《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)06_Bacteria Pathogenesis

Section III BacteriologyPathogenesis of Bacterial InfectionSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Section III Bacteriology Pathogenesis of Bacterial Infection SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

KEY TERMS PathogenExtra/intracellular pathogenCompromised hostOpportunistic infection InfectionExotoxinEndotoxin Infectious diseases Koch's postulatesAutoimmunity TransmissionBioterrorismAdhesion PenetrationInvasiveness/spreadSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
KEY TERMS Pathogen Opportunistic infection Infection Infectious diseases Koch’s postulates Transmission Adhesion Penetration Invasiveness/spread Extra/intracellular pathogen Compromised host Exotoxin Endotoxin Autoimmunity Bioterrorism SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

GLOSSARYAeasonaachmnhossInvaoThposswheyacteriaanmaparasitewhichbacteriasticktothesurfacesofhostcells.Oncefugindirustispin the bodybacriahntthymNonpathogenAmicroorganismthatdoesnotcausedisinitialstepintheinfectionprocess.Thetermsadherease:maybepartofthenormalfloraenceadsonandatachmntarftenusedintchangeably.OpportunisticpathogenAnagentcapableofcausinCarrierAeronoranmalwithasymptomaticinfectiodiseaseonlywhenthehost'sresistanceisimpaired(iewhenthepatientis"mmunocompromised")thatcanbetransmittedtoanothersusceptiblepersonPathgenmicoorganmapablecaungdiseasor animal.InfectionMultiplicatiofaninfectiousagentwithinthePathogenicityTheabilityofaninfectiousagenttocausepody.Multiplicationfthebacteriathatarepartfthdisease seealso virulenceToxigenicityTheabilityfamicroorganismproduceamahtrsakerallynotconsideredaninfectionontheotherhandtoxinthatcontributestothedevelopmentofdiseaseViruunttiltaumultplicatioanbriaamaspecies)evenifthepersonisasymptomaticsdisease.Virulentagentscausedisease when introduceddeemed an infection.intothehostinsmallnumbers.Virulenceinvolvesinvasionand toxigenicity (see above)SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Pathogen Definition: a microorganism capable ofcausing diseaseCharacteristicsTransmissibility Adherence to host cellsInvasion of host cells and tissuesToxigenicityAbility to evade the host's immune systemSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Pathogen Definition: a microorganism capable of causing disease Characteristics Transmissibility Adherence to host cells Invasion of host cells and tissues Toxigenicity Ability to evade the host’s immune system SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
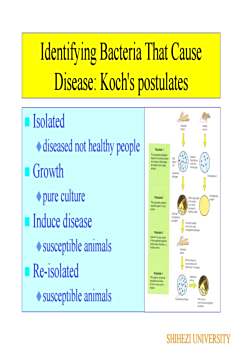
Identifying Bacteria That CauseDisease:Koch's postulates Isolateddiseased not healthy peoplePostulale 1The sutpectad penogirnipaninshauldtencasdlftetoard ataerthon ecthnGrowthmnddbiod on pure culture39Postulate2hesusoecdona8gmetashoaid be ponimpreueolthyanindsuspec Induce diseasepithognosalehealhatBsuspendpatogerPostulate3Calb tomapuectechtesedogait susceptible animalsshold caisedehaty armeoetentbymosep Re-isolatedPestulate 4The opaniomshoud bedudstonibeteseasteF susceptible animalsPurealnesoidsfpatrognasbesameogerisnas beteSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Identifying Bacteria That Cause Disease: Koch's postulates Isolated diseased not healthy people Growth pure culture Induce disease susceptible animals Re-isolated susceptible animals SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
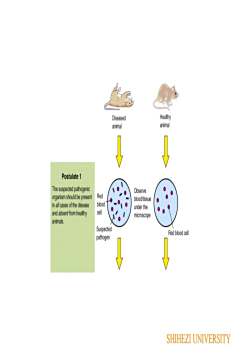
HealthyDiseasedanimalanimalPostulate1The suspected pathogenicObserveRedorganismshouldbepresentblood/issuebloodinall casesofthediseaseunderthecelland absentfrom healthymicroscopeanimas.SuspectedRed blood cellpathogenSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
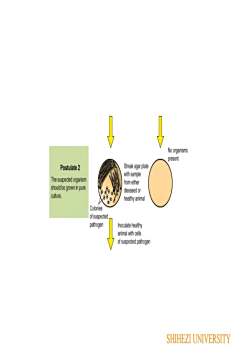
No organismspresentStreak agar platePostulate2with sampleThe suspectedorganismfrom eithershould be grownin purediseased orculture.healthy animalColoniesof suspectedpathogenInoculate healthyanimal withcellsof suspected pathogenSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
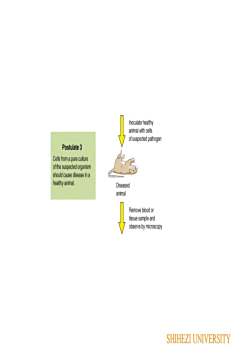
Inoculate heathyanimal with ellsof suspected pathogenPostulate 3Cells froma pure cutureofthesuspectedorganismshouldcausediseaseinahealthy animal.DiseasedanimalRemove blood ortisue sample andobserve by microscopySHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
