重庆医科大学:《生物化学》课程教学大纲(留学生生物化学大纲)
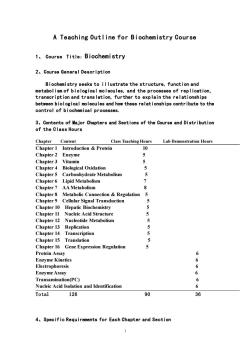
A Teaching Outline for Biochemistry Course 1.Course Title:Biochemistry 2,Course General Description Biochemistry seeks to il lustrate the structure,function and metabolism of biological molecules,and the processes of replication, transcription and trans lation,further to explain the relationships between biological molecules and how these relationships contribute to the control of biochemical processes. 3,Contents of Major Chapters and Sections of the Course and Distribution of the Class Hours Chapter Content Class Teaching Hours Lab Demonstration Hours Chapter 1 Introduction Protein 10 Chapter 2 Enzyme 5 Chapter 3 Vitamin 5 Chapter 4 Biological Oxidation 5 Chapter 5 Carbonhydrate Metabolism 5 Chapter 6 Lipid Metabolism > Chapter 7 AA Metabolism 6 Chapter 8 Metabolic Connection Regulation Chapter 9 Cellular Signal Transduction 心 Chapter 10 Hepatic Biochemistry 5 Chapter 11 Nucleic Acid Structure 5 Chapter 12 Nucleotide Metabolism 5 Chapter 13 Replication 5 Chapter 14 Transcription 5 Chapter 15 Translation 5 Chapter 16 Gene Expression Regulation 5 Protein Assay 6 Enzyme Kinetics 6 Electrophoresis 6 Enzyme Assay 6 Transamination(PC) 6 Nucleic Acid Isolation and Identification 6 Total 126 90 36 4,Specific Requirements for Each Chapter and Section
1 A Teaching Outline for Biochemistry Course 1、 Course Title:Biochemistry 2、Course General Description Biochemistry seeks to illustrate the structure, function and metabolism of biological molecules, and the processes of replication, transcription and translation, further to explain the relationships between biological molecules and how these relationships contribute to the control of biochemical processes. 3、Contents of Major Chapters and Sections of the Course and Distribution of the Class Hours Chapter Content Class Teaching Hours Lab Demonstration Hours Chapter 1 Introduction & Protein 10 Chapter 2 Enzyme 5 Chapter 3 Vitamin 5 Chapter 4 Biological Oxidation 5 Chapter 5 Carbonhydrate Metabolism 5 Chapter 6 Lipid Metabolism 7 Chapter 7 AA Metabolism 8 Chapter 8 Metabolic Connection & Regulation 5 Chapter 9 Cellular Signal Transduction 5 Chapter 10 Hepatic Biochemistry 5 Chapter 11 Nucleic Acid Structure 5 Chapter 12 Nucleotide Metabolism 5 Chapter 13 Replication 5 Chapter 14 Transcription 5 Chapter 15 Translation 5 Chapter 16 Gene Expression Regulation 5 Protein Assay 6 Enzyme Kinetics 6 Electrophoresis 6 Enzyme Assay 6 Transamination(PC) 6 Nucleic Acid Isolation and Identification 6 Total 126 90 36 4、Specific Requirements for Each Chapter and Section

Chapter 1 the Structure and Function of Protein [Teaching objective and requirement 1.the physiological function and classification of protein; 2.the structure of natural amino acids and the composition of protein,the structural level of protein, the relationship between structure and function of protein: 3.the principle and application of techniques used to research protein [Teaching contents] 1.composition of protein:composition of elements and building-blocks,the structure of natural amino acid,characteristics and classification of side chains of natural amino acids: 2.the main category of protein,based on their shapes, 3.The structural levels of protein and the interaction to maintain its structure:primary structure, peptide bond and polypeptide chain,the amino acid sequence of polypeptide chain;secondary structure and its classification;tertiary structure and spacial structure;quaternary structure and subunit.Covalent and noncovalent interaction to maintain structure of protein.Protein conformation: 4.the relationship between protein structure and its function:conformation determines function while primary structure together with environmental factors determines conformation; 5.the physical and chemic properties of protein macromolecular property,ultraviolet absorbance,amphoteric ionization and isoelectric point,denaturation,renaturation,allosterism and precipitation,colour development; 6.familiar to the basic way about protein separation and purification and its corresponding structure and character foundation. [Teaching key points and difficulties] 1.the concept and classification of natural amino acid,property of its side chain (R group); 2.structural levels of protein and the interaction to maintain its structure,distinguish the tertiary and quaternary structure; 3.the effects of primary structure and environmental factor on the structure and function of protein; 4.distinguish denaturation,allosterism and precipitation Chapter2 Enzyme [Teaching objective and requirement 1.enzyme and ribozyme; 2.the properties of enzyme catalysis,kinetics and effective factors; 3.molecular composition,active center,essential groups,cofactors,isoenzyme and zymogen; 4.enzymatic inhibitor:concept and classification;the changing of enzymatic kinetic constant caused by different inhibitors; 5.the classification and nomenclation of enzyme [Teaching contents]
