《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 3 Analog-to-Digital Conversion(Preview、Measure of Information、Quantization)

Analog-to-Digital Conversion Preview Measure of Information Quantization
Analog-to-Digital Conversion Preview Measure of Information Quantization

Why ADC Many sources are Analog by nature Speech,Image,Telemetry sources,. ■Digital is easier ■To process ■To communicate ■To store
Why ADC ? ◼ Many sources are Analog by nature ◼ Speech, Image, Telemetry sources, . ◼ Digital is easier ◼ To process ◼ To communicate ◼ To store

Data Compression Quantization (Lossy data compression) Analog source is quantized into a finite number of levels Limit on the performance is given by rate-distortion bound Noiseless coding(Lossless data compression) Compress digital data to reduce data bit Source coding techniques Limit on the compression is given by the entropy of the source
Data Compression ◼ Quantization (Lossy data compression) ◼ Analog source is quantized into a finite number of levels ◼ Limit on the performance is given by rate-distortion bound ◼ Noiseless coding(Lossless data compression) ◼ Compress digital data to reduce data bit ◼ Source coding techniques ◼ Limit on the compression is given by the entropy of the source

Common-sense Information Measure Consider three headlines in newspaper 1)Tomorrow the sun will rise in the east ■ 2)United States invades Cuba 3)Cuba invades United States Information surprise ~1/Probability Headline Surprise Probability Information 1 Never Always No 2 Much Small Much 3 Very Much Very Small Very Much Suggested Information Measure I oclog p
Common-sense Information Measure ◼ Consider three headlines in newspaper ◼ 1) Tomorrow the sun will rise in the east ◼ 2) United States invades Cuba ◼ 3) Cuba invades United States ◼ Information ~ surprise ~ 1/Probability ◼ Suggested Information Measure ◼ 1 I log P Headline Surprise Probability Information 1 Never Always No 2 Much Small Much 3 Very Much Very Small Very Much

Engineering-sense Information Measure From the engineering point of view The information in a message is the time to transmit the message Message with higher probability can be transmitted in a shorter time than that required for a message with lower probability ■Morse Code Shorter code word for symbol e,t,a,o which occurs more frequently Longer code word for symbols x,k,q,z which occurs less frequently The time required to transmit a symbol with probability of occurrence P is proportional to log(1/P)
Engineering-sense Information Measure ◼ From the engineering point of view ◼ The information in a message is the time to transmit the message ◼ Message with higher probability can be transmitted in a shorter time than that required for a message with lower probability ◼ Morse Code ◼ Shorter code word for symbol e,t,a,o which occurs more frequently ◼ Longer code word for symbols x,k,q,z which occurs less frequently ◼ The time required to transmit a symbol with probability of occurrence P is proportional to log(1/P)

Definition of Information Measure The information sent from a digital source when the jth message transmitted is given by "I,=lg(分bs The Unit [bits] Binary Unit Since the base 2 logarithm is used 。Unit of information Do not confuse the bit used in computer(unit of binary data)
Definition of Information Measure ◼ The information sent from a digital source when the jth message transmitted is given by ◼ ◼ The Unit [bits] ◼ Binary Unit ◼ Since the base 2 logarithm is used ◼ Unit of information ◼ Do not confuse the bit used in computer (unit of binary data) 2 1 log ( ) [ ] j j I bits P =

