《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19A_Haemophilus_Bordetella

Section III BacteriologyHaemophilus & BordetellaSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Section III Bacteriology Haemophilus & Bordetella SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

KEY TERMS Haemophilus influenzae satellite phenomenon Bordetlla pertussis Respiratory infectionSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
KEY TERMS Haemophilus influenzae satellite phenomenon Bordetella pertussis Respiratory infection SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

HaemophilusSmall, gram-negative, pleomorphic bacteriarequires enriched media. usually containing blood or itsderivatives, for cultureHaemophilus influenzae type b is an importanthuman pathogenHaemophilus ducreyi, a sexually transmittedpathogen, causes chancroidOther species are among the normal flora of mucousmembranes and only occasionally cause diseaseSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Haemophilus Small, gram-negative, pleomorphic bacteria requires enriched media, usually containing blood or its derivatives, for culture Haemophilus influenzae type b is an important human pathogen Haemophilus ducreyi, a sexually transmitted pathogen, causes chancroid Other species are among the normal flora of mucous membranes and only occasionally cause disease SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
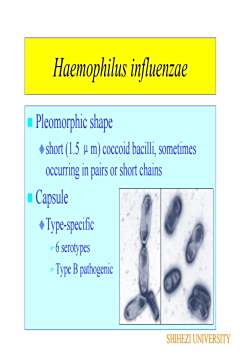
Haemophilus influenzae Pleomorphic shapeshort(1.5 μ m) coccoid bacilli, sometimesoccurring in pairs or short chainsCapsuleType-specific- 6 serotypes Type B pathogenicSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
Haemophilus influenzae Pleomorphic shape short (1.5 μm) coccoid bacilli, sometimes occurring in pairs or short chains Capsule Type-specific 6 serotypes Type B pathogenic SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
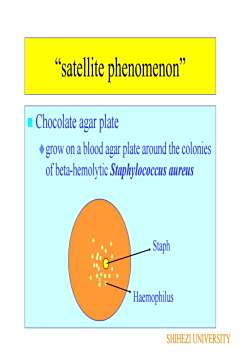
satellite phenomenonChocolate agar plategrow on a blood agar plate around the coloniesof beta-hemolytic Staphylococcus aureusStaphHaemophilusSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Chocolate agar plate grow on a blood agar plate around the colonies of beta-hemolytic Staphylococcus aureus “satellite phenomenon” Staph Haemophilus SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

X- and V-FactorsGrow on a plate (Mueller-Hinton agarthat has been fortified with both X.factor (found to be hemin) and V-factor (found to be NAD)+ but not either one aloneThe above plate has been streakedWith enough Haemophilus influenza toform a lawn on the plate. but there isonly growth around the XV filterwhich has been fortified with both Xand V factor (Hemin and NAD)* NAD: Nicotinamide adenine nucleotide, acoenzymeHaemophilus infuenzae fnutritionalfactorsX-hemin Y=WADSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
X- and V-Factors Grow on a plate (Mueller-Hinton agar) that has been fortified with both X- factor (found to be hemin) and V- factor (found to be NAD) but not either one alone The above plate has been streaked with enough Haemophilus influenza to form a lawn on the plate, but there is only growth around the XV filter, which has been fortified with both X and V factor (Hemin and NAD) * NAD: Nicotinamide adenine nucleotide, a coenzyme SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Pathogenesis: Virulent Factor Capsuleantiphagocytic in the absence of specific anticapsularantibodies The polyribose phosphate capsule of type b Hinfluenzae is the major virulence factor The nonencapsulated H influenzae is a regularmember of the normal respiratory flora ofhumansSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Pathogenesis: Virulent Factor Capsule antiphagocytic in the absence of specific anticapsular antibodies The polyribose phosphate capsule of type b H influenzae is the major virulence factor The nonencapsulated H influenzae is a regular member of the normal respiratory flora of humans SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
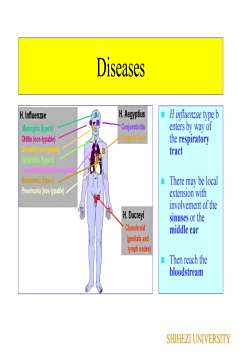
DiseasesH.AegyptiusH influenzae type bH.Infuenzae2enters by way ofCorjunctitisMeningitis(typeb)Purpuriefeverthe respiratoryOtitis (non-typable)Sinustis (non-typable)tractEpigltitistype bTrachaoranchtis npabeBaterermia (typeb)There may be localPneumonia(non-typable)extension with1involvement of theH. Ducreyisinuses or theChanchroidmiddle ear(genitals andlymph nodes)Then reach thebloodstreamSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Diseases H influenzae type b enters by way of the respiratory tract There may be local extension with involvement of the sinuses or the middle ear Then reach the bloodstream SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Pathogenesis H influenzae type b+One of the 2 most common etiologic agents ofbacterial otitis media and acute sinusitis Anther is pneumococciThe most common cause of bacterial meningitis inchildren age 5 months to5 yearsBacteremiaSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Pathogenesis H influenzae type b One of the 2 most common etiologic agents of bacterial otitis media and acute sinusitis Anther is pneumococci The most common cause of bacterial meningitis in children age 5 months to 5 years Bacteremia SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Diagnostic Laboratory TestsSpecimens+ nasopharyngeal swabs, pus, blood, and spinal fluidDirect IdentificationCommercial kits are available for immunologicdetection of H influenzae antigens in spinal fluidA positive test indicates that the fluid contains highconcentrations of specific polysaccharide from H influenzaetype b Culture IsoVitaleX-enriched chocolate agarSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Diagnostic Laboratory Tests Specimens nasopharyngeal swabs, pus, blood, and spinal fluid Direct Identification Commercial kits are available for immunologic detection of H influenzae antigens in spinal fluid A positive test indicates that the fluid contains high concentrations of specific polysaccharide from H influenzae type b Culture IsoVitaleX-enriched chocolate agar SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)22_Lab Diagnosis for Bacterial Infections.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)21_Non-spore-forming G+ bacilli_Corynebacterium_Listeria_Actinomycetes.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)20_Yersinia_Pasteurella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19B_Brucella_Francisella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)01 绪论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)02 细菌形态结构.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)09-1 微生物感染的病原学检查法.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)03 细菌生理.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)06 真菌的基本性状.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)05 病毒基本性状.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)07 微生物感染与致病机制.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)08 抗感染免疫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)09-2 微生物感染的预防原则.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)10 微生物感染的控制.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)13 奈瑟菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)12 链球菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)11 葡萄球菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)14 埃希菌属菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)16 沙门菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)18 梭菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)17_Pseudomonoads_acinetobacter.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)18_Virio_Vampylo_Helico.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)10_Staphylococcus.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)12_Nesseria.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)13_Enterobacteriaceae.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)07_Normal microbial flora.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)06_Bacteria Pathogenesis.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)04_Microbial Metabolism.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)05_Bacteria Genetics.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)08_Spore-forming G+ bacilli_Clostridia.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)02_Bacteria Growth_Survival_Death_01.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_Cultivation of Microorganisms.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_BacterialPhysiology.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)00_Introduction.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)01_BacterialStructure.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第36章 真菌学总论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第35章 阮粒(Prion).pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第37章 主要病原性真菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第34章 其他病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第33章 反转录病毒.pdf
