重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)hypertension

HYPERTENSION Luo kailiang,MD,Prof. The Second Affiliated Hospital Chongqing University of Medical Sciences
HYPERTENSION Luo kailiang, MD, Prof. The Second Affiliated Hospital Chongqing University of Medical Sciences

1.Definition Hypertension: SBP≥140 or DBP≥90mmHg primary hypertension (essential hypertension):In 95%of cases no cause can be found. Secondary Hypertension: In 5%a cause can be found. 2
2 1. Definition Hypertension: SBP > 140 or DBP > 90mmHg primary hypertension (essential hypertension): In 95% of cases no cause can be found. Secondary Hypertension: In 5% a cause can be found

Definitions and classification of blood pressure level (WHO/ISH,1999) Category SBP(mmHg) DBP(mmHg) Optimal <120 <80 Normal <130 <85 High normal 130~139 85≈89 Grade 1 HPN(mild) 140~159 9099 Grade 2 HPN (morderate) 160~179 100~109 Grade 3 HPN(severe) ≥180 ≥110 ISH ≥140 90
3 Definitions and classification of blood pressure level (WHO/ISH,1999) Category SBP(mmHg) DBP(mmHg) Optimal <120 <80 Normal <130 <85 High normal 130~139 85~89 Grade 1 HPN(mild) 140~159 90~99 Grade 2 HPN(morderate) 160~179 100~109 Grade 3 HPN(severe) ≥180 ≥110 ISH ≥140 <90

When a patient's systolic and diastolic blood pressures fall into different categories,the higher category should apply. Blood pressure is a continuous variable, The definition of hypertension has been arbitrarily set as:That blood pressure above which the benefits of treatment outweigh the risks in term of morbidity and mortality
4 ▪ When a patient’s systolic and diastolic blood pressures fall into different categories, the higher category should apply. ▪ Blood pressure is a continuous variable, The definition of hypertension has been arbitrarily set as: That blood pressure above which the benefits of treatment outweigh the risks in term of morbidity and mortality

A diagnosis of high blood pressure should not be based on a single reading,except when it is extremely high-for example, above 170-180/105-110.Otherwise several measurements taken over a period of time are generally needed to confirm a diagnosis. 5
5 ▪ A diagnosis of high blood pressure should not be based on a single reading, except when it is extremely high—for example, above 170–180/105–110. Otherwise several measurements taken over a period of time are generally needed to confirm a diagnosis
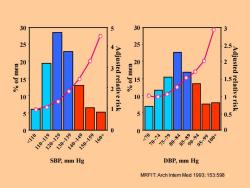
30 5 30 25 25 2. 20 20 2 3 5 1051000 15 1.5 2 10 10 1 Adjusted relative risk 5 0.5 0 0 <110 00-19⊙9149 210 120 30 40 ☑088] SBP,mm Hg DBP,mm Hg MRFIT:Arch Intern Med 1993;153:598
6 SBP, mm Hg % of men 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Adjusted relative risk 5 4 3 2 1 0 DBP, mm Hg % of men 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Adjusted relative risk 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 MRFIT: Arch Intern Med 1993; 153:598

The continuous relationship between the level of blood pressure and the risk of cardiovascular events,and arbitrary nature of the definition of hypertension have contributed to the variation in the definitions issued by various national and international authorities. 7
7 The continuous relationship between the level of blood pressure and the risk of cardiovascular events, and arbitrary nature of the definition of hypertension have contributed to the variation in the definitions issued by various national and international authorities
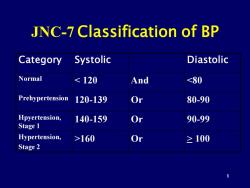
JNC-7 Classification of BP Category Systolic Diastolic Normal 160 Or ≥100 Stage 2
8 JNC-7 Classification of BP Category Systolic Diastolic Normal 160 Or > 100

2.Epidemiology
2. Epidemiology

Prevalence of hypertension in adult 28.79% 20 15 11.88% 10 7.736 5.11% 5 0 1959 1979 1991 1999-2000 CHINA USA
10 11.88% 7.73% 5.11% Prevalence of hypertension in adult 1959 1979 1991 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1999~2000 CHINA USA 28.79%
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)HEART FAILURE.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Glomerulardisease.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Generalintroductionofrenaldisease.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chronic Renal Failure.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Cardiomyopathies.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)高血压病 PRIMARY HYPERTENTION.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)心肌病(附属第二医院心内科:高大中).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)心脏瓣膜病(valvular heart disease).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)心肌炎(myocarditis).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程授课教案(七年制)贫血总论 - 陈姝.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程授课教案(七年制)血小板减少性紫癜 - 邓建川.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程授课教案(七年制)胃食管反流病 - 冯晓霞.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程授课教案(七年制)胃炎 - 宁波.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程授课教案(七年制)肾上腺皮质功能亢进 - 程伟.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程授课教案(七年制)肝硬化 - 沈薇.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程授课教案(七年制)肝性脑病 - 沈薇.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程授课教案(七年制)缺铁性贫血 - 陈姝.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程授课教案(七年制)糖尿病 - 龙敏.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程授课教案(七年制)白血病 - 陈林.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程授课教案(七年制)甲亢 - 李荣.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Leukemia(一).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Pericardial diease.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)系统性红斑狼疮狼疮性肾炎(Systemic Lupus Erythematosus,SLE).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)冠状动脉粥样硬化型心脏病 Coronary Atherosclerotic Heart Disease.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)心律失常 Cardiac Arrhythmia.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Leukemia(二).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)再生障碍性贫血 Aplastic Anemia.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)功能性胃肠病 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七篇 内分泌和代谢疾病 第一章 总论.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七篇 内分泌和代谢疾病 第九章 甲状腺功能亢进症 Hyperthyroidism.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七篇 内分泌和代谢疾病 第六章 尿崩症.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七篇 内分泌和代谢疾病 第十三章 库欣综合征(Cushing’s syndrome).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七篇 内分泌和代谢疾病 第十六章 嗜铬细胞瘤.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七篇 内分泌和代谢疾病 第十四章 原发性醛固酮增多症.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)糖尿病.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)缺铁性贫血 Iron deficiency anemia.ppt
- 《运动解剖学》课程文献资料(脑科学)中国科学院脑科学与智能技术卓越创新中心非人灵长类研究平台.pdf
- 《运动解剖学》课程文献资料(脑科学)中国脑科学计划进展.pdf
- 《运动解剖学》课程文献资料(脑科学)农村小学科学课程资源对教学效果的影响研究.pdf
- 《运动解剖学》课程文献资料(脑科学)双减背景下六步项目化”学习在初中科学教学中的研究.pdf