2 Chapter 1 the Structure and Function of Protein [Teaching objective and requirement] 1. the physiological function and classification of protein; 2. the structure of natural amino acids and the composition of protein, the structural level of protein, the relationship between structure and function of protein; 3. the principle and application of techniques used to research protein [Teaching contents] 1. composition of protein: composition of elements and building-blocks; the structure of natural amino acid,characteristics and classification of side chains of natural amino acids; 2. the main category of protein, based on their shapes; 3. The structural levels of protein and the interaction to maintain its structure: primary structure, peptide bond and polypeptide chain,the amino acid sequence of polypeptide chain; secondary structure and its classification; tertiary structure and spacial structure; quaternary structure and subunit. Covalent and noncovalent interaction to maintain structure of protein. Protein conformation; 4. the relationship between protein structure and its function: conformation determines function while primary structure together with environmental factors determines conformation; 5. the physical and chemic properties of protein : macromolecular property, ultraviolet absorbance, amphoteric ionization and isoelectric point, denaturation, renaturation , allosterism and precipitation, colour development; 6. familiar to the basic way about protein separation and purification and its corresponding structure and character foundation. [Teaching key points and difficulties] 1. the concept and classification of natural amino acid, property of its side chain (R group); 2. structural levels of protein and the interaction to maintain its structure, distinguish the tertiary and quaternary structure; 3. the effects of primary structure and environmental factor on the structure and function of protein; 4. distinguish denaturation, allosterism and precipitation Chapter 2 Enzyme [Teaching objective and requirement ] 1. enzyme and ribozyme; 2. the properties of enzyme catalysis, kinetics and effective factors; 3. molecular composition, active center, essential groups, cofactors, isoenzyme and zymogen; 4. enzymatic inhibitor: concept and classification; the changing of enzymatic kinetic constant caused by different inhibitors; 5. the classification and nomenclation of enzyme [Teaching contents]

1.the concept of enzyme and robozyme; 2.the catalytic properties of enzyme,the high efficiency of enzyme action,the specificity of enzyme and its classification,the sensitivity of enzymatic activity to circumstance factors: 3.the molecular composition and the active center of enzyme,distinguish cofactor,coenzyme and prosthetic group; 4.enzyme-substrate complex and general mechanism of enzyme action; 5.factors affecting enzyme reaction rate:enzyme concentration,substance concentration,the Michaelis-Menten rate equationon single substrate,the kinetic constants of enzyme reaction;the effect of pH and temperature on reactive rate; 6.inhibition on enzyme,the difference between inhibition and protein denaturation;irreversible inhibition and reversible inhibition;typical irreversible inhibitor,the characteristic change of kinetic parameters of enzyme reaction caused by different reversible inhibitor: 7.activator of enzyme and its example; 8.isoenzyme,concepts and example,LDH,CK: 9.zymogen and its activation:the mechanism of its activation,typical changes during its activation, examples; 10.regulation on enzymatic activity:allosteric regulation,covalent modification and the regulation ofen☑ymatic content, the application of enzyme in medicine:analysis and diagnosis,processing,drug