《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(AM,Amplitude Modulation)

Analog Modulation AM(Amplitude Modulation) Demodulation of AM Signals Angle Modulation
Analog Modulation AM(Amplitude Modulation) Demodulation of AM Signals Angle Modulation

Why modulate Ease of radiation ■The size of antenna oc入l4=cl4f If we wish to throw a piece of paper(baseband signal),it cannot go too far by itself.But by wrapping it around a stone(carrier),it can be thrown over a longer distance Simultaneous transmission of several signals FDM(Frequency Division Modulation) Reduce the influence of interference ·Frequency Hopping Effecting the exchange of SNR with B Shannon's equation:C=Blog,(1+SNR) C is rate of information change per second(bit/s)
Why modulate ? ◼ Ease of radiation ◼ The size of antenna /4 = c/4f ◼ If we wish to throw a piece of paper(baseband signal), it cannot go too far by itself. But by wrapping it around a stone(carrier), it can be thrown over a longer distance ◼ Simultaneous transmission of several signals ◼ FDM(Frequency Division Modulation) ◼ Reduce the influence of interference ◼ Frequency Hopping ◼ Effecting the exchange of SNR with B ◼ Shannon’s equation : ◼ C is rate of information change per second (bit/s) 2 C B SNR = + log (1 )

Properties of analog modulation ■ Time domain representation of the modulated signal Frequency domain representation of the modulated signal Bandwidth of the modulated signal Power component of the modulated signal SNR after demodulation Message Modulated ■ Modulator Signal Signal (or modulating Signal)
Properties of analog modulation ◼ Time domain representation of the modulated signal ◼ Frequency domain representation of the modulated signal ◼ Bandwidth of the modulated signal ◼ Power component of the modulated signal ◼ SNR after demodulation ◼ Modulator Message Signal (or modulating Signal) Modulated Signal

AM (Amplitude modulation) Also known as "Linear modulation) Small bandwidth,Power inefficient ■Applications AM radio,TV video broadcasting(VSB),Point-to-point communications(SSB),Transmission of many telephone channels over microwave links ■ Class of AM DSB-AM(Double Side Band-AM) BW=2W=2*BW of the message signal SSB-AM(Single Side Band-AM) BW=W VSB-AM(Vestigial Side Band-AM) ■BW=W~2W
AM (Amplitude modulation) ◼ Also known as “Linear modulation) ◼ Small bandwidth, Power inefficient ◼ Applications ◼ AM radio, TV video broadcasting(VSB), Point-to-point communications(SSB), Transmission of many telephone channels over microwave links ◼ Class of AM ◼ DSB-AM(Double Side Band – AM) ◼ BW = 2W = 2 * BW of the message signal ◼ SSB-AM(Single Side Band – AM) ◼ BW = W ◼ VSB-AM(Vestigial Side Band – AM) ◼ BW = W ~ 2W
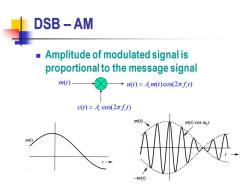
DSB-AM Amplitude of modulated signal is proportional to the message signal m(t)_ (t)=Am(t)cos(2πft) c(t)=A.cos(2πft) m(t) m(t)cos wr m() -m(t)
DSB – AM ◼ Amplitude of modulated signal is proportional to the message signal ( ) cos(2 ) c c c t A f t = ( ) ( )cos(2 ) m t( ) u t A m t f t = c c
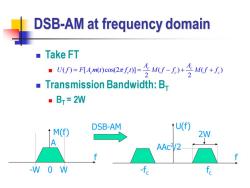
DSB-AM at frequency domain ■Take FT =A0eo2af1=U-+冬MU+月 ■( Transmission Bandwidth:B ·B=2W DSB-AM M(f) ↑U(f) 2W A AAC/2 -W 0 W -fc fe
DSB-AM at frequency domain ◼ Take FT ◼ ◼ Transmission Bandwidth: BT ◼ BT = 2W ( ) [ ( )cos(2 )] ( ) ( ) 2 2 c c c c c c A A U f F A m t f t M f f M f f = = − + + -W 0 W f M(f) f U(f) fc -fc 2W DSB-AM A AAc2 /2
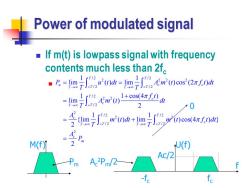
Power of modulated signal If m(t)is lowpass signal with frequency contents much less than 2f ■R=m7∫do0dh=m7」%m(0cos(2rf0h -tm0+e由 = 0 -号-i0a+ega0 A m M(f)元 2 U(f) Ac/2 A2Pm/2→ -fc fe
Power of modulated signal ◼ If m(t) is lowpass signal with frequency contents much less than 2fc ◼ / 2 / 2 2 2 2 2 / 2 / 2 / 2 2 2 / 2 2 / 2 / 2 2 2 / 2 / 2 2 1 1 lim ( ) lim ( ) cos (2 ) 1 1 cos(4 ) lim ( ) 2 1 1 {lim ( ) lim ( ) cos(4 ) } 2 2 T T u c c T T T T T c c T T T T c c T T T T c m P u t dt A m t f t dt T T f t A m t dt T A m t dt m t f t dt T T A P → → − − → − → → − − = = + = = + = 0 f U(f) fc -fc Ac/2 M(f) Pm Ac 2Pm/2

