《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)05_Bacteria Genetics

Section IFundaments of MicrobiologyMacrobial GeneticsSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Section I Fundaments of Microbiology Macrobial Genetics SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
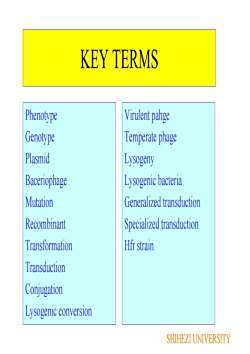
KEY TERMSPhenotypeVirulent pahgeGenotypeTemperate phage PlasmidLysogenyBaceriophageLysogenic bacteriaMutationGeneralized transductionRecombinantSpecialized transductionHfr strainTransformationTransductionConjugationLysogenic conversionSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
KEY TERMS Phenotype Genotype Plasmid Baceriophage Mutation Recombinant Transformation Transduction Conjugation Lysogenic conversion Virulent pahge Temperate phage Lysogeny Lysogenic bacteria Generalized transduction Specialized transduction Hfr strain SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

GeneticsGeneticsdefines and analyzes heredity, or constancy and changein the physiologic properties of organisms.GeneThe unit of heredity, a segment of DNA that carriesgenetic information for a specific biochemical orphysiologic property Phenotypethe collective structural and physiologic propertiesofacell or an organism Genotypethe sequence ofDNA within a gene or the organizationof genesSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
Genetics Genetics defines and analyzes heredity, or constancy and change in the physiologic properties of organisms. Gene The unit of heredity, a segment of DNA that carries genetic information for a specific biochemical or physiologic property Phenotype the collective structural and physiologic properties of a cell or an organism Genotype the sequence of DNA within a gene or the organization of genes SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
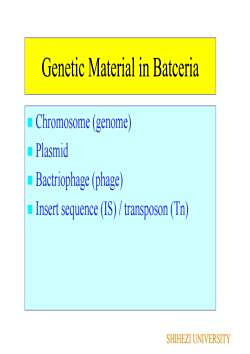
Genetic Material in BatceriaChromosome (genome Plasmid Bactriophage (phage)Insert sequence (IS) / transposon (TnSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Genetic Material in Batceria Chromosome (genome) Plasmid Bactriophage (phage) Insert sequence (IS) / transposon (Tn) SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