development, evolution of species [Teaching key points and difficulties] 1.the properties of enzymatic activity and classification of enzyme specificity; 2.composition of active enzyme,distinguish coenzyme and prosthetic group; 3.the mechanism of zymogen activation:structure determine function; 4.the regulation of enzyme activity 5.the relationship between conformation and function Chapter3 Vitamin and Coenzyme [Teaching objective and requirement] 1.be familiar to the concept and difference of vitamin and nutriment; 2.understand the action and mechanism of primary vitamin:transformed into cofactor of enzyme [Teaching contents] 1.vitamin and its physiological action,the difference of vitamin and nutriment; 2.the active form of lipid-soluble vitamin present in vivo and mechanism of its action; 3.water-soluble vitamins and corresponding coenzymes,physiological function and mechanism, role in a metabolic pathway; 4.B group vitamin: Vit B1,Vit B2,Vit B6,Vit B5(pantothenic acid )Vit H(biotin),Vit pp,Vit B12,Vit B9(folacin) lipoic acid: 5.primary physiological action of vitamin C [Teaching key points and difficulties] 1.the metabolic relationship between vitamin and cofactor of enzyme; 2.distinguish coenzyme and prosthetic group,using terminology of enzymeology
3 1. the concept of enzyme and robozyme; 2. the catalytic properties of enzyme ,the high efficiency of enzyme action, the specificity of enzyme and its classification ,the sensitivity of enzymatic activity to circumstance factors; 3. the molecular composition and the active center of enzyme, distinguish cofactor, coenzyme and prosthetic group; 4. enzyme-substrate complex and general mechanism of enzyme action; 5. factors affecting enzyme reaction rate: enzyme concentration, substance concentration, the Michaelis-Menten rate equationon single substrate, the kinetic constants of enzyme reaction; the effect of pH and temperature on reactive rate; 6. inhibition on enzyme, the difference between inhibition and protein denaturation; irreversible inhibition and reversible inhibition; typical irreversible inhibitor, the characteristic change of kinetic parameters of enzyme reaction caused by different reversible inhibitor; 7. activator of enzyme and its example; 8. isoenzyme, concepts and example, LDH, CK; 9. zymogen and its activation: the mechanism of its activation, typical changes during its activation, examples; 10. regulation on enzymatic activity: allosteric regulation, covalent modification and the regulation of enzymatic content; the application of enzyme in medicine: analysis and diagnosis, processing, drug development, evolution of species [Teaching key points and difficulties] 1. the properties of enzymatic activity and classification of enzyme specificity; 2. composition of active enzyme, distinguish coenzyme and prosthetic group; 3. the mechanism of zymogen activation: structure determine function; 4. the regulation of enzyme activity 5. the relationship between conformation and function Chapter 3 Vitamin and Coenzyme [Teaching objective and requirement] 1. be familiar to the concept and difference of vitamin and nutriment; 2. understand the action and mechanism of primary vitamin :transformed into cofactor of enzyme [Teaching contents] 1. vitamin and its physiological action, the difference of vitamin and nutriment; 2. the active form of lipid-soluble vitamin present in vivo and mechanism of its action; 3. water-soluble vitamins and corresponding coenzymes, physiological function and mechanism, role in a metabolic pathway; 4. B group vitamin: Vit B1, Vit B2, Vit B6, Vit B5(pantothenic acid), Vit H(biotin), Vit pp, Vit B12, Vit B9(folacin) lipoic acid; 5. primary physiological action of vitamin C [Teaching key points and difficulties] 1. the metabolic relationship between vitamin and cofactor of enzyme; 2. distinguish coenzyme and prosthetic group, using terminology of enzymeology

