《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)18_Virio_Vampylo_Helico

Section III BacteriologyVibrios, Campylobacter, HelicobacterSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Section III Bacteriology Vibrios, Campylobacter, Helicobacter SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

KEY TERMS Vibrio choleraeCholeragen Vero toxin (Shiga-like(cholera toxin)Campylobacter HemolysinJejunipiliHelicobacter pyloriYersinia entercoliticaSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
KEY TERMS Vibrio cholerae Vero toxin (Shiga-like) Choleragen (cholera toxin) Hemolysin Campylobacter jejuni pili Helicobacter pylori Yersinia entercolitica SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Bacteria InfectedGastrointestinal TractEnterobacteriaceaeescherichia. shigella. salmonella enterobacterklebsiella, serratia, proteus, and others Vibrio CampylobacterHelicobacterSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
Bacteria Infected Gastrointestinal Tract Enterobacteriaceae escherichia, shigella, salmonella, enterobacter, klebsiella, serratia, proteus, and others Vibrio Campylobacter Helicobacter SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

VibiosVibio choleraKINGCHOLERAVibio parahaemolyticusSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Vibios Vibio cholera Vibio parahaemolyticus SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

The Vibrios Vibrios are among the most common bacteria insurface waters worldwide They are curved aerobic rods and are motilepossessing a polar flagellumV cholerae serogroups O1 and 0139 causecholera in humans+while other vibrios may cause sepsis or enteritisSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
The Vibrios Vibrios are among the most common bacteria in surface waters worldwide They are curved aerobic rods and are motile, possessing a polar flagellum V cholerae serogroups O1 and O139 cause cholera in humans while other vibrios may cause sepsis or enteritis SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
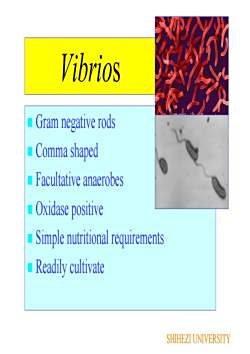
VibriosGram negative rods Comma shapedFacultative anaerobes Oxidase positive Simple nutritional requirements Readily cultivateSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Vibrios Gram negative rods Comma shaped Facultative anaerobes Oxidase positive Simple nutritional requirements Readily cultivate SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

CultureThiosulfate-citrate-bile-sucrose (TCBSagar1 oxidase-positivegrow at a very high pH (8.5-9.5)+ rapidly killed by acid.SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Culture Thiosulfate-citrate-bile-sucrose (TCBS) agar oxidase-positive grow at a very high pH (8.5–9.5) rapidly killed by acid. SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
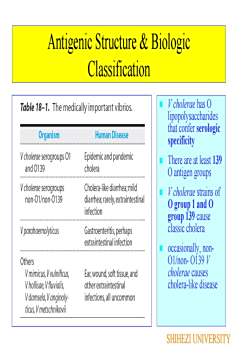
Antigenic Structure & BiologicClassification V cholerae has OTable 18-1. The medically important vibrioslipopolysaccharidesthat confer serologicOrganismHuman DiseasespecificityVcholerae serogroups 01Epidemic and pandemicThere are at least 139and 0139choleraO antigen groupsVcholerae serogroupsCholera-ike diarhea mildV cholerae strains ofnon-01/non-0139diarrhea; rarely, extraintestinalO group 1 and Oinfectiongroup 139 causeclassic choleraV parahaemolyticusGastrentrtis perhapsextraintestinalinfection occasionally, non-01/non- 0i39 V Otherscholerae causesV mimicus,Vvulnifcus,Eawoundofttissueancholera-like diseaseVhliae fuialis,other extraintestinalV damsela, V anginolyinfections,all uncommonticus,VmetschnikoviSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
Antigenic Structure & Biologic Classification V cholerae has O lipopolysaccharides that confer serologic specificity There are at least 139 O antigen groups V cholerae strains of O group 1 and O group 139 cause classic cholera occasionally, non- O1/non- O139 V cholerae causes cholera-like disease SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Serotypes & BiotypesV cholerae serogroup O1 antigen has determinantsthat make further typing:The main serotypes are Ogawa and InabaTwo biotypes of epidemic V cholerae have been definedclassic and EI TorThe EITor biotype producesahemolysin gives positive resultson the Voges-Proskauer test, and is resistant to polymyxinBMolecular techniques can also be used to type V choleraeTyping is used for epidemiologic studies, and testsgenerally are done only in reference laboratoriesSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Serotypes & Biotypes V cholerae serogroup O1 antigen has determinants that make further typing: The main serotypes are Ogawa and Inaba Two biotypes of epidemic V cholerae have been defined, classic and El Tor The El Tor biotype produces a hemolysin, gives positive results on the Voges-Proskauer test, and is resistant to polymyxin B. Molecular techniques can also be used to type V cholerae Typing is used for epidemiologic studies, and tests generally are done only in reference laboratories SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Occurrence - choleraCholera,2002-2003Third world?Common+ Food hygiene* Ingestion ofsea-food Other locations* Travelers,uncommonCountrieslareasreporingcholeracaseCountrieswithimportedcholeracasesSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Occurrence - cholera Third world Common * Food hygiene * Ingestion of sea-food * Other locations * Travelers, uncommon SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)17_Pseudomonoads_acinetobacter.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19A_Haemophilus_Bordetella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)22_Lab Diagnosis for Bacterial Infections.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)21_Non-spore-forming G+ bacilli_Corynebacterium_Listeria_Actinomycetes.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)20_Yersinia_Pasteurella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)19B_Brucella_Francisella.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)01 绪论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)02 细菌形态结构.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)09-1 微生物感染的病原学检查法.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)03 细菌生理.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)06 真菌的基本性状.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)05 病毒基本性状.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)07 微生物感染与致病机制.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)08 抗感染免疫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)09-2 微生物感染的预防原则.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)10 微生物感染的控制.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)13 奈瑟菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)12 链球菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)11 葡萄球菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)14 埃希菌属菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)10_Staphylococcus.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)12_Nesseria.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)13_Enterobacteriaceae.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)07_Normal microbial flora.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)06_Bacteria Pathogenesis.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)04_Microbial Metabolism.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)05_Bacteria Genetics.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)08_Spore-forming G+ bacilli_Clostridia.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)02_Bacteria Growth_Survival_Death_01.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_Cultivation of Microorganisms.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)03_BacterialPhysiology.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)00_Introduction.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(英文)01_BacterialStructure.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第36章 真菌学总论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第35章 阮粒(Prion).pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第37章 主要病原性真菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第34章 其他病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第33章 反转录病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第28章 急性胃肠炎病毒(Acute gastroenteritis virus).pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(2012)第27章 肠道病毒 enterovirus.pdf
