《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Binary Signal Transmission)

Baseband Digital Transmission Binary Signal Transmission Multiamplitude Signal Transmission Multidimensional Signals
Baseband Digital Transmission Binary Signal Transmission Multiamplitude Signal Transmission Multidimensional Signals
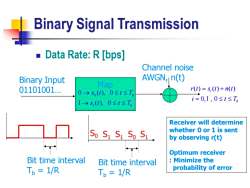
Binary Signal Transmission Data Rate:R [bps] Channel noise Binary Input AWGN,n(t) Map 01101001. r(t)=S,(t)+n(t) 0→S(t),0≤t≤T i=0,1,0≤t≤T6 1→S(),0≤t≤T Receiver will determine So S1S1 So S1 whether 0 or 1 is sent by observing r(t) Optimum receiver Bit time interval Bit time interval Minimize the To 1/R To 1/R probability of error
Binary Signal Transmission ◼ Data Rate: R [bps] Binary Input 01101001. Map 0 1 0 ( ), 0 1 ( ), 0 b b s t t T s t t T → → Channel noise AWGN, n(t) ( ) ( ) ( ) 0,1 , 0 i b r t s t n t i t T = + = Bit time interval Tb = 1/R Bit time interval Tb = 1/R S0 S1 S1 S0 S1 Receiver will determine whether 0 or 1 is sent by observing r(t) Optimum receiver : Minimize the probability of error
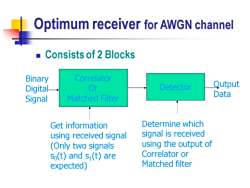
Optimum receiver for AWGN channel ■ Consists of 2 Blocks Binary Correlator Digital. Or Detector Qutput Signal Matched Filter Data Get information Determine which using received signal signal is received (Only two signals using the output of so(t)and si(t)are Correlator or expected) Matched filter
Optimum receiver for AWGN channel ◼ Consists of 2 Blocks Correlator Or Matched Filter Detector Binary Digital Signal Output Data Get information using received signal (Only two signals s0 (t) and s1 (t) are expected) Determine which signal is received using the output of Correlator or Matched filter
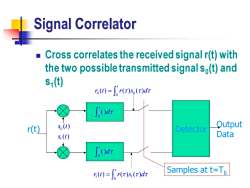
Signal Correlator ■ Cross correlates the received signal r(t)with the two possible transmitted signal so(t)and s1() (=r()s,()dr [dr r(t) 5(t) Output Detector s(t) Data i0=∫r(r)s(r)d Samples at t=Tp
Signal Correlator ◼ Cross correlates the received signal r(t) with the two possible transmitted signal s0 (t) and s1 (t) 0 ( ) t d 0 ( ) t d r(t) Detector 0 1 ( ) ( ) s t s t Output Data 0 0 0 ( ) ( ) ( ) t r t r s d = 1 1 0 ( ) ( ) ( ) t r t r s d = Samples at t=Tb
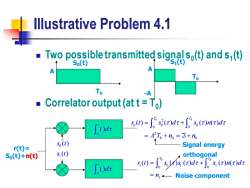
Illustrative Problem 4.1 Two possible transmitted signalso(t)and s(t) So(t) s,(t) A Tb -A Correlator output(at t=To) ((dr+"s(n(r)dr =AT,+n=5+n r(t)= 50(t) Signal energy So(t)+n(t) S,() orthogonal Odr ((d((dr =n←-Noise component
Illustrative Problem 4.1 ◼ Two possible transmitted signal s0 (t) and s1 (t) ◼ Correlator output (at t = T0 ) A Tb A Tb S0(t) S1(t) -A 0 ( ) t d 0 ( ) t d r(t)= S0(t)+n(t) 0 1 ( ) ( ) s t s t 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) T T b b b r t s d s n d A T n n = + = + = + 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) T T b b r t s s d s n d n = + = orthogonal Signal energy Noise component
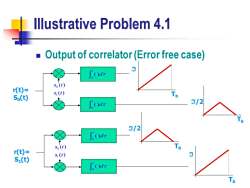
Illustrative Problem 4.1 Output of correlator(Error free case) dr So(t) r(t)= S,(t) So(t) Od: 3/2 3/2 Odr r(t)= s (t) S1(t) Odr
Illustrative Problem 4.1 ◼ Output of correlator (Error free case) 0 ( ) t d 0 ( ) t d r(t)= S0(t) 0 1 ( ) ( ) s t s t Tb Tb /2 0 ( ) t d 0 ( ) t d r(t)= S1(t) 0 1 ( ) ( ) s t s t Tb Tb /2