Chapter4 Biological Oxidation [Teaching Objective and Requirement] 1.Master the concept of biological oxidation and Mitochondrion oxidation system,be familiar with other oxidized systems. 2.Master the composition and arrangement of respiratory chian,the concept of Oxidative phosphorylation and P/O ratio;be familiar with the influence factors of oxidative phosphorylation,the concept of high-energy compound. 3.Master the biological function of glycerophosphate shuttle and malate-asparate shuttle. 4.Familiar the function of monooxygenase,dioxygenase,peroxisome,catalase,perosidase, and superoxide dismutase;comprehend the differences between dehydrogenase the aerobic dehydrogenase and the oxydase [Teaching contents 1.Mitochondrion oxidation system:complex of respiratory chian;the composition, arrangement and function of two respiratory chians;oxidiative phosphorylation and substrate level phosphorylation ATP and energy metabolism. 2.Other oxidized systems:monooxygenase,peroxisome,superoxide dismutase(SOD). [Teaching key points and difficulties] Key Mitochondrion oxidation system Difficulties:Oxidation and phosphorylation Chapter 5 Carbohydrate Metabolism [Teaching objective and requirement 1.Master the concept,process,key enzyme and physiological role of glycolysis and aerobic oxidation. 2.Master the concept of krebs cycle and Comprehend the regulation of krebs cycle. 3.Master the concept and physiological role of pentose phosphate pathway.Familiar the process of NADPH and 5-phosphoribose production. 4.Master the synthesis of glycogen,degradation of glycogen and its regulation (glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen synthase are the targets for regulation,mainly by chemical modification).Master the cause of glycogen in muscle cannot reduce to glucose. 5.Master the concept of glucogenesis,three irreversibly metabolic pathways,Lactate cycle and its physiological role.Comprehend the major process of glucogenesis with materials such as pyruvate, lactate,glycerol and some special amino acids.Comprehend the physiological role of glucogenesis. 6.Master the concept of blood glucose,source and fate of blood glucose.Comprehend the blood glucose regulation include hormone and organ regulation.Familiar the concept of glucose tolerance. [Teaching contents] 1.The major function of carbohydrate,the digestion and absorption of carbohydrate 2.glycolysis;
4 Chapter 4 Biological Oxidation [Teaching Objective and Requirement] 1. Master the concept of biological oxidation and Mitochondrion oxidation system, be familiar with other oxidized systems. 2.Master the composition and arrangement of respiratory chian, the concept of Oxidative phosphorylation and P/O ratio; be familiar with the influence factors of oxidative phosphorylation, the concept of high-energy compound. 3. Master the biological function of glycerophosphate shuttle and malate-asparate shuttle. 4.Familiar the function of monooxygenase, dioxygenase , peroxisome, catalase, perosidase, and superoxide dismutase; comprehend the differences between dehydrogenase ,the aerobic dehydrogenase and the oxydase. [Teaching contents] 1.Mitochondrion oxidation system: complex of respiratory chian; the composition , arrangement and function of two respiratory chians; oxidiative phosphorylation and substrate level phosphorylation ; ATP and energy metabolism. 2.Other oxidized systems: monooxygenase, peroxisome, superoxide dismutase(SOD). [Teaching key points and difficulties] Key : Mitochondrion oxidation system Difficulties : Oxidation and phosphorylation Chapter 5 CarbohydrateMetabolism [Teaching objective and requirement] 1. Master the concept, process, key enzyme and physiological role of glycolysis and aerobic oxidation. 2. Master the concept of krebs cycle and Comprehend the regulation of krebs cycle. 3. Master the concept and physiological role of pentose phosphate pathway. Familiar the process of NADPH and 5-phosphoribose production. 4. Master the synthesis of glycogen, degradation of glycogen and its regulation (glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen synthase are the targets for regulation, mainly by chemical modification). Master the cause of glycogen in muscle cannot reduce to glucose. 5. Master the concept of glucogenesis, three irreversibly metabolic pathways, Lactate cycle and its physiological role. Comprehend the major process of glucogenesis with materials such as pyruvate, lactate, glycerol and some special amino acids. Comprehend the physiological role of glucogenesis. 6. Master the concept of blood glucose, source and fate of blood glucose. Comprehend the blood glucose regulation include hormone and organ regulation. Familiar the concept of glucose tolerance. [Teaching contents] 1. The major function of carbohydrate, the digestion and absorption of carbohydrate 2. glycolysis;