SNR for DSB-AM Equal to baseband SNR o E U()1 R(f)1 A2Pm/2 Transmit -Distortion -LOSs N(f) White Gaussian Noise N/2 WNo 2W
SNR for DSB-AM ◼ Equal to baseband SNR ◼ 0 0 ( ) S PR N N W = fc U(f) Ac 2Pm/2 Transmit -Distortion -Loss fc R(f) PR N(f) 2W N0 White Gaussian Noise /2 WN0

Demodulation of AM signals Demodulation The process of extracting the message signal from modulated signal Type of demodulation Coherent demodulation Local oscillator with same frequency and phase of the carrier at the receiver ■DSB-AM,SSB-AM Noncoherent demodulaion Envelope detector which does not require same frequency and phase of carrier Easy to implement with low cost:Conventional AM
Demodulation of AM signals ◼ Demodulation ◼ The process of extracting the message signal from modulated signal ◼ Type of demodulation ◼ Coherent demodulation ◼ Local oscillator with same frequency and phase of the carrier at the receiver ◼ DSB – AM , SSB – AM ◼ Noncoherent demodulaion ◼ Envelope detector which does not require same frequency and phase of carrier ◼ Easy to implement with low cost : Conventional AM
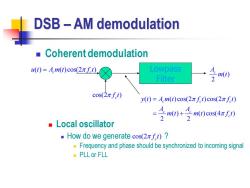
DSB-AM demodulation Coherent demodulation )=A,m(t)cos(2πf) Lowpass Filter m(t) 2 cos(2πft) y(t)=A,m(t)cos(2πft)cos(2πft) =子m0+子m0eo4af0 Local oscillator ■How do we generate cos(2πft)? Frequency and phase should be synchronized to incoming signal PLL or FLL
DSB – AM demodulation ◼ Coherent demodulation ◼ Local oscillator ◼ How do we generate ? ◼ Frequency and phase should be synchronized to incoming signal ◼ PLL or FLL cos(2 ) c f t ( ) ( )cos(2 ) u t A m t f t = c c Lowpass Filter ( ) ( ) cos(2 ) cos(2 ) ( ) ( ) cos(4 ) 2 2 c c c c c c y t A m t f t f t A A m t m t f t = = + ( ) 2 Ac m t cos(2 ) c f t
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 1 Basic Matlab.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第1章 matlab基础知识.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第3章 图形处理与simulink仿真.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_第2章 matlab语言入门.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(模拟调制系统).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(模拟信号的数字传输).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(二进制基带系统).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真电子教案_matlab在通信中的应用(PSK频带传输系统).doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 DDS信号发生器周期信号的傅里叶级数拟合.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 方波信号展开为傅里叶级数.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 实验四 DDS信号发生器与周期函数的傅里叶级数拟合.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第四讲 DDS信号发生器周期信号的傅里叶级数拟合.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第二讲 System Generator for DSP.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第二讲 实验二 Nexys 3实验板及设计软件.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第三讲 实验三 DA芯片的型号及时序.pdf
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第三讲 实验三 DA芯片的型号及时序.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第一讲 XilinxFPGA介绍.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第一讲 实验一 FPGA.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)FPGA通信系统设计——第一讲 simulink教程(Simulink建模和仿真).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)CDMA移动通信系统实验.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(Conventional AM).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(SSB – AM).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 7 Spread Spectrum Communication Systems.doc
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Analog Modulation(Frequency Modulation、Phase Modulation).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 2 Transmitters and Receivers.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 3 Analog-to-Digital Conversion(Preview、Measure of Information、Quantization).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 3 Analog-to-Digital Conversion(Pulse Amplitude Modulation、Pulse Code Modulation).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Binary Signal Transmission).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Multiamplitude Signal Transmission).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 4 Baseband Digital Transmission(Multidimensional Signals).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 5Digital Transmission Through Bandlimited Channels.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(1/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(2/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)MATLAB与通信仿真(英文)Chapter 6 Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling(3/3).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第01讲 HDL语言概述.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第02讲 Verilog HDL语言基础.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第03讲 门级与结构建模.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第04讲 数据流建模.ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第05讲 行为建模(1/2).ppt
- 《通信原理实验》课程电子教案(PPT讲稿)Verilog HDL数字系统设计与综合实验——第06讲 行为建模(2/2).ppt