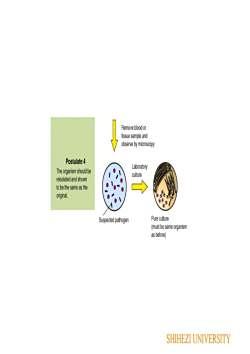
Remove blood ortissue sample andobserve by microscopyPostulate 4LaboratoryThe organism should beculturereisolatedand shownto bethe same as theorginal.0Q080Pure cuureSuspected pathogen(must besameorganismas before)SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Table9GuidelinesforestablishingthecausesofinfectiousdiseasesMolecular Koch'sPostulatesKoch's Postulates1. The microorganism1. The phenotype or prop-should be found in allerty underinvestigationcases of the disease inshould be significantyquestion,and its distri-associated with patho-bution in the bodygenic trains ofa speciesshould be in accordanceand not with nonpatho-with the lesionsgenic trains.observed.2. The microorganism2. Specificinactvation ofshould be grown in purethe gene or genesasso-culture in vitro (or outsideciated with the sus-the body of the host) forpected virulence tritseveral generations.should lead to ameasurable decrease inpathogenicity orvirulence.3. When such a pure cul-3. Reversion or replaceture isinoculated intoment ofthe mutatedsusceptible animalgene with the wild-typespecies the typical dis-gene should lead torestoration of patho-ease must result.genicity or virulence.4. The microorganism mustagain be isolated fromthe lesions of suchexperimentaly produceddisease.SHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)07_Normal microbial flora.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)13_Enterobacteriaceae.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)12_Nesseria.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)10_Staphylococcus.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)18_Virio_Vampylo_Helico.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)17_Pseudomonoads_acinetobacter.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19A_Haemophilus_Bordetella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)22_Lab Diagnosis for Bacterial Infections.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)21_Non-spore-forming G+ bacilli_Corynebacterium_Listeria_Actinomycetes.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)20_Yersinia_Pasteurella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19B_Brucella_Francisella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)01 绪论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)02 细菌形态结构.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)09-1 微生物感染的病原学检查法.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)03 细菌生理.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)06 真菌的基本性状.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)05 病毒基本性状.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)07 微生物感染与致病机制.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)08 抗感染免疫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)09-2 微生物感染的预防原则.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)04_Microbial Metabolism.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)05_Bacteria Genetics.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)08_Spore-forming G+ bacilli_Clostridia.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)02_Bacteria Growth_Survival_Death_01.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_Cultivation of Microorganisms.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_BacterialPhysiology.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)00_Introduction.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)01_BacterialStructure.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第36章 真菌学总论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第35章 阮粒(Prion).pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第37章 主要病原性真菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第34章 其他病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第33章 反转录病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第28章 急性胃肠炎病毒(Acute gastroenteritis virus).pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第27章 肠道病毒 enterovirus.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第30章 虫媒病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第32章 疱疹病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第29章 肝炎病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第26章 呼吸道病毒 Viruses associated with respiratory infections.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第24章 病毒的感染与免疫.pdf