Illustrative Problem 4.1 ■Noise components AWGN:E[n()]=0,E[n(t)"n(t)]= No 2 no,n are Gaussian process With zero mean n]=E可s,(r)m(r)dr=∫s,(e)Lrdr]=0 En]=E可s()nr)dr]=∫s(r)Erdr]=0 ■And variances o=En]=E可∫s)s(r)n0n(r)dida]=∫∫s()s,(a)E[nu)n(didr =六50x(e-h-0h=3i=l2
Illustrative Problem 4.1 ◼ Noise components ◼ AWGN: ◼ n0 , n1 are Gaussian process ◼ With zero mean ◼ And variances 0 [ ( )] 0, [ ( ) ( )] 2 T N E n t E n t n t = = 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 [ ] [ ( ) ( ) ] ( ) [ ( )] ] 0 [ ] [ ( ) ( ) ] ( ) [ ( )] ] 0 b b b b T T T T E n E s n d s E n d E n E s n d s E n d = = = = = = 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 [ ] [ ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ) [ ( ) ( )] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) , 1, 2 2 2 2 b b b b b b T T T T i i i i i i T T i i i E n E s t s n t n dtd s t s E n t n dtd N N N s t s t dt s t dt i = = = = − = = =
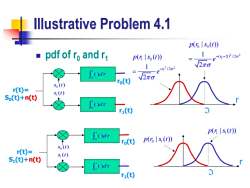
lllustrative Problem 4.1 p(r lso(t)) pdf of ro and r p(n lso(t)) e(6-d/2o e1212o2 2πo ro(t) V2π 5o(I) r(t)= S,(t) So(t)+n(t) Od: r1() Odr p(s(t)) ro(t) p(rls(t)) So(t) r(t)= S1(t)+n(t) Odr ri(t) 3
Illustrative Problem 4.1 ◼ pdf of r0 and r1 2 2 0 0 0 ( ) / 2 ( | ( )) 1 2 r p r s t e − − = 0 ( ) t d 0 ( ) t d r(t)= S0(t)+n(t) 0 1 ( ) ( ) s t s t r 2 2 1 1 0 / 2 ( | ( )) 1 2 r p r s t e − = 0 ( ) t d 0 ( ) t d r(t)= S1(t)+n(t) 0 1 ( ) ( ) s t s t r 0 1 p r s t ( | ( )) 1 1 p r s t ( | ( )) r0(t) r1(t) r0(t) r1(t)

The detector o I Decides the transmitted signal is so(t)or s(t) by observing the output of correlator(ro or r) ■Optimum detector Detector that has minimum probability of error
The detector ◼ Decides the transmitted signal is s0 (t) or s1 (t) by observing the output of correlator (r0 or r1 ) ◼ Optimum detector ◼ Detector that has minimum probability of error

Illustrative Problem 4.3 Optimal Detector ▣0ifro>r1 r ■1ifro<r1 To <r1 ■Probability of error If so(t)is transmitted,but it detect s(t) p(|s(t)) p(rls(t)) 了 Error Probability of error
Illustrative Problem 4.3 ◼ Optimal Detector ◼ 0 if r0 > r1 ◼ 1 if r0 r1 r0 < r1 r0 r1 0 1 r 0 0 p r s t ( | ( )) 1 0 p r s t ( | ( ))Error Probability of error
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 3 Analog-to-Digital Conversion(Pulse Amplitude Modulation、Pulse Code Modulation).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 3 Analog-to-Digital Conversion(Preview、Measure of Information、Quantization).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Transmitters and Receivers.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(Frequency Modulation、Phase Modulation).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 7 Spread Spectrum Communication Systems.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(SSB – AM).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(Conventional AM).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(AM,Amplitude Modulation).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 1 Basic Matlab.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第1章 matlab基础知识.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第3章 图形处理与simulink仿真.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第2章 matlab语言入门.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(模拟调制系统).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(模拟信号的数字传输).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(二进制基带系统).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(PSK频带传输系统).doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 DDS信号发生器周期信号的傅里叶级数拟合.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 方波信号展开为傅里叶级数.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 实验四 DDS信号发生器与周期函数的傅里叶级数拟合.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 DDS信号发生器周期信号的傅里叶级数拟合.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Multiamplitude Signal Transmission).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Multidimensional Signals).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 5Digital Transmission Through Bandlimited Channels.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(1/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(2/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(3/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第01讲 HDL语言概述.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第02讲 Verilog HDL语言基础.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第03讲 门级与结构建模.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第04讲 数据流建模.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第05讲 行为建模(1/2).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第06讲 行为建模(2/2).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第07讲 综合建模与仿真.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第08讲 可综合设计.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)嵌入式系统设计实验——第1章 嵌入式系统概述.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)嵌入式系统设计实验——第2章 嵌入式系统工程设计.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)嵌入式系统设计实验——第3章 ARM7体系结构(1/2).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)嵌入式系统设计实验——第3章 ARM7体系结构(2/2).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)嵌入式系统设计实验——第4章 ARM7TDMI(-S)指令系统.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)嵌入式系统设计实验——第5章 LPC2000系列ARM(1/4).ppt
