《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding

Structure and Bonding Based on McMurry's Organic Chemistry,6th edition, Chapter 1
Structure and Bonding Based on McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition, Chapter 1

Organic Chemistry A study of carbon compounds H He Be B Ne Na Mg Al Si Ar Sc Ti Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Ga Ge Se Br Kr Rb Sr Zr Nb Sn Xe Cs Ba La Hf Ta Re Os Ir Au Hg T Pb Bi Po At Rn Fr Ra Ac Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt 2004 Thon Although C is the principal element in organic compounds,most also contain H,and many contain N,O,P,S.CI or other elements
Organic Chemistry A study of carbon compounds Although C is the principal element in organic compounds, most also contain H, and many contain N, O, P, S. Cl or other elements

Why is Carbon Special? ■ Being a Group 4 element,carbon can share four valence electrons and form four strong covalent bonds. ■Carbon can bond to one another,forming long chains and rings. Bond angle Bond GC 109.5 length 110pm H
Why is Carbon Special? Being a Group 4 element, carbon can share four valence electrons and form four strong covalent bonds. Carbon can bond to one another, forming long chains and rings
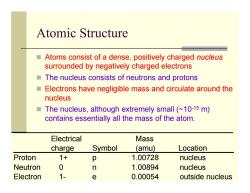
Atomic Structure Atoms consist of a dense,positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons ■ The nucleus consists of neutrons and protons ■ Electrons have negligible mass and circulate around the nucleus ■ The nucleus,although extremely small(~10-15 m) contains essentially all the mass of the atom. Electrical Mass charge Symbol (amu) Location Proton 1+ p 1.00728 nucleus Neutron 0 n 1.00894 nucleus Electron 1- e 0.00054 outside nucleus
Atomic Structure Atoms consist of a dense, positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons The nucleus consists of neutrons and protons Electrons have negligible mass and circulate around the nucleus The nucleus, although extremely small (~10-15 m) contains essentially all the mass of the atom. ____________________________________________________ Electrical Mass charge Symbol (amu) Location Proton 1+ p 1.00728 nucleus Neutron 0 n 1.00894 nucleus Electron 1- e 0.00054 outside nucleus

Atomic Number and Atomic Mass The atomic number(Z)is the number of protons in the atom's nucleus The mass number (A)is the number of protons plus neutrons All the atoms of a given element have the same atomic number ■ Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and therefore different mass numbers The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass in atomic mass units (amu)of an element's naturally occurring isotopes
Atomic Number and Atomic Mass The atomic number ( Z) is the number of protons in the atom's nucleus The mass number ( A) is the number of protons plus neutrons All the atoms of a given element have the same atomic number Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and therefore different mass numbers The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average mass in atomic mass units (amu) of an element’s naturally occurring isotopes

Atomic Structure:Orbitals How are the electrons distributed in an atom? ■ Quantum mechanics:behavior of a specific electron in an atoms is descrbied by a mathematical expression called a wave equation The solution of the wave equation is called an orbital An orbital describes the volume of space around a nucleus where an electron is mostly likely to be found
Atomic Structure: Orbitals Quantum mechanics: behavior of a specific electron in an atoms is descrbied by a mathematical expression called a wave equation The solution of the wave equation is called an orbital An orbital describes the volume of space around a nucleus where an electron is mostly likely to be found How are the electrons distributed in an atom?
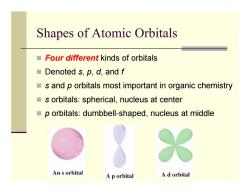
Shapes of Atomic Orbitals Four different kinds of orbitals ■Denoted s,p,d,andf s and p orbitals most important in organic chemistry s orbitals:spherical,nucleus at center p orbitals:dumbbell-shaped,nucleus at middle An s orbital A p orbital A d orbital
Shapes of Atomic Orbitals Four different kinds of orbitals Denoted s, p, d, and f s and p orbitals most important in organic chemistry s orbitals: spherical, nucleus at center p orbitals: dumbbell-shaped, nucleus at middle
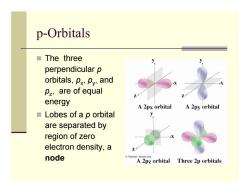
p-Orbitals ■The three perpendicular p orbitals,px,py,and pz,are of equal energy A 2px orbital A 2py orbital ■Lobes of a p orbital are separated by region of zero electron density,a node Thomson-Brooks Col A 2pz orbital Three 2p orbitals
p-Orbitals The three perpendicular p orbitals, p x, p y, and p z, are of equal energy Lobes of a p orbital are separated by region of zero electron density, a node

