《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 03 Organic Compounds - Alkanes and Cycloalkanes

Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry's Organic Chemistry,6th edition,Chapter 3
Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition, Chapter 3

Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features The common structural feature that makes it possible to classify compounds by reactivity are called functional groups Functional group-collection of atoms at a site within a molecule with a common bonding pattern The group reacts in a typical way,generally independent of the rest of the molecule For example,the double bonds in simple and complex alkenes react with bromine in the same way
Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features The common structural feature that makes it possible to classify compounds by reactivity are called functional groups Functional group - collection of atoms at a site within a molecule with a common bonding pattern The group reacts in a typical way, generally independent of the rest of the molecule For example, the double bonds in simple and complex alkenes react with bromine in the same way
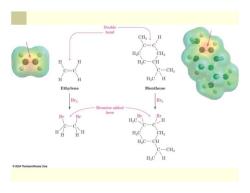
Double bond CH C=C CH2 H2C一CH C-CH3 H H HC H Ethylene Menthene Br2 Br2 Bromine added here Br Br -H C-C H.C CH2 HC一CH C-CH HC 日 2004 Thomson/Brooks Cole
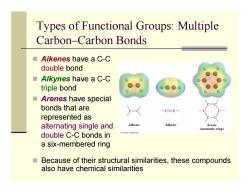
Types of Functional Groups:Multiple Carbon-Carbon Bonds ■Alkenes have a C-C double bond ■Alkynes have a C-C triple bond ■Arenes have special bonds that are 一C三C represented as alternating single and Alkene Alkyne Arene (aromatic ring) double C-C bonds in a six-membered ring Because of their structural similarities,these compounds also have chemical similarities
Types of Functional Groups: Multiple Carbon–Carbon Bonds Alkenes have a C-C double bond Alkynes have a C-C triple bond Arenes have special bonds that are represented as alternating single and double C-C bonds in a six-membered ring Because of their structural similarities, these compounds also have chemical similarities

Functional Groups with Carbon Singly Bonded to an Electronegative Atom Alkyl halide:C bonded to halogen (C-X) Alcohol:C bonded O of a hydroxyl group(C-OH) Ether:Two C's bonded to the same O(C-O-C) Amine:C bonded to N(C-N) ■ Thiol:C bonded to SH group(C-SH) ■ Sulfide:Two C's bonded to same S(C-S-C) Bonds are polar,with partial positive charge on C (+)and partial negative charge(⑧-)on electronegative atom
Functional Groups with Carbon Singly Bonded to an Electronegative Atom Alkyl halide: C bonded to halogen (C-X ) Alcohol: C bonded O of a hydroxyl group ( C OH ) Ether: Two C’s bonded to the same O ( C O C ) Amine : C bonded to N ( C N ) Thiol : C bonded to SH group ( C SH ) Sulfide: Two C’s bonded to same S ( C S C ) Bonds are polar, with partial positive charge on C ( δ+) and partial negative charge (δ−) on electronegative atom

Groups with a Carbon-Oxygen Double Bond (Carbonyl Groups) Aldehyde:one hydrogen bonded to C=O Ketone:two C's bonded to the C=O Carboxylic acid:-OH bonded to the C=O Ester:C-O bonded to the C=O Amide:C-N bonded to the C=O Acid chloride:CI bonded to the C=O ■Carbonyl C has partial positive charge(δ+) Carbonyl O has partial negative charge(5-)
Groups with a Carbon–Oxygen Double Bond (Carbonyl Groups) Aldehyde: one hydrogen bonded to C=O Ketone: two C’s bonded to the C=O Carboxylic acid: ⎯OH bonded to the C=O Ester: C-O bonded to the C=O Amide: C-N bonded to the C=O Acid chloride: Cl bonded to the C=O Carbonyl C has partial positive charge ( δ+) Carbonyl O has partial negative charge ( δ-)

Alkanes and Alkane Isomers Alkanes:Compounds with C-C single bonds and C-H bonds only(no functional groups) ■ Connecting carbons can lead to large or small molecules The formula for an alkane with no rings in it must be C H2n+2 where the number of C's is n ■ Alkanes are saturated with hydrogen(no more can be added They are also called aliphatic compounds HH HHH HHHH H一C-H H-C-C-H H-C-C-C-H H-C-C-C-C-H ...and so on H HH HHH H丑HH Methaneosca Ethane Propane Butane
Alkanes and Alkane Isomers Alkanes: Compounds with C-C single bonds and C-H bonds only (no functional groups) Connecting carbons can lead to large or small molecules The formula for an alkane with no rings in it must be C n H2n+2 where the number of C’s is n Alkanes are saturated with hydrogen (no more can be added They are also called aliphatic compounds