3.aerobic oxidation, 4.pentose phosphate pathway; 5.synthesis and degradation of glycogen; 6.glucogenesis: 7.blood glucose and regulation. [Teaching key points and difficulties] Key:Glycolysis,aerobic oxidation,pentose phosphate pathway and glucogenesis. Difficulty:The process of glycolysis and aerobic oxidation. Chapter 6 Lipid Metabolism [Teaching Objective and Requirement] 1.Comprehend the digestion,absorption,and function of Lipids 2.Master the concept and key enzymes of fatty acid breakdown:comprehend the type, distribution and function of lipase. 3.Master the activation and transport into mitochondria of the fatty acid;Master the spot, pathway and energy yield of the beta-oxidation pathway;Master the production and use of ketone bodies. 4.Master the fatty acids transport into the cytosol,the pathway of synthesis and the formation of double bonds. 5.Familiar the pathway and raw materials of prostaglandin(PG),thromboxane A2(TXA2) and lenkotriene(LT). 6.Familiar the function and biosynthesis of cholesterol comprehend rrgulation of cholesterol biosynthesis;Master the excretory form of cholesterol,such as bile salts and vitamin D. 7.Master the composition,distribution and function of lipoproteins;comprehend the metabolism of VLDL,LDL,HDL and CM. 8.Familiar the metabolism of glycerophosphatide. [Teaching contents] 1.Structures and roles of fatty acids (teaches generally) 2.fatty acid breakdown (key teaches) 3.bata-Oxidation pathway (key teaches) 4.the production and use of ketone bodies (key teaches) 4.Fatty sunthesis(teaches generally) 5.metabolism of triacyglycerols (teaches generally) 6.cholesterol metabolism (key teaches) 7.glycerophosphatide metabolism(teaches generally) 8.lipoproteins metabolism (teaches generally) [Teaching key points and difficulties Key:bata-Oxidation,the production and use of ketone bodies,phosphatide metabolism, Difficulty:cholesterol metabolism,pathyway of fatty acid breakdown,cholesterol metabolism Chapter 7 Amino Acids Metabolism
5 3. aerobic oxidation; 4. pentose phosphate pathway; 5. synthesis and degradation of glycogen; 6. glucogenesis; 7. blood glucose and regulation. [Teaching key points and difficulties] Key: Glycolysis, aerobic oxidation, pentose phosphate pathway and glucogenesis. Difficulty: The process of glycolysis and aerobic oxidation. Chapter 6 Lipid Metabolism [Teaching Objective and Requirement] 1.Comprehend the digestion ,absorption,and function of Lipids. 2. Master the concept and key enzymes of fatty acid breakdown;comprehend the type, distribution and function of lipase. 3. Master the activation and transport into mitochondria of the fatty acid; Master the spot, pathway and energy yield of the beta - oxidation pathway; Master the production and use of ketone bodies. 4. Master the fatty acids transport into the cytosol , the pathway of synthesis and the formation of double bonds. 5. Familiar the pathway and raw materials of prostaglandin (PG), thromboxane A2(TXA2) and lenkotriene(LT) . 6. Familiar the function and biosynthesis of cholesterol ; comprehend rrgulation of cholesterol biosynthesis; Master the excretory form of cholesterol,such as bile salts and vitamin D. 7. Master the composition, distribution and function of lipoproteins; comprehend the metabolism of VLDL, LDL, HDL and CM. 8. Familiar the metabolism of glycerophosphatide. [Teaching contents] 1. Structures and roles of fatty acids (teaches generally) 2.fatty acid breakdown (key teaches) 3. bata-Oxidation pathway (key teaches) 4. the production and use of ketone bodies (key teaches) 4. Fatty sunthesis (teaches generally) 5. metabolism of triacyglycerols (teaches generally) 6.cholesterol metabolism (key teaches) 7. glycerophosphatide metabolism (teaches generally) 8. lipoproteins metabolism (teaches generally) [Teaching key points and difficulties] Key: bata-Oxidation, the production and use of ketone bodies, phosphatide metabolism, Difficulty: cholesterol metabolism, pathyway of fatty acid breakdown, cholesterol metabolism Chapter 7 Amino AcidsMetabolism

