《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 02 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases

Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Based on McMurry's Organic Chemistry,6th edition,Chapter 2
Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Based on McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition, Chapter 2

Polar Covalent Bonds:Electronegativity Covalent bonds can have ionic character Bonding electrons attracted more strongly by one atom than by the other ■ Electron distribution between atoms in not symmetrical These are polar covalent bonds Ionic character X:X X+Y:- Symmetrical covalent Polar covalent Ionic bond bond bonds Thomson-Brooks Cole
Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity Covalent bonds can have ionic character Bonding electrons attracted more strongly by one atom than by the other Electron distribution between atoms in not symmetrical These are polar covalent bonds

Bond Polarity and Electronegativity ■ Electronegativity (EN):intrinsic ability of an atom to attract the shared electrons in a covalent bond Differences in EN produce bond polarity Metals on left side of periodic table attract electrons weakly,lower EN Halogens and other reactive nonmetals on right side of periodic table attract electrons strongly,higher electronegativities F is most electronegative(EN 4.0),Cs is least(EN =0.7) ■EN of C=2.5
Bond Polarity and Electronegativity Electronegativity (EN): intrinsic ability of an atom to attract the shared electrons in a covalent bond Differences in EN produce bond polarity Metals on left side of periodic table attract electrons weakly, lower EN Halogens and other reactive nonmetals on right side of periodic table attract electrons strongly, higher electronegativities F is most electronegative (EN = 4.0), Cs is least (EN = 0.7) EN of C = 2.5
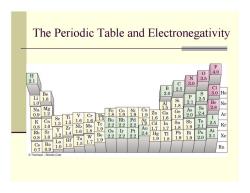
The Periodic Table and Electronegativity F 4.0 H 0 2.1 N . 3.0 B 2.5 CI Be 3.0 8 1.6 P S Mg Si 1.8 0.9 2 V Cr 遇 g a 41059 54 Br 2.8 8 Se Ti 6 I Ar 1.6 1.6 R 1.0 1.3 1.5 Te 2.2 Rh 0.8 Nb Mo 2 Cd Sn 1.9 1 2 .8 组 Kr Rb Sr 1.4 1.6 1.8 1.2 Re 2.2 2.2 2西 Hg I 的 Po At .8 1.0 Ta 1.9 1.8 .0 2.1 La H 1.9 Cs Ba . 1.5 1.7 0.70.9 .0 Rn ⊙Thomson-Brooks Cole
The Periodic Table and Electronegativity
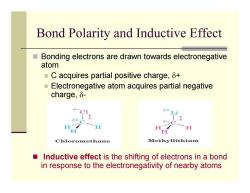
Bond Polarity and Inductive Effect ■ Bonding electrons are drawn towards electronegative atom ■C acquires partial positive charge,δt ■ Electronegative atom acquires partial negative charge,δ- H Chloromethane Methyllithium Inductive effect is the shifting of electrons in a bond in response to the electronegativity of nearby atoms
Bond Polarity and Inductive Effect Bonding electrons are drawn towards electronegative atom C acquires partial positive charge, δ + Electronegative atom acquires partial negative charge, δ - Inductive effect is the shifting of electrons in a bond in response to the electronegativity of nearby atoms
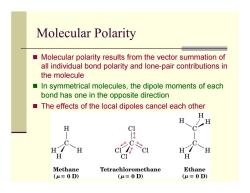
Molecular Polarity Molecular polarity results from the vector summation of all individual bond polarity and lone-pair contributions in the molecule ■ In symmetrical molecules,the dipole moments of each bond has one in the opposite direction The effects of the local dipoles cancel each other H H H H C1 必C& H H H H CI H Methane Tetrachloromethane Ethane (u=0D) (u=0D) (u=0D)
Molecular Polarity Molecular polarity results from the vector summation of all individual bond polarity and lone-pair contributions in the molecule In symmetrical molecules, the dipole moments of each bond has one in the opposite direction The effects of the local dipoles cancel each other

Water and ammonia have relatively large dipole moments because O and N are more electronegative than H and because they have lone-pairs electrons Lone pair Net Net Two lone pairs Water,H2O(u=1.85 D) Ammonia,NHg (u =1.47 D) G2004 Thomson-Brooks/Cole
Water and ammonia have relatively large dipole moments because O and N are more electronegative than H and because they have lone-pairs electrons