bacteriumplasmidbacterialchromosomeProkaryotic Genome Double-stranded, circular DNA1um Size: 580kb (mycoplasma) ~ 4,600kb (E. coli)Semi-conservative replication Pathogenecity island The pathogenic determinant genes are oftenclustered together in the DNA and are referred to aspathogenicity islands+Quite largeup to at least 200 kb+Code for many virulence genes, including adhesinsinvasins, exotoxins, and mobilizationSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Prokaryotic Genome Double-stranded, circular DNA Size: 580kb (mycoplasma) ~ 4,600kb (E. coli) Semi-conservative replication Pathogenecity island The pathogenic determinant genes are often clustered together in the DNA and are referred to as pathogenicity islands Quite large— up to at least 200 kb Code for many virulence genes, including adhesins, invasins, exotoxins, and mobilization SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Table 7-1. Comparison of genome sizes inseekaathndiruSize(kbp)OrganismProkaryotesArchae1660Methanococusjannaschi2180Archaeoglobus fulgidus580EubacteraMycoplasma genitalium820Mycoplasmapneumonide910Boreliaburgdoreri1040Chiamydia tachomatis1110Ricktsi prowazeki1140Treponema palldum1230Chiamyiapneumoniae1670Heliobacter pyori1830Hdemophilusinfuenzae2180Neiseria meningitidisserogroupA2270Nesria meningidisserogroup B4210Bacils sutlis4410Mycobacterum tuberculosis4640Escherichia oli48LambdaBacteriophageVariola186Viruses192Vaccinia229CytomegalovirusSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
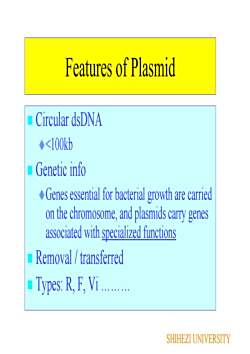
Features of Plasmid Circular dsDNA<100kbGenetic infoGenes essential for bacterial growth are carriedon the chromosome, and plasmids carry genesassociated with specialized functionsRemoval / transferred Types: R, F, ViSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
Features of Plasmid Circular dsDNA <100kb Genetic info Genes essential for bacterial growth are carried on the chromosome, and plasmids carry genes associated with specialized functions Removal / transferred Types: R, F, Vi . . . SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
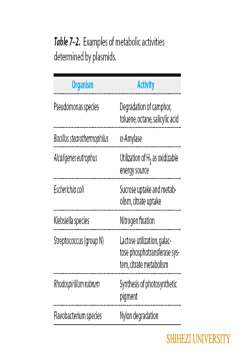
Table7-2.Examplesof metabolicactivitiesdetermined by plasmids.ActivityOrganismPseudomonaspeciesDegradation of camphortoluene,octane,salicylic acidBacilsstearothermophilusα-AmylaseAlcaligenes eutrophusUtilizationofHasoxidizabeenergy sourceEscherichia oliSucrose uptake andmetabolism,citrate uptakeKlesiellaspeciesNitrogen fixationStreptococcus (group N)Lactose utilization,galatose phosphotransferasesystem,citrate metabolismRhodosprilum rubrumSynthesis of photosyntheticpigmentFlavobacterium speciesNylon degradationSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Plasmids Definition: Extrachromosomal geneticelements that are capable of autonomousreplication (replicon)Episome - a plasmid that can integrate intothe chromosomeSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
Plasmids Definition: Extrachromosomal genetic elements that are capable of autonomous replication (replicon) Episome - a plasmid that can integrate into the chromosome SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Classification of Plasmids Transfer propertiesConjugativeNonconjugative Phenotypic effectsFertilityBacteriocinogenic plasmidResistance plasmid (R factorsSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Classification of Plasmids Transfer properties Conjugative Nonconjugative Phenotypic effects Fertility Bacteriocinogenic plasmid Resistance plasmid (R factors) SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)04_Microbial Metabolism.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)06_Bacteria Pathogenesis.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)07_Normal microbial flora.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)13_Enterobacteriaceae.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)12_Nesseria.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)10_Staphylococcus.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)18_Virio_Vampylo_Helico.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)17_Pseudomonoads_acinetobacter.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19A_Haemophilus_Bordetella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)22_Lab Diagnosis for Bacterial Infections.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)21_Non-spore-forming G+ bacilli_Corynebacterium_Listeria_Actinomycetes.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)20_Yersinia_Pasteurella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19B_Brucella_Francisella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)01 绪论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)02 细菌形态结构.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)09-1 微生物感染的病原学检查法.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)03 细菌生理.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)06 真菌的基本性状.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)05 病毒基本性状.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)07 微生物感染与致病机制.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)08_Spore-forming G+ bacilli_Clostridia.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)02_Bacteria Growth_Survival_Death_01.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_Cultivation of Microorganisms.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_BacterialPhysiology.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)00_Introduction.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)01_BacterialStructure.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第36章 真菌学总论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第35章 阮粒(Prion).pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第37章 主要病原性真菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第34章 其他病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第33章 反转录病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第28章 急性胃肠炎病毒(Acute gastroenteritis virus).pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第27章 肠道病毒 enterovirus.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第30章 虫媒病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第32章 疱疹病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第29章 肝炎病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第26章 呼吸道病毒 Viruses associated with respiratory infections.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第24章 病毒的感染与免疫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第23章 病毒学.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第25章 病毒感染的检查方法与防治原则.pdf