[Teaching objective and requirement] 1.Being familiar with the functions of proteins.Knowing essential amino acids well. 2.Having a good knowledge of nitrogen balance,protein requirements and complementary effect of dietary proteins. 3.Understanding the concept of protein putrefaction.Knowing the nutritional benefits and toxicities of putrefaction products 4.Grasping the general pathway of amino acid catabolism.Understanding amino acid metabolic pool.Being familiar with the way of amino acids deamination:including oxidative deamination,transamination and coupling of transamination with glutamate dehydrogenase. Knowing the metabolism of the carbon skeleton of amino acids. 5.Knowing the concept of glucogenic amino acids,ketogenic amino acids and both ketogenic and glucogenic amino acids. 6.Having a good knowledge of the source of ammonia in blood,the metabolic pathway of ammonia,and the transport of ammonia in blood(alanine-glucose cycle.transporting ammonia by glutamine) 7.Being familiar with the ornithine cycle(or urea cycle)the reactions of urea formation the key enzymes,and the regulation in urea biosynthesis.Konwing the concept of hyperammonemia and the mechanism of the toxic effects of high levels of ammonia. 8.Mastering the knowledge of decarboxylation of amino acids and the important products of decarboxylation. 9.Having a good knowledge of the metabolism of one carbon units:the conception and the sorts of one carbon units,the carrier of one carbon units(tetrahydrofolate,FH4). 10.Mastering the pathway of methionine cycle and its physiologic function.Understanding the connection of methionine cycle and one carbon units,and the role of vitamin B12 in it 11.Knowing the syntheses of creatine and creatine phosphate,and the formation of the active sulfate group(PAPS) 12.Metabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine :the formation of tyrosine from phenyalanine,phenylalaine hyfroxylase and its coenzyme,the products transformed by tyrosine(catecholamine,melanin,thyroid hormone);the causes of albinism and phenylketonuria. Teaching key points】 Nitrogen balance;essential amino acid;oxidative deamination,transamination,coupling of transamination with glutamate dehydrogenase;metabolism of a-keto acids:the metabolic integration of amino acids,glucose and lipids;the source and metabolic pathway of ammonia. The site,reaction and key enzyme of urea synthesis;the regulation and physiologic function of urea biosynthesis,hyperammonemia and the toxic effects of high levels of ammonia. Decarboxylation of amino acids,the formation and function of amine and polyamine;the conception,sorts,carrier,production and function of one carbon units;the connection between methionine cycle and one carbon units,and the effect of vitamin B12 in it. Teaching difficulties 1.Deamination of amino acids 2.The metabolic pathway of ornithine cycle and its function 3.The formation of polyamine and its important role in cell proliferation and tissue growgh 4.Methionine cycle and methylation 5.Metabolism of aromatic amino acids 6
6 [Teaching objective and requirement] 1. Being familiar with the functions of proteins. Knowing essential amino acids well. 2. Having a good knowledge of nitrogen balance,protein requirements and complementary effect of dietary proteins. 3. Understanding the concept of protein putrefaction .Knowing the nutritional benefits and toxicities of putrefaction products. 4. Grasping the general pathway of amino acid catabolism. Understanding amino acid metabolic pool. Being familiar with the way of amino acids deamination:including oxidative deamination,transamination and coupling of transamination with glutamate dehydrogenase . Knowing the metabolism of the carbon skeleton of amino acids. 5. Knowing the concept of glucogenic amino acids,ketogenic amino acids and both ketogenic and glucogenic amino acids. 6. Having a good knowledge of the source of ammonia in blood,the metabolic pathway of ammonia,and the transport of ammonia in blood(alanine-glucose cycle. transporting ammonia by glutamine) 7. Being familiar with the ornithine cycle(or urea cycle),the reactions of urea formation,the key enzymes,and the regulation in urea biosynthesis.Konwing the concept of hyperammonemia and the mechanism of the toxic effects of high levels of ammonia. 8. Mastering the knowledge of decarboxylation of amino acids and the important products of decarboxylation. 9. Having a good knowledge of the metabolism of one carbon units:the conception and the sorts of one carbon units;the carrier of one carbon units(tetrahydrofolate,FH4). 