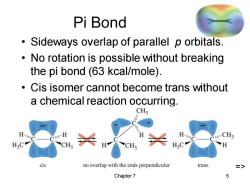
Pi Bond Sideways overlap of parallel p orbitals. No rotation is possible without breaking the pi bond (63 kcal/mole). Cis isomer cannot become trans without a chemical reaction occurring. CH3 CH3 CH cis no overlap with the ends perpendicular trans Chapter 7 5
Chapter 7 5 Pi Bond • Sideways overlap of parallel p orbitals. • No rotation is possible without breaking the pi bond (63 kcal/mole). • Cis isomer cannot become trans without a chemical reaction occurring. =>

Elements of Unsaturation A saturated hydrocarbon:CH2n+2 0 Each pi bond (and each ring)decreases the number of H's by two. Each of these is an element of unsaturation. To calculate:find number of H's if it were saturated,subtract the actual number of H's, then divide by 2. => Chapter 7 6
Chapter 7 6 Elements of Unsaturation • A saturated hydrocarbon: CnH2n+2 • Each pi bond (and each ring) decreases the number of H’s by two. • Each of these is an element of unsaturation. • To calculate: find number of H’s if it were saturated, subtract the actual number of H’s, then divide by 2. =>

Propose a Structure: for CsHs First calculate the number of elements of unsaturation. ·Remember: >A double bond is one element of unsaturation. >A ring is one element of unsaturation. >A triple bond is two elements of unsaturation.= Chapter 7 7
Chapter 7 7 Propose a Structure: • First calculate the number of elements of unsaturation. • Remember: ➢A double bond is one element of unsaturation. ➢A ring is one element of unsaturation. ➢A triple bond is two elements of unsaturation. => for C5H8

Heteroatoms Halogens take the place of hydrogens,so add their number to the number of H's. Oxygen doesn't change the C:H ratio,so ignore oxygen in the formula. Nitrogen is trivalent,so it acts like half a carbon. HH H -C-C-N-C- => HHHH Chapter 7 8
Chapter 7 8 Heteroatoms • Halogens take the place of hydrogens, so add their number to the number of H’s. • Oxygen doesn’t change the C:H ratio, so ignore oxygen in the formula. • Nitrogen is trivalent, so it acts like half a carbon. C H H C H H N C H H H =>

Structure for CH-N? Since nitrogen counts as half a carbon, the number of H's if saturated is 2(6.5)+2=15. Number of missing H's is 15-7=8. ·Elements of unsaturation is8÷2=4. 二> Chapter 7 9
Chapter 7 9 Structure for C6H7N? • Since nitrogen counts as half a carbon, the number of H’s if saturated is 2(6.5) + 2 = 15. • Number of missing H’s is 15 – 7 = 8. • Elements of unsaturation is 8 ÷ 2 = 4. =>

IUPAC Nomenclature Parent is longest chain containing the double bond. -ane changes to -ene.(or -diene,-triene) Number the chain so that the double bond has the lowest possible number. In a ring,the double bond is assumed to be between carbon 1 and carbon 2. 二> Chapter 7 10
Chapter 7 10 IUPAC Nomenclature • Parent is longest chain containing the double bond. • -ane changes to -ene. (or -diene, -triene) • Number the chain so that the double bond has the lowest possible number. • In a ring, the double bond is assumed to be between carbon 1 and carbon 2. =>
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules(西北农林科技大学,2010).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review(西北农林科技大学,2010).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 06 Haluros de Alquilo - Substitución Nucleofílica y Eliminación.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition, L. G. Wade, Jr.Pearson Education)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
