《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers

Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2006,Prentice Hall
Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2006, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Introduction A polymer is a large molecule composed of many smaller repeating units. First synthetic polymers: >Poly(vinyl chloride)in 1838 >Polystyrene in 1839 Now,250 billion pounds produced annually,worldwide. => Chapter 26
Chapter 26 2 Introduction • A polymer is a large molecule composed of many smaller repeating units. • First synthetic polymers: ➢Poly(vinyl chloride) in 1838 ➢Polystyrene in 1839 • Now, 250 billion pounds produced annually, worldwide. =>
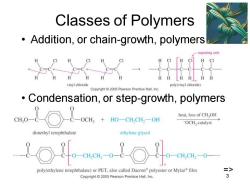
Classes of Polymers Addition,or chain-growth,polymers epeating unit H CI a.a vinyl chloride poly(vinyl chloride) Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc Condensation,or step-growth,polymers eHo-8-○&-+o-Gual-0m heat,loss of CHOH -OCH catalyst dimethyl terephthalate ethylene glycol 110-10 -CH,CH2O-- poly(ethylene terephthalate)or PET,also called Dacron polyester or Mylar film => Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Chapter 26 3 Classes of Polymers • Addition, or chain-growth, polymers • Condensation, or step-growth, polymers =>

Addition Polymers Three kinds of intermediates: >Free radicals >Carbocations >Carbanions ● Examples of addition polymers: >polypropylene plastics >polystyrene foam insulation >poly(acrylonitrile)Orlon fiber >poly(methyl a-methacrylate) Plexiglas. Chapter 26
Chapter 26 4 Addition Polymers • Three kinds of intermediates: ➢Free radicals ➢Carbocations ➢Carbanions • Examples of addition polymers: ➢polypropylene plastics ➢polystyrene foam insulation ➢poly(acrylonitrile) Orlon® fiber ➢poly(methyl -methacrylate) Plexiglas ® =>
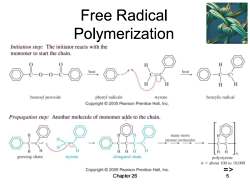
Free Radical Polymerization Initiation step:The initiator reacts with the monomer to start the chain. heat benzoyl peroxide phenyl radicals styrene benzylic radical Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Propagation step:Another molecule of monomer adds to the chain. many more styrene molecules H growing chain styrene elongated chain polystyrene n=about 100 to 10.000 Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. => Chapter 26 5
Chapter 26 5 Free Radical Polymerization =>
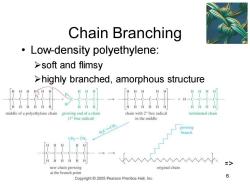
Chain Branching Low-density polyethylene: >soft and flimsy >highly branched,amorphous structure middle of a polyethylene chain growing end of a chain chain with 2 free radical terminated chain (1 free radical) in the middle H,C=CH2 growing branch CH2一CH new chain growing original chain at the branch point 6 Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Chapter 26 6 Chain Branching • Low-density polyethylene: ➢soft and flimsy ➢highly branched, amorphous structure =>

Cationic Polymerization Alkene is treated with an acid. Intermediate must be a stable carbocation. Initiation steps:The catalyst protonates the monomer,starting the chain. H CH, CH B*+HO: +F一B一OE CH. CH H isobutylene initiated chain Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Propagation step:Another molecule of monomer adds to the chain. tertiary carbocation CH CH CH CH CH H CH,H CH. growing chain isobutylene elongated chain polymer Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. 三>
Chapter 26 7 Cationic Polymerization • Alkene is treated with an acid. • Intermediate must be a stable carbocation. =>
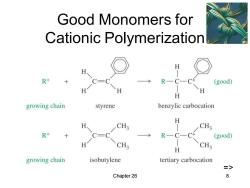
Good Monomers for Cationic Polymerization H R+ R—C-C (good) H growing chain styrene benzylic carbocation H CH3 CH3 R+ C= R一C一 (good) CH3 CH3 H growing chain isobutylene tertiary carbocation => Chapter 26 8
Chapter 26 8 Good Monomers for Cationic Polymerization =>

Anionic Polymerization Alkene must have an electron-withdrawing group like C=O,C=N,or NO2. Initiator:Grignard or organolithium reagent. Initiation step:The initiator adds to the monomer to the form an anion. H、 CN CN Bu-Li Bu- H H butyllithium acrylonitrile stabilized anion 三> Propagation step:Another molecule of monomer adds to the chain. H growing chain acrylonitrile elongated chain polymer Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Chapter 26 9 Anionic Polymerization • Alkene must have an electron-withdrawing group like C=O, CN, or NO2 . • Initiator: Grignard or organolithium reagent. =>
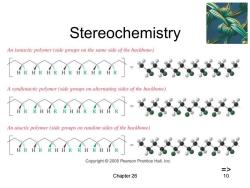
Stereochemistry An isotactic polymer(side groups on the same side of the backbone) A syndiotactic polymer (side groups on alternating sides of the backbone) R An atactic polymer (side groups on random sides of the backbone) Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. => Chapter 26 10
Chapter 26 10 Stereochemistry =>
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 08 Alkenes - Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 06 Haluros de Alquilo - Substitución Nucleofílica y Eliminación.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review(西北农林科技大学,2010).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules(西北农林科技大学,2010).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
