《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)00_Introduction

Medical Microbiology?An IntroductionSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Medical Microbiology: An Introduction SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Main TopicsAn overview of Medical Microbiology- Classification of microorganisms? Brief history? Challenges we meet now? How to study? AssessmentSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Main Topics •An overview of Medical Microbiology –Classification of microorganisms •Brief history •Challenges we meet now •How to study? •Assessment SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Five Characteristics of Life1. Cells2. Maintain structure by taking up chemicalsand energy from the environment3. Respond to stimuli in the externalenvironment4. Reproduce and pass on their organization totheir ffspring5. Evolve and adapt to the environmentSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Five Characteristics of Life 1. Cells 2. Maintain structure by taking up chemicals and energy from the environment 3. Respond to stimuli in the external environment 4. Reproduce and pass on their organization to their offspring 5. Evolve and adapt to the environment SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

5 Kingdoms of Living Organisms1. Animalia2. Plantae3.Fungi4. Protista5. Monera - Bacteria and CyanobacteriEukaryotic vs. ProkaryoticSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
5 Kingdoms of Living Organisms 1. Animalia 2. Plantae 3. Fungi 4. Protista 5. Monera - Bacteria and Cyanobacteria Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
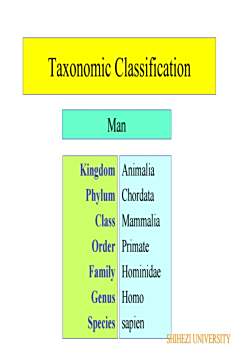
Taxonomic ClassificationManKingdom AnimaliaChordataPhylumClassMammalia1OrderPrimateFamilyHominidaeGenusHomoSpeciessapienSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Taxonomic Classification Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Animalia Chordata Mammalia Primate Hominidae Homo sapien Man SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Binomial System of TaxonomicClassification Use only the Genus and species- Homo sapien- Felis domestica- Escherichia coli· Genus and species are either underlined oritalicized- Genus is always capitilized- species is never capitilizedSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Binomial System of Taxonomic Classification •Use only the Genus and species –Homo sapien –Felis domestica –Escherichia coli •Genus and species are either underlined or italicized –Genus is always capitilized –species is never capitilized SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Classification SystemThree Domains1978 Carl Woese1. Bacteria· Unicellular prokaryotes with cell wall containingpeptidoglycan2. Archaea· Unicellular prokaryotes with no peptidoglycan incell wall3. Eukarya? Protista· Fungi? Plantae? AnimaliaSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
Classification System Three Domains 1978 Carl Woese 1. Bacteria •Unicellular prokaryotes with cell wall containing peptidoglycan 2. Archaea •Unicellular prokaryotes with no peptidoglycan in cell wall 3. Eukarya •Protista •Fungi •Plantae •Animalia SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

What is Microbiology?: Micro- too small to be seen with the naked eye? Bio - life? ology - study ofMicrobiology -Science about small living things· The morphology and structures? Physiology· Pathogenesis and Immunology (medical microbiology Treatment and prevention (medical microbiologySHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
What is Microbiology? • Micro - too small to be seen with the naked eye • Bio - life • ology - study of Microbiology –Science about small living things •The morphology and structures •Physiology •Pathogenesis and Immunology (medical microbiology) •Treatment and prevention (medical microbiology) SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
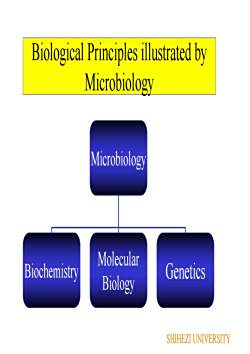
Biological Principles llustrated bMicrobiologyMicrobiologyMolecularGeneticsBiochemistryBiologySHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Biological Principles illustrated by Microbiology Microbiology Biochemistry Molecular Biology Genetics SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Evolution· Microorganisms are the products ofevolution- the biologic consequence of natural selectionoperating upon avast array of geneticalydiverse organismsSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Evolution •Microorganisms are the products of evolution –the biologic consequence of natural selection operating upon a vast array of genetically diverse organisms SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_BacterialPhysiology.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_Cultivation of Microorganisms.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)02_Bacteria Growth_Survival_Death_01.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)08_Spore-forming G+ bacilli_Clostridia.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)05_Bacteria Genetics.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)04_Microbial Metabolism.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)06_Bacteria Pathogenesis.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)07_Normal microbial flora.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)13_Enterobacteriaceae.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)12_Nesseria.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)10_Staphylococcus.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)18_Virio_Vampylo_Helico.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)17_Pseudomonoads_acinetobacter.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19A_Haemophilus_Bordetella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)22_Lab Diagnosis for Bacterial Infections.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)21_Non-spore-forming G+ bacilli_Corynebacterium_Listeria_Actinomycetes.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)20_Yersinia_Pasteurella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19B_Brucella_Francisella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)01 绪论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)02 细菌形态结构.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)01_BacterialStructure.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第36章 真菌学总论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第35章 阮粒(Prion).pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第37章 主要病原性真菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第34章 其他病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第33章 反转录病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第28章 急性胃肠炎病毒(Acute gastroenteritis virus).pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第27章 肠道病毒 enterovirus.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第30章 虫媒病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第32章 疱疹病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第29章 肝炎病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第26章 呼吸道病毒 Viruses associated with respiratory infections.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第24章 病毒的感染与免疫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第23章 病毒学.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第25章 病毒感染的检查方法与防治原则.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第22章 螺旋体.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第20章 立克次体.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第18章 放线菌属与诺卡菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第16章 动物源性细菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第17章 其他细菌.pdf
