《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(SSB – AM)

Analog Modulation SSB-AM
Analog Modulation SSB – AM
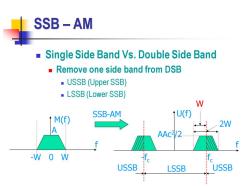
SSB-AM Single Side Band Vs.Double Side Band Remove one side band from DSB USSB(Upper SSB) ■LSSB(Lower SSB) W SSB-AM ↑U(f) M(f) 2W A AAC/2 -W 0 W f。 USSB LSSB USSB :
SSB – AM ◼ Single Side Band Vs. Double Side Band ◼ Remove one side band from DSB ◼ USSB (Upper SSB) ◼ LSSB (Lower SSB) -W 0 W f M(f) f U(f) fc -fc 2W SSB-AM A AAc2 /2 USSB LSSB USSB W
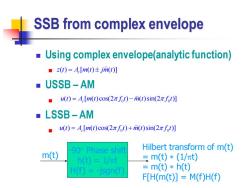
SSB from complex envelope Using complex envelope(analytic function) ■z(t)=A[m(t)±jm(t)] ■USSB-AM u(t)=A.[m(t)cos(2πft)-m(t)sin(2πft)] ■LSSB-AM u(t)=A[m(t)cos(2πft)+m(t)sin(2πft)] 90°Phase shift Hilbert transform of m(t) m(t) h()=1/πt 三m(t)*(1/πt) H(f)=-jsgn(f) =m(t)*h(t) F[H(m(t)]M(f)H(f)
SSB from complex envelope ◼ Using complex envelope(analytic function) ◼ ◼ USSB – AM ◼ ◼ LSSB – AM ◼ ( ) [ ( ) ( )] c z t A m t jm t = 0 0 ( ) [ ( )cos(2 ) ( )sin(2 )] u t A m t f t m t f t = − c -90 Phase shift h(t) = 1/t H(f) = -jsgn(f) m(t) Hilbert transform of m(t) = m(t) (1/t) = m(t) h(t) F[H(m(t)] = M(f)H(f) 0 0 ( ) [ ( )cos(2 ) ( )sin(2 )] u t A m t f t m t f t = + c
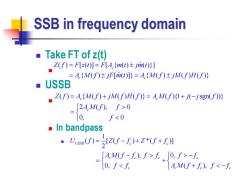
SSB in frequency domain ■Take FT of z()t Z(f)=F[z(t)]=F[A {m(t)+jm(t);] =A.{M(f)±jf[m(t]}=A{M(f)±jM(f)H(f)} ■USSB Z(f)=A.(M(f)+jM(fH(=AM(f)(1+j(-jsgn(f))) 2AM(f),f>0 0, ff.[0,f>-f. 0,f<f AM(f+f),f<-f
SSB in frequency domain ◼ Take FT of z(t) ◼ ◼ USSB ◼ ◼ In bandpass ◼ ( ) [ ( )] [ { ( ) ( )}] { ( ) [ ( )]} { ( ) ( ) ( )} c c c Z f F z t F A m t jm t A M f jF m t A M f jM f H f = = = = ( ) { ( ) ( ) ( )} ( ){1 ( sgn( ))} 2 ( ), 0 0, 0 c c c Z f A M f jM f H f A M f j j f A M f f f = + = + − = 1 ( ) [ ( ) * ( )] 2 ( ), 0, 0, ( ), USSB c c c c c c c c c c U f Z f f Z f f A M f f f f f f f f A M f f f f = − + + − − = + + −

