《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 09 Stereochemistry
Stereochemistry Based on McMurry's Organic Chemistry,6th edition,Chapter 9
Stereochemistry Based on McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition, Chapter 9
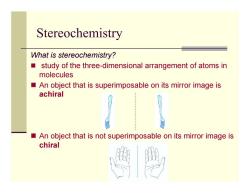
Stereochemistry What is stereochemistry? study of the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in molecules An object that is superimposable on its mirror image is achiral An object that is not superimposable on its mirror image is chiral
Stereochemistry What is stereochemistry? study of the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in molecules An object that is superimposable on its mirror image is achiral An object that is not superimposable on its mirror image is chiral
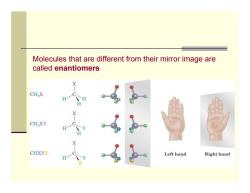
Molecules that are different from their mirror image are called enantiomers CH X CH2XY CHXYZ Left hand Right hand
Molecules that are different from their mirror image are called enantiomers
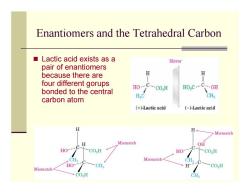
Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon Lactic acid exists as a Mirror pair of enantiomers because there are H H four different gorups HO bonded to the central C-co.H H0,C一C0H H.C CH carbon atom (+)-Lactic acid (-)-Lactic acid H H Mismatch H Mismatch OH C -C HO- CO.,H HO CO,H CH Mismatch CH. HO- Mismatch CH3 H- -CO2H CO2H CH3
Enantiomers and the Tetrahedral Carbon Lactic acid exists as a pair of enantiomers because there are four different gorups bonded to the central carbon atom

The Reason for Handedness:Chirality Achiral molecule:has a plane of symmetry and is superimposable on its mirror image A plane of symmetry is a plane that passes through a molecule in such a way that what is on one side of the plane is the exact reflection of what is on the other side NOT Symmetry symmetry plane plane CH CH H H H OH CO,H CO,H OH CH CH2CO.H CH CHCO,H Propanoic acid Lactic acid (achiral) (chiral)
The Reason for Handedness: Chirality Achiral molecule: has a plane of symmetry and is superimposable on its mirror image A plane of symmetry is a plane that passes through a molecule in such a way that what is on one side of the plane is the exact reflection of what is on the other side

Chirality ■ Chiral molecule does not have a plane of symmetry and is therefore not superimposable on their mirror image. The most common cause of chirality in an organic molecule is the presence of a carbon atom bonded to four different groups.Such carbon atoms are referred to as chiral centres or stereogenic centres. A chiral molecule usually has at least one chiral center Substituents on carbon 5 Br 一H CHCH2CH,CH2CH,CCH,CH,CH2CH 一Br H 一CH2CHCH2CH3(butyl) 5-Bromodecane (chiral) -CH2CH2CH2CH2CHg(pentyl)
Chirality Chiral molecule : does not have a plane of symmetry and is therefore not superimposable on their mirror image. The most common cause of chirality in an organic molecule is the presence of a carbon atom bonded to four different groups. Such carbon atoms are referred to as chiral centres or stereogenic centres. A chiral molecule usually has at least one chiral center
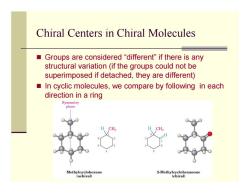
Chiral Centers in Chiral Molecules ■ Groups are considered"different"if there is any structural variation(if the groups could not be superimposed if detached,they are different) In cyclic molecules,we compare by following in each direction in a ring Symmetry plane Methylcyclohexane 2-Methylcyclohexanone (achiral) (chiral)
Chiral Centers in Chiral Molecules Groups are considered “different” if there is any structural variation (if the groups could not be superimposed if detached, they are different) In cyclic molecules, we compare by following in each direction in a ring

Optical activity ■ Chiral compounds exhibit optical activity and are said to be optically active.Achiral compounds are optically inactive Optical activity is the ability of a compound to rotate the plane of polarized light Enantiomers of an enantiomeric pair are identical in all their physical properties except optical activity Unpolarized Light source Achiral Polarized compound Sample cell Analyzer
Optical Activity Chiral compounds exhibit optical activity and are said to be optically active. Achiral compounds are optically inactive Optical activity is the ability of a compound to rotate the plane of polarized light Enantiomers of an enantiomeric pair are identical in all their physical properties except optical activity

Unpolarized Light source light Chiral Polarized compound light Rotated polarized ligh Sample cell The two enantiomers of a pair of enantiomers rotate the plane of polarized light by the same degree but in opposite directions One enantiomer rotates light in the clockwise direction and is called dextrorotatory (+ The other enantiomer rotates light in the anticlockwise direction and is called levorotatory(-)
The two enantiomers of a pair of enantiomers rotate the plane of polarized light by the same degree but in opposite directions One enantiomer rotates light in the clockwise direction and is called dextrorotatory (+) The other enantiomer rotates light in the anticlockwise direction and is called levorotatory (-)

Optical Activity The direction of rotation of the polarized light is indicated in the names of the enantiomers by placing (+)or(-)as prefixes to their names eg (+)-glyceraldehyde (-)-2-methylbutanoic acid Rotation,in degrees,is a specific rotation,[a]p for an optically active compound is the angle observed for 1 g/mL in solution in cell with a 10 cm path using sodium D line (ie light of 589 nanometers) [a]p observed rotation/(pathlength x concentration) =al(Ix C)=degrees/(dm x g/mL)
Optical Activity The direction of rotation of the polarized light is indicated in the names of the enantiomers by placing (+) or (-) as prefixes to their names eg (+) - glyceraldehyde ( – ) - 2-methylbutanoic acid Rotation, in degrees, is α specific rotation, [ α ] D for an optically active compound is the angle observed for 1 g/mL in solution in cell with a 10 cm path using sodium D line (ie light of 589 nanometers) [ α ] D = observed rotation/(pathlength x concentration) = α/(l x C) = degrees/(dm x g/mL)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 08 Alkynes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 07 Alkenes - Reactions and Synthesis.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 06 Alkenes - Structure and Reactivity.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 05 An Overview of Organic Reactions.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 04 Stereochemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 03 Organic Compounds - Alkanes and Cycloalkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 02 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2008—2009学年第二学期ORGANIC CHEMISTRY课程A卷(答案).doc
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2008—2009学年第二学期ORGANIC CHEMISTRY课程A卷(试题).doc
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012—2013学年第2学期课程A卷(答案).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012—2013学年第2学期课程A卷(试题).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2004年有机化学期末测试题B(双语)试题.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2004年有机化学期末测试题B(双语)答案.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Solution manual Organic Chemistry(SIXTH EDITION, 2005, L. G. Wade, Jr., Jan William Simek).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L . G . WA D E , J R ..pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry(7th Edition)Prentice Hall(2009, L.G. Wade, Jr. Whitman College).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry-Prentice Hall(8th Edition, 2012, L.G.WADE,JR., Jan William Simek).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry With Biological Applications, 2nd Edition -Brooks Cole(2010, John McMurry, Cornell University).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic chemistry-Brooks(7th edition, 2014, William H. Brown Brent L. Iverson Eric V. Anslyn Christopher S. Foote Bruce M. Novak).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 10 Alkyl Halides.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 08 Alkenes - Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 12 Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 14 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds.ppt