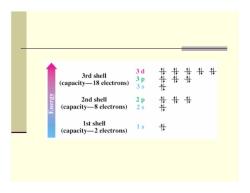
Orbitals and Shells ■ Orbitals are organized into shells of increasing size and energy ■ Different shells contain different numbers and kinds of orbitals Each orbital can be occupied by two electrons First shell contains one s orbital,denoted 1s ■ Second shell contains one s orbital(2s)and three p orbitals(2p) Third shell contains an s orbital(3s),three p orbitals (3p),and five d orbitals (3d)
Orbitals and Shells Orbitals are organized into shells of increasing size and energy Different shells contain different numbers and kinds of orbitals Each orbital can be occupied by two electrons First shell contains one s orbital, denoted 1 s Second shell contains one s orbital ( 2 s) and three p orbitals ( 2 p ) Third shell contains an s orbital ( 3 s), three p orbitals ( 3 p), and five d orbitals (3 d )
3d 3rd shell # (capacity-18 electrons) 3s 2nd shell 2 (capacity-8 electrons) 2s 鞋 1st shell (capacity-2 electrons) #
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2008—2009学年第二学期ORGANIC CHEMISTRY课程A卷(答案).doc
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2008—2009学年第二学期ORGANIC CHEMISTRY课程A卷(试题).doc
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012—2013学年第2学期课程A卷(答案).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012—2013学年第2学期课程A卷(试题).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2004年有机化学期末测试题B(双语)试题.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2004年有机化学期末测试题B(双语)答案.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Solution manual Organic Chemistry(SIXTH EDITION, 2005, L. G. Wade, Jr., Jan William Simek).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L . G . WA D E , J R ..pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry(7th Edition)Prentice Hall(2009, L.G. Wade, Jr. Whitman College).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry-Prentice Hall(8th Edition, 2012, L.G.WADE,JR., Jan William Simek).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry With Biological Applications, 2nd Edition -Brooks Cole(2010, John McMurry, Cornell University).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic chemistry-Brooks(7th edition, 2014, William H. Brown Brent L. Iverson Eric V. Anslyn Christopher S. Foote Bruce M. Novak).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Keynotes in Organic Chemistry, Second Edition, Andrew F. Parsons(Wiley, 2014).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)The Vocabulary and Concepts of Organic Chemistry, 2nd Ed 2005, Milton Orchin, Roger S. Macomber, Allan R. Pinhas, R. Marshall Wilson.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Schaum's Outline of Organic Chemistry 4th Ed 2009, 1806 fully solved problems.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry I as a Second Language Translating the Basic Concepts 2nd 2008, DR. DAVID R. KLEIN Johns Hopkins University.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry, 3rd Ed, Janice Gorzynski Smith 2011, University of Hawai’i at Ma-noa.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Keynotes in Organic Chemistry 2003, Andrew F. Parsons, Blackwell Science.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Instant Notes in Organic Chemistry, Second Edition, G. L. Patrick.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)TUTORIAL CHEMISTRY TEXTS(6)Functional Group Chemistry, RSC 2001, by JAMES.R.HANSON.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 02 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 03 Organic Compounds - Alkanes and Cycloalkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 04 Stereochemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 05 An Overview of Organic Reactions.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 06 Alkenes - Structure and Reactivity.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 07 Alkenes - Reactions and Synthesis.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 08 Alkynes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 09 Stereochemistry.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 10 Alkyl Halides.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 08 Alkenes - Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