SSB in frequency domain ■LSSB Z(f)=A.(M(f)-jM(fH(f))=4.M(f)(1-j(-jsgn(f))) 0, f>0 2A.M(f), ff,∫AM(f+f),f>-f A.M(f-f),f<f0, f<-fo Check the difference between text book and this result Scale difference
SSB in frequency domain ◼ LSSB ◼ ◼ In bandpass ◼ ◼ Check the difference between text book and this result ◼ Scale difference ( ) { ( ) ( ) ( )} ( ){1 ( sgn( ))} 0, 0 2 ( ), 0 c c c Z f A M f jM f H f A M f j j f f A M f f = − = − − = 1 ( ) [ ( ) * ( )] 2 0, ( ), ( ), 0, LSSB c c c c c c c c c c U f Z f f Z f f f f A M f f f f A M f f f f f f = − + − + − = + − −
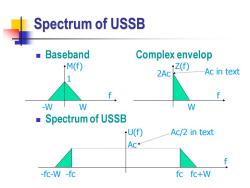
Spectrum of USSB ■Baseband Complex envelop +M(f) ↑Z(f) 2Ac Ac in text 1 f f -W W W ■Spectrum of USSB U(f) Ac/2 in text Ac* f -fc-W -fc fcfc+W
Spectrum of USSB ◼ Baseband Complex envelop ◼ Spectrum of USSB M(f) f -W W 1 Z(f) f W 2Ac Ac in text U(f) f -fc-W -fc fc fc+W Ac Ac/2 in text
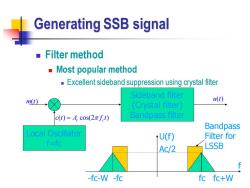
Generating SSB signal ■Filter method Most popular method Excellent sideband suppression using crystal filter Sideband filter m(t) (t) (Crystal filter) c(t)=Acos(2πft) Bandpass filter Bandpass Local Oscillator tU(f) Filter for f=fc Ac/2 LSSB -fc-W -fc fc fc+W
Generating SSB signal ◼ Filter method ◼ Most popular method ◼ Excellent sideband suppression using crystal filter U(f) f -fc-W -fc fc fc+W Ac/2 Bandpass Filter for LSSB ( ) cos(2 ) c c c t A f t = Sideband filter (Crystal filter) Bandpass filter m t( ) Local Oscillator f=fc u t( )
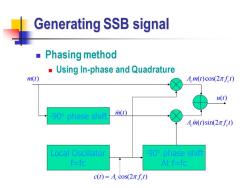
Generating SSB signal ■Phasing method Using In-phase and Quadrature m(t) A.m(t)cos(2πft) u(t) -90°phase shift m(t Am(t)sin(2πft) Local Oscillator -90°phase shift f=fc At f=fc c(t)=Acos(2πft)
Generating SSB signal ◼ Phasing method ◼ Using In-phase and Quadrature ( ) cos(2 ) c c c t A f t = -90 phase shift At f=fc m t( ) Local Oscillator f=fc -90 phase shift m t( ) ( )cos(2 ) A m t f t c c ( )sin(2 ) A m t f t c c u t( )

BW,Power,SNR of SSB BW of SSB is half the BW of DSB BT=W Power in SSB ■=20.+P]=4PP=P) Half of the power of DSB Because One side band is removed SNR of SSB ■Same as DSB:( NW Both Power and Noise are half of DSB
BW, Power, SNR of SSB ◼ BW of SSB is half the BW of DSB ◼ BT = W ◼ Power in SSB ◼ ◼ Half of the power of DSB ◼ Because One side band is removed ◼ SNR of SSB ◼ Same as DSB: ◼ Both Power and Noise are half of DSB 1 1 2 2 ( ) [ ] ( ) 2 2 4 c u m m c m m m A P P P A P P P = + = = 0 0 ( ) S PR N N W =
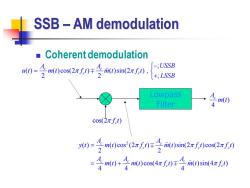
SSB-AM demodulation Coherent demodulation 0=子nm0)cos(2xf0年子0sin2zf0, -;USSB +LSSB Lowpass Filter m(t) 4 cos(2πft) 0=4m0)cos'(2π0)于4ml0sin2πf0os(2xf) 2 40+手m0)co4rf0年手0sin4rf
SSB – AM demodulation ◼ Coherent demodulation cos(2 ) c f t ; ( ) ( ) cos(2 ) ( ) sin(2 ) , 2 2 ; c c c c A A USSB u t m t f t m t f t LSSB − = + Lowpass Filter 2 ( ) ( ) cos (2 ) ( ) sin(2 ) cos(2 ) 2 2 ( ) ( ) cos(4 ) ( ) sin(4 ) 4 4 4 c c c c c c c c c c A A y t m t f t m t f t f t A A A m t m t f t m t f t = = + ( ) 4 Ac m t
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(Conventional AM).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(AM,Amplitude Modulation).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 1 Basic Matlab.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第1章 matlab基础知识.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第3章 图形处理与simulink仿真.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第2章 matlab语言入门.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(模拟调制系统).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(模拟信号的数字传输).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(二进制基带系统).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(PSK频带传输系统).doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 DDS信号发生器周期信号的傅里叶级数拟合.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 方波信号展开为傅里叶级数.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 实验四 DDS信号发生器与周期函数的傅里叶级数拟合.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 DDS信号发生器周期信号的傅里叶级数拟合.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第二讲 System Generator for DSP.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第二讲 实验二 Nexys 3实验板及设计软件.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第三讲 实验三 DA芯片的型号及时序.pdf
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第三讲 实验三 DA芯片的型号及时序.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第一讲 XilinxFPGA介绍.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第一讲 实验一 FPGA.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 7 Spread Spectrum Communication Systems.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(Frequency Modulation、Phase Modulation).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Transmitters and Receivers.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 3 Analog-to-Digital Conversion(Preview、Measure of Information、Quantization).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 3 Analog-to-Digital Conversion(Pulse Amplitude Modulation、Pulse Code Modulation).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Binary Signal Transmission).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Multiamplitude Signal Transmission).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Multidimensional Signals).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 5Digital Transmission Through Bandlimited Channels.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(1/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(2/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(3/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第01讲 HDL语言概述.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第02讲 Verilog HDL语言基础.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第03讲 门级与结构建模.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第04讲 数据流建模.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第05讲 行为建模(1/2).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第06讲 行为建模(2/2).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第07讲 综合建模与仿真.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第08讲 可综合设计.ppt
