《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids

Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2006,Prentice Hall
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2006, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Introduction Carbonyl (-C=O)and hydroxyl (-OH)on the same carbon is carboxyl group. Carboxyl group is usually written-COOH. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to -COOH. Aromatic acids have an aryl group. Fatty acids are long-chain aliphatic acids. R-C-0-H+H,0:→ +H,O+ pK,=5 (K≡105) acid => 2 carboxylate
Chapter 20 2 Introduction • Carbonyl (-C=O) and hydroxyl (-OH) on the same carbon is carboxyl group. • Carboxyl group is usually written -COOH. • Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to -COOH. • Aromatic acids have an aryl group. • Fatty acids are long-chain aliphatic acids. =>
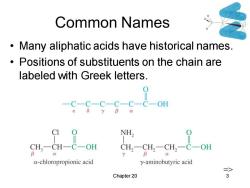
Common Names Many aliphatic acids have historical names. Positions of substituents on the chain are labeled with Greek letters. 0 -C-C-C-C-C-C-0H NH, CH3-CH一C一OH CH2一CH2-CH2-C一OH a-chloropropionic acid y-aminobutyric acid => Chapter 20 3
Chapter 20 3 Common Names • Many aliphatic acids have historical names. • Positions of substituents on the chain are labeled with Greek letters. =>

IUPAC Names Remove-e from alkane (or alkene) name,add -oic acid. The carbon of the carboxyl group is #1. CIO H CHCH-CHC-OH CC、 H COOH 2-chlorobutanoic acid trans-3-phenyl-2-propenoic acid (cinnamic acid) => Chapter 20 4
Chapter 20 4 IUPAC Names • Remove -e from alkane (or alkene) name, add -oic acid. • The carbon of the carboxyl group is #1. CH3 CH2 CHC Cl OH O 2-chlorobutanoic acid Ph C H C H COOH trans-3-phenyl-2-propenoic acid (cinnamic acid) =>
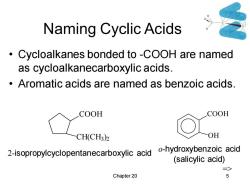
Naming Cyclic Acids Cycloalkanes bonded to -COOH are named as cycloalkanecarboxylic acids. Aromatic acids are named as benzoic acids. COOH COOH CH(CH3)2 OH 2-isopropylcyclopentanecarboxylic acid -hydroxybenzoic acid (salicylic acid) => Chapter 20 5
Chapter 20 5 Naming Cyclic Acids • Cycloalkanes bonded to -COOH are named as cycloalkanecarboxylic acids. • Aromatic acids are named as benzoic acids. COOH CH(CH3 ) 2 2-isopropylcyclopentanecarboxylic acid COOH OH o-hydroxybenzoic acid (salicylic acid) =>

Dicarboxylic Acids Aliphatic diacids are usually called by their common names (to be memorized). For IUPAC name,number the chain from the end closest to a substituent. Two carboxyl groups on a benzene ring indicate a phthalic acid. COOH Br HOOCCH2CHCH2CH2COOH COOH 3-bromohexanedioic acid 1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid β-bromoadipic acid m-phthalic acid => Chapter 20 6
Chapter 20 6 Dicarboxylic Acids • Aliphatic diacids are usually called by their common names (to be memorized). • For IUPAC name, number the chain from the end closest to a substituent. • Two carboxyl groups on a benzene ring indicate a phthalic acid. HOOCCH2 CHCH2 CH2 COOH Br 3-bromohexanedioic acid -bromoadipic acid COOH COOH 1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid m-phthalic acid =>
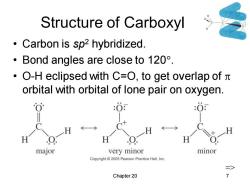
Structure of Carboxyl Carbon is sp2 hybridized. ·Bond angles are close to120°. ·O-H eclipsed with C=O,to get overlap ofπ orbital with orbital of lone pair on oxygen. :O :0 major very minor minor Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 20
Chapter 20 7 Structure of Carboxyl • Carbon is sp2 hybridized. • Bond angles are close to 120. • O-H eclipsed with C=O, to get overlap of orbital with orbital of lone pair on oxygen. =>
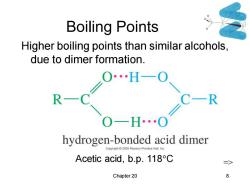
Boiling Points Higher boiling points than similar alcohols, due to dimer formation. C一R OH0 hydrogen-bonded acid dimer Copyright 2005 Pe on Prentice Hall,In Acetic acid,b.p.118C Chapter 20 8
Chapter 20 8 Boiling Points Higher boiling points than similar alcohols, due to dimer formation. Acetic acid, b.p. 118C =>

Melting Points Aliphatic acids with more than 8 carbons are solids at room temperature. Double bonds (especially cis)lower the melting point.Note these 18-C acids: >Stearic acid (saturated):72C >Oleic acid (one cis double bond):16C >Linoleic acid (two cis double bonds):-5C => Chapter 20 9
Chapter 20 9 Melting Points • Aliphatic acids with more than 8 carbons are solids at room temperature. • Double bonds (especially cis) lower the melting point. Note these 18-C acids: ➢Stearic acid (saturated): 72C ➢Oleic acid (one cis double bond): 16C ➢Linoleic acid (two cis double bonds): -5C =>

Solubility Water solubility decreases with the length of the carbon chain. Up to 4 carbons,acid is miscible in water. More soluble in alcohol. Also soluble in relatively nonpolar solvents like chloroform because it dissolves as a dimer. Chapter 20 10
Chapter 20 10 Solubility • Water solubility decreases with the length of the carbon chain. • Up to 4 carbons, acid is miscible in water. • More soluble in alcohol. • Also soluble in relatively nonpolar solvents like chloroform because it dissolves as a dimer. =>
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 08 Alkenes - Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 06 Haluros de Alquilo - Substitución Nucleofílica y Eliminación.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review(西北农林科技大学,2010).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules(西北农林科技大学,2010).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