Resonance Double bond to this oxygen? H :0: Nitromethane Or to this oxygen? Thomson-Brooks Cole N-O=130pm N=0=116pm Nitrogen-oxygen bond in nitro-methane 122pm Neither of the two Lewis structures is correct by itself. True structure is intermediate between the two The two individual Lewis structures are called resonance forms
Resonance Neither of the two Lewis structures is correct by itself. True structure is intermediate between the two The two individual Lewis structures are called resonance forms N-O = 130pm N=O = 116pm Nitrogen-oxygen bond in nitro-methane = 122pm

Resonance Hybrids A structure with resonance forms does not alternate between the forms Instead,it is a hybrid of the two resonance forms,so the structure is called a resonance hybrid For example,benzene(CHe)has two resonance forms with alternating double and single bonds In the resonance hybrid,the actual structure,all its C-C bonds equivalent,midway between double and single Benzene (twe nance forms Tomson-Brooks Cale
Resonance Hybrids A structure with resonance forms does not alternate between the forms Instead, it is a hybrid of the two resonance forms, so the structure is called a resonance hybrid For example, benzene (C 6 H 6) has two resonance forms with alternating double and single bonds In the resonance hybrid, the actual structure, all its C-C bonds equivalent, midway between double and single

Rules for Resonance Forms Individual resonance forms are imaginary-the real structure is a hybrid (only by knowing the contributors can you visualize the actual structure) ■ Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their x or nonbonding electrons-neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another The red curved arrow indicates that a lone pair of electrons moves from the top oxygen The new resonance structure atom to become part of an N=O double bond. has a double bond here... H :0: H N+ H 父 O: H 0: Simultaneously,two electrons from the ..and has a lone pair N=O double bond move onto the bottom of electrons here. oxygen atom to become a lone pair
Rules for Resonance Forms Individual resonance forms are imaginary - the real structure is a hybrid (only by knowing the contributors can you visualize the actual structure) Resonance forms differ only in the placement of their π or nonbonding electrons – neither the position nor the hybridization of any atom changes from one resonance form to another
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2008—2009学年第二学期ORGANIC CHEMISTRY课程A卷(答案).doc
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2008—2009学年第二学期ORGANIC CHEMISTRY课程A卷(试题).doc
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012—2013学年第2学期课程A卷(答案).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012—2013学年第2学期课程A卷(试题).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2004年有机化学期末测试题B(双语)试题.pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2004年有机化学期末测试题B(双语)答案.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Solution manual Organic Chemistry(SIXTH EDITION, 2005, L. G. Wade, Jr., Jan William Simek).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition, L . G . WA D E , J R ..pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry(7th Edition)Prentice Hall(2009, L.G. Wade, Jr. Whitman College).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry-Prentice Hall(8th Edition, 2012, L.G.WADE,JR., Jan William Simek).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry With Biological Applications, 2nd Edition -Brooks Cole(2010, John McMurry, Cornell University).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic chemistry-Brooks(7th edition, 2014, William H. Brown Brent L. Iverson Eric V. Anslyn Christopher S. Foote Bruce M. Novak).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Keynotes in Organic Chemistry, Second Edition, Andrew F. Parsons(Wiley, 2014).pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)The Vocabulary and Concepts of Organic Chemistry, 2nd Ed 2005, Milton Orchin, Roger S. Macomber, Allan R. Pinhas, R. Marshall Wilson.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Schaum's Outline of Organic Chemistry 4th Ed 2009, 1806 fully solved problems.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry I as a Second Language Translating the Basic Concepts 2nd 2008, DR. DAVID R. KLEIN Johns Hopkins University.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Organic Chemistry, 3rd Ed, Janice Gorzynski Smith 2011, University of Hawai’i at Ma-noa.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Keynotes in Organic Chemistry 2003, Andrew F. Parsons, Blackwell Science.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Instant Notes in Organic Chemistry, Second Edition, G. L. Patrick.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 03 Organic Compounds - Alkanes and Cycloalkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 04 Stereochemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 05 An Overview of Organic Reactions.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 06 Alkenes - Structure and Reactivity.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 07 Alkenes - Reactions and Synthesis.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 08 Alkynes.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 09 Stereochemistry.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition)Chapter 10 Alkyl Halides.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Organic Chemistry,5th Edition,L. G. Wade, Jr.,Prentice Hall)Chapter 26 Synthetic Polymers.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 01 Introduction and Review.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 02 Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 03 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 04 The Study of Chemical Reactions.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 05 Stereochemistry.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 07 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 08 Alkenes - Reactions of Alkenes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 09 Alkynes.ppt
- 《有机化学》课程PPT教学课件(Official PPT of Organic Chemistry 6th LG Wade by Prentice Hall,L. G. Wade, Jr.)Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols.ppt
