《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions

Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate lons Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2006,Prentice Hall
Chapter 22 Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2006, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr

Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,C=O. Step 1:Deprotonation Step 2:Attack on electrophile base: enolate ion Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. > Chapter 22 2
Chapter 22 2 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl, C=O. =>

Condensation with Aldehyde or Ketone Enolate ion attacks a C=O and the alkoxide is protonated.The net result is addition. RO enolate ketone addition product => Chapter 22 3
Chapter 22 3 Condensation with Aldehyde or Ketone Enolate ion attacks a C=O and the alkoxide is protonated. The net result is addition. =>
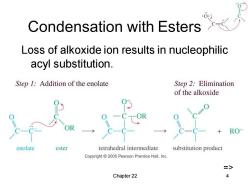
Condensation with Esters Loss of alkoxide ion results in nucleophilic acyl substitution. Step 1:Addition of the enolate Step 2:Elimination of the alkoxide RO enolate ester tetrahedral intermediate substitution product Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. => Chapter 22 4
Chapter 22 4 Condensation with Esters Loss of alkoxide ion results in nucleophilic acyl substitution. =>

Keto-Enol Tautomers Tautomers are isomers which differ in the placement of a hydrogen. One may be converted to the other. ·In base: Step 1:Deprotonation on C Step 2:Reprotonation on O HO: OH +OH H enol form keto form enolate ion (vinyl alcohol) Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. => Chapter 22 5
Chapter 22 5 Keto-Enol Tautomers • Tautomers are isomers which differ in the placement of a hydrogen. • One may be converted to the other. • In base: =>
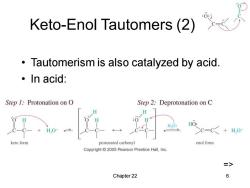
Keto-Enol Tautomers(2) Tautomerism is also catalyzed by acid. ·In acid: Step 1:Protonation on O Step 2:Deprotonation on C H H.O: HO: HO+ >c=C+H,0 keto form protonated carbonyl enol form Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. => Chapter 22 6
Chapter 22 6 Keto-Enol Tautomers (2) • Tautomerism is also catalyzed by acid. • In acid: =>

Equilibrium Amounts For aldehydes and ketones,the keto form is greatly favored at equilibrium. An enantiomer with an enolizable hydrogen can form a racemic mixture. enolizable hydrogens 1 CH H+orOH H a carbons (R)configuration enol (achiral) (S)configuration Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. => Chapter 22 7
Chapter 22 7 Equilibrium Amounts • For aldehydes and ketones, the keto form is greatly favored at equilibrium. • An enantiomer with an enolizable hydrogen can form a racemic mixture. =>

Acidity of a-Hydrogens pKa for a-H of aldehyde or ketone ~20. Much more acidic than alkane or alkene (pKa 40)or alkyne (pKa 25). Less acidic than water(pKa =15.7)or alcohol (pKa 16-19). In the presence of hydroxide or alkoxide ions,only a small amount of enolate ion is present at equilibrium. => Chapter 22 8
Chapter 22 8 Acidity of -Hydrogens • pKa for -H of aldehyde or ketone ~20. • Much more acidic than alkane or alkene (pKa > 40) or alkyne (pKa = 25). • Less acidic than water (pKa = 15.7) or alcohol (pKa = 16-19). • In the presence of hydroxide or alkoxide ions, only a small amount of enolate ion is present at equilibrium. =>
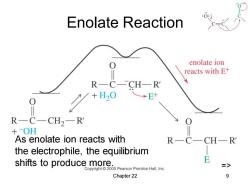
Enolate Reaction enolate ion reacts with E+ RC-CHR →E+ R一C一CH2-R +OH As enolate ion reacts with RC CHR the electrophile,the equilibrium shifts to produce more. E Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Chapter 22 9
Chapter 22 9 Enolate Reaction => As enolate ion reacts with the electrophile, the equilibrium shifts to produce more
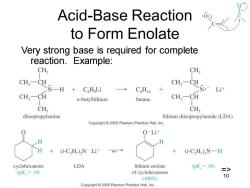
Acid-Base Reaction to Form Enolate Very strong base is required for complete reaction.Example: CHs CH, CH,一C CH一C N-一H C.H Li CaH10 CN: Li计 CH3-CH n-butyllithium butane CH:-CH CH CH; diisopropylamine lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. O-Lit (i-CH)N-Li+ (i-C,H)2N-H cyclohexanone LDA lithium enolate (pK,=36 (pK.=I19) => of cyclohexanone 10 (100%) Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Chapter 22 10 Acid-Base Reaction to Form Enolate Very strong base is required for complete reaction. Example: =>
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 19 Amines.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 08 Alkenes - Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 23 Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 25 Lipids.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 06 Haluros de Alquilo - Substitución Nucleofílica y Eliminación.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review(西北农林科技大学,2010).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules(西北农林科技大学,2010).ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 06 Alkyl Halides - Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 08 Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
