《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)07_Normal microbial flora

Section IIIBacteriologyNormal Microbial Florain Human BodySHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Section III Bacteriology Normal Microbial Flora in Human Body SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

KEY TERMS PathogenOpportunistic infectionMicrodysbiosis Translocation Medical Microecology Nosocomial InfectionSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
KEY TERMS Pathogen Opportunistic infection Microdysbiosis Translocation Medical Microecology Nosocomial Infection SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Pathogenic BacteriaNot allbacteriadiseasecause少数细菌总有致病性y bacteria areally pathogenic许多细菌具有潜在致病00性209大多细菌不具有致病性
少 数 少 数 细细菌菌 总 有 致病 总 有 致病 性 性 许多多 细细菌菌 具 有 潜 在 致病 具 有 潜 在 致病 性 性 大 多 大 多 细细菌菌 不 具 有 致病 性 不 具 有 致病 性 Pathogenic Bacteria

Normal Microbial Florathe population of microorganisms thatinhabit the skin and mucous membranes ofhealthy normal personsIt is doubtful whether a normal yiral floraexists in humansSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
Normal Microbial Flora the population of microorganisms that inhabit the skin and mucous membranes of healthy normal persons It is doubtful whether a normal viral flora exists in humans SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Normal Microbiota= Normal Flora Normal microbiota Normal microflora Physiological microbiotaSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Normal Microbiota= Normal Flora Normal microbiota Normal microflora Physiological microbiota SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Normal Microbial Flora Groups Resident floraconsists of relatively fixed types ofmicroorganisms regularly found in a given areaat a given ageIf disturbed tpromptly reestablishes itself Transient floraconsists of nonpathogenic or potentiallypathogenic microorganisms that inhabit theskin or mucous membranes for hours, or daysSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Normal Microbial Flora Groups Resident flora consists of relatively fixed types of microorganisms regularly found in a given area at a given age If disturbed, it promptly reestablishes itself Transient flora consists of nonpathogenic or potentially pathogenic microorganisms that inhabit the skin or mucous membranes for hours, or days SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Transient FloraIt is derived from the environment, does notproduce disease, and does not establish itselfpermanently on the surface Members of the transient flora are generally oflitle significance so long as the normal residentflora remains intact If the resident flora is disturbed, transientmicroorganisms may colonize, proliferate, andproduce diseaseSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
Transient Flora It is derived from the environment, does not produce disease, and does not establish itself permanently on the surface Members of the transient flora are generally of little significance so long as the normal resident flora remains intact If the resident flora is disturbed, transient microorganisms may colonize, proliferate, and produce disease SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Classifications of Normal FloraEnviromentAutochthony (=aboriginesAllochthony (=foreignRelation with host Symbiotic flora Parasitism floraSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Classifications of Normal Flora Enviroment Autochthony (= aborigines) Allochthony (= foreign) Relation with host Symbiotic flora Parasitism flora SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
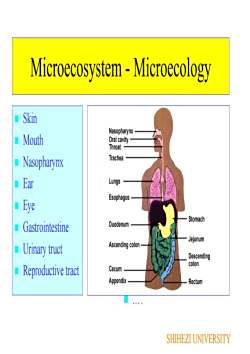
Microecosystem - MicroecologySkinNasopharynx MouthOral cavityThroatTrachea NasopharynxLungsEarEsophagusEyeStomachDuodenumGastrointestineJejunumAscending colon Urinary tructDescendingcolonCecumReproductive tractAppendixRectumSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Microecosystem - Microecology Skin Mouth Nasopharynx Ear Eye Gastrointestine Urinary truct Reproductive tract Staphy E. coli Pseudomonas Strepto Nesseria Corynebacteria . . . . SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
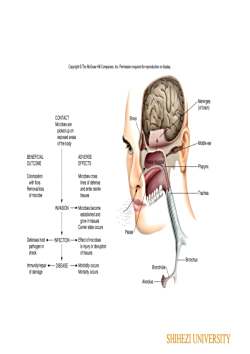
CyhrawirdMeninges(of brain)CONTACTSinusMicrobes arepicked up onexposed areasMiddle earof the bodyADVERSEBENEFICIALNasalmucosaOUTCOMEEFFECTSPharynxColonizationMicrobes crosswithfloralines of defenseRemovalossand enter sterileTracheaof microbetissuesINVASION→Microbes becomeestablished andgrow in tssuesCarrier state occursPalateDefenses holdINFECTION→Effect of microbespathogen inis injury ordisruptioncheckof tissuesBronchusImmunity/repairDISEASE→MorbidityoccursBronchioleof damageMortalty occursAlveolusSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)13_Enterobacteriaceae.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)12_Nesseria.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)10_Staphylococcus.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)18_Virio_Vampylo_Helico.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)17_Pseudomonoads_acinetobacter.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19A_Haemophilus_Bordetella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)22_Lab Diagnosis for Bacterial Infections.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)21_Non-spore-forming G+ bacilli_Corynebacterium_Listeria_Actinomycetes.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)20_Yersinia_Pasteurella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19B_Brucella_Francisella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)01 绪论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)02 细菌形态结构.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)09-1 微生物感染的病原学检查法.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)03 细菌生理.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)06 真菌的基本性状.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)05 病毒基本性状.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)07 微生物感染与致病机制.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)08 抗感染免疫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)09-2 微生物感染的预防原则.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)10 微生物感染的控制.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)06_Bacteria Pathogenesis.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)04_Microbial Metabolism.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)05_Bacteria Genetics.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)08_Spore-forming G+ bacilli_Clostridia.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)02_Bacteria Growth_Survival_Death_01.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_Cultivation of Microorganisms.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_BacterialPhysiology.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)00_Introduction.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)01_BacterialStructure.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第36章 真菌学总论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第35章 阮粒(Prion).pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第37章 主要病原性真菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第34章 其他病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第33章 反转录病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第28章 急性胃肠炎病毒(Acute gastroenteritis virus).pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第27章 肠道病毒 enterovirus.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第30章 虫媒病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第32章 疱疹病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第29章 肝炎病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第26章 呼吸道病毒 Viruses associated with respiratory infections.pdf