Alkane Isomers ■ CH4=methane,C2H6=ethane,C3H8=propane The molecular formula of an alkane with more than three carbons can give more than one structure Ca(butane)=butane and isobutane Cs(pentane)=pentane,2-methylbutane,and 2,2- dimethylpropane Alkanes with C's connected to no more than 2 other C's are straight-chain or normal alkanes Alkanes with one or more C's connected to 3 or 4 C's are branched-chain alkanes
Alkane Isomers CH 4 = methane, C 2 H 6 = ethane, C 3 H 8= propane The molecular formula of an alkane with more than three carbons can give more than one structure C4 (butane) = butane and isobutane C5 (pentane) = pentane, 2-methylbutane, and 2,2- dimethylpropane Alkanes with C’s connected to no more than 2 other C’s are straight-chain or normal alkanes Alkanes with one or more C’s connected to 3 or 4 C’s are branched-chain alkanes
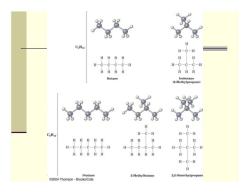
H-C一C-C一H HHH Butane Isobutane (2-Methylpropane) C.Hiz H H H H一C H Pentane 2-Methylbutane 2,2-Dimethylpropane 2004 Thomson Brooks/Cole

Constitutional Isomers ■ Isomers that differ in how their atoms are arranged in chains are called constitutional isomers ■ Compounds other than alkanes can be constitutional isomers of one another They must have the same molecular formula to be isomers Different carbon CH3 skeletons C,H10 CH CHCH and CH CH2CH2CHa 2-Methylpropane Butane (Isobutane) Different functional CHCH,OH and CHOCH3 groups C.HO Ethyl alcohol Dimethyl ether Different position of NH2 functional groups C.HoN CH CHCH3 and CH:CH2CH2NH2 Isopropylamine Propvlamine Thomson-Brooks Cole
Constitutional Isomers Isomers that differ in how their atoms are arranged in chains are called constitutional isomers Compounds other than alkanes can be constitutional isomers of one another They must have the same molecular formula to be isomers
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 02 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2008—2009学年第二学期ORGANIC CHEMISTRY课程A卷(答案).doc
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2008—2009学年第二学期ORGANIC CHEMISTRY课程A卷(试题).doc
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012—2013学年第2学期课程A卷(答案).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012—2013学年第2学期课程A卷(试题).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2004年有机化学期末测试题B(双语)试题.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2004年有机化学期末测试题B(双语)答案.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Solution manual Organic Chemistry(SIXTH EDITION, 2005, L. G. Wade, Jr., Jan William Simek).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L . G . WA D E , J R ..pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry(7th Edition)Prentice Hall(2009, L.G. Wade, Jr. Whitman College).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry-Prentice Hall(8th Edition, 2012, L.G.WADE,JR., Jan William Simek).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry With Biological Applications, 2nd Edition -Brooks Cole(2010, John McMurry, Cornell University).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic chemistry-Brooks(7th edition, 2014, William H. Brown Brent L. Iverson Eric V. Anslyn Christopher S. Foote Bruce M. Novak).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Keynotes in Organic Chemistry, Second Edition, Andrew F. Parsons(Wiley, 2014).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)The Vocabulary and Concepts of Organic Chemistry, 2nd Ed 2005, Milton Orchin, Roger S. Macomber, Allan R. Pinhas, R. Marshall Wilson.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Schaum's Outline of Organic Chemistry 4th Ed 2009, 1806 fully solved problems.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry I as a Second Language Translating the Basic Concepts 2nd 2008, DR. DAVID R. KLEIN Johns Hopkins University.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry, 3rd Ed, Janice Gorzynski Smith 2011, University of Hawai’i at Ma-noa.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Keynotes in Organic Chemistry 2003, Andrew F. Parsons, Blackwell Science.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 04 Stereochemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 05 An Overview of Organic Reactions.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 06 Alkenes - Structure and Reactivity.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 07 Alkenes - Reactions and Synthesis.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 08 Alkynes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 09 Stereochemistry.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 10 Alkyl Halides.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 08 Alkenes - Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 11 Reactions of Alcohols.ppt