Definition of Entropy The average information measure(or Entropy)of digital source is ·n-2P以,-豆Pg白a网 Where m is number of possible different source message e For the binary message with probability p and(1-p) The Entropy is ·从-2gg分=pe方0-pa2 See Figure 4.1 at page 132 mlfp→1orp→0,there are no information p=0.5 gives maximum information
Definition of Entropy ◼ The average information measure(or Entropy) of digital source is ◼ ◼ Where m is number of possible different source message ◼ For the binary message with probability p and (1-p), The Entropy is ◼ ◼ See Figure 4.1 at page 132 ◼ If p→1 or p→0, there are no information ◼ p=0.5 gives maximum information 2 1 1 1 log ( ) [ ] m m j j j j j j H P I P bits = = P = = 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 log ( ) log (1 )log 1 b j j j H P p p = P p p = = + − −
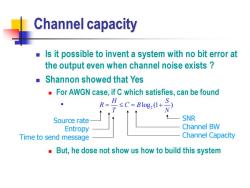
Channel capacity Is it possible to invent a system with no bit error at the output even when channel noise exists Shannon showed that Yes For AWGN case,if C which satisfies,can be found R=7≤G=slg,0+3 Source rate SNR Entropy Channel BW Time to send message Channel Capacity But,he dose not show us how to build this system
Channel capacity ◼ Is it possible to invent a system with no bit error at the output even when channel noise exists ? ◼ Shannon showed that Yes ◼ For AWGN case, if C which satisfies, can be found ◼ ◼ But, he dose not show us how to build this system 2 log (1 ) H S R C B T N = = + SNR Channel BW Channel Capacity Source rate Entropy Time to send message

Noiseless coding Reduce number of bits required for the representation of a source output for perfect recovery Prefect reconstruction of source is possible to use a code with a rate as close to the entropy of the source,but it is not possible to use a code with a rate less than a source entropy Huffman coding and Lempel-Ziv coding are popular
Noiseless coding ◼ Reduce number of bits required for the representation of a source output for perfect recovery ◼ Prefect reconstruction of source is possible to use a code with a rate as close to the entropy of the source, but it is not possible to use a code with a rate less than a source entropy ◼ Huffman coding and Lempel-Ziv coding are popular

Huffman coding Assign longer code word to the less probable source output and shorter code word to the more probable ones lllustrative problem 3.1 See figure 3.2 for Huffman code tree Entropy of the source H=3.0371 Average code word length L=3.1 bits/source output ■H<L
Huffman coding ◼ Assign longer code word to the less probable source output and shorter code word to the more probable ones ◼ Illustrative problem 3.1 ◼ See figure 3.2 for Huffman code tree ◼ Entropy of the source H = 3.0371 ◼ Average code word length L = 3.1 bits/source output ◼ H < L
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Transmitters and Receivers.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(Frequency Modulation、Phase Modulation).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 7 Spread Spectrum Communication Systems.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(SSB – AM).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(Conventional AM).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(AM,Amplitude Modulation).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 1 Basic Matlab.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第1章 matlab基础知识.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第3章 图形处理与simulink仿真.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第2章 matlab语言入门.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(模拟调制系统).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(模拟信号的数字传输).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(二进制基带系统).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(PSK频带传输系统).doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 DDS信号发生器周期信号的傅里叶级数拟合.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 方波信号展开为傅里叶级数.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 实验四 DDS信号发生器与周期函数的傅里叶级数拟合.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 DDS信号发生器周期信号的傅里叶级数拟合.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第二讲 System Generator for DSP.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第二讲 实验二 Nexys 3实验板及设计软件.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 3 Analog-to-Digital Conversion(Pulse Amplitude Modulation、Pulse Code Modulation).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Binary Signal Transmission).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Multiamplitude Signal Transmission).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Multidimensional Signals).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 5Digital Transmission Through Bandlimited Channels.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(1/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(2/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(3/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第01讲 HDL语言概述.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第02讲 Verilog HDL语言基础.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第03讲 门级与结构建模.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第04讲 数据流建模.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第05讲 行为建模(1/2).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第06讲 行为建模(2/2).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第07讲 综合建模与仿真.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第08讲 可综合设计.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)嵌入式系统设计实验——第1章 嵌入式系统概述.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)嵌入式系统设计实验——第2章 嵌入式系统工程设计.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)嵌入式系统设计实验——第3章 ARM7体系结构(1/2).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)嵌入式系统设计实验——第3章 ARM7体系结构(2/2).ppt