10. Mastering the pathway of methionine cycle and its physiologic function.Understanding the connection of methionine cycle and one carbon units,and the role of vitamin B12 in it. 11. Knowing the syntheses of creatine and creatine phosphate,and the formation of the active sulfate group(PAPS) 12. Metabolism of phenylalanine and tyrosine :the formation of tyrosine from phenyalanine,phenylalaine hyfroxylase and its coenzyme,the products transformed by tyrosine(catecholamine,melanin,thyroid hormone);the causes of albinism and phenylketonuria. [Teaching key points ] Nitrogen balance; essential amino acid; oxidative deamination, transamination, coupling of transamination with glutamate dehydrogenase; metabolism of α-keto acids; the metabolic integration of amino acids,glucose and lipids; the source and metabolic pathway of ammonia. The site,reaction and key enzyme of urea synthesis; the regulation and physiologic function of urea biosynthesis; hyperammonemia and the toxic effects of high levels of ammonia. Decarboxylation of amino acids; the formation and function of amine and polyamine; the conception , sorts,carrier, production and function of one carbon units; the connection between methionine cycle and one carbon units,and the effect of vitamin B12 in it. [Teaching difficulties] 1.Deamination of amino acids 2.The metabolic pathway of ornithine cycle and its function 3.The formation of polyamine and its important role in cell proliferation and tissue growgh 4.Methionine cycle and methylation 5.Metabolism of aromatic amino acids

Chapter8 Metabolic Connection Regulation [Teaching objective and requirement 1.To familiar with the concepts on metabolism regulation 2.To master the concepts of multi-enzyme system and that of limiting velocity enzymes. Fast-regulation of enzyme,allosteric regulation,the meanings of allosteric regulation.The concepts and meanings of chemical modification.The concepts of Protein kinase.The functions of protein kinase A and C. 3.To familiar with local distribution of enzymes in the body. [Teaching methods] Teaching is major,along with discussion and self-study,pay attention to sufficient application of diagrammatical presentation and model at the same time.Pay attention to make a comparison and find the distinction between eukaryotic and prokaryotic gene regulatory rule Chapter9 Cellular Signal Transduction [Teaching objective and requirement] 1.To master transmembrane-signal transduction is the major way of signal transfer among the cells. the characters of receptors.the transfer routes of signals. 2.To familiar with major intercellular and intracellular informatic substances.The classes general structure and functions of receptors. 3.To know inter-connection among different ways. [Teaching contents] 1.Ligands,receptors and the effects one another 2.The routes of intercellular signal transduction.Receptor-cAMP-protein kinase route and Ca'-calmodulin one Receptor-protein kinase C route,cGMP-protein kinase G route, receptor-tyrosine-protein kinase route. [Teaching key points and difficulties] The teaching importance of the chapter is Transmembrane-singal transduction and relations between the biofunctions of cells.The difficulties are the routes of cell-signal-transduction. Chapter 10 Hepatic Biochemistry [Teaching objective and requirementl 1.To know the functions of hepatic in metabolism of three nutrients hormones and that of vitamines 2.To master the concepts about non-nutrients and about biotransformation,the characters of biotransformation,the types of biotransformatic reaction including I phase reaction and II phase reaction 3.To familiar with representative examples of each biotransformatic reactions including oxidation(the function of the amine oxidase,hydrogenase and oxygenase)deoxidization. hydrolyzation;II phase reaction(combined with sulfate acids,glucuronic acids,acetyls),and the >
7 Chapter 8 Metabolic Connection & Regulation [Teaching objective and requirement] 1.To familiar with the concepts on metabolism regulation 2.To master the concepts of multi-enzyme system and that of limiting velocity enzymes. Fast-regulation of enzyme, allosteric regulation, the meanings of allosteric regulation. The concepts and meanings of chemical modification. The concepts of Protein kinase. The functions of protein kinase A and C. 3.To familiar with local distribution of enzymes in the body. [Teaching methods] Teaching is major, along with discussion and self-study, pay attention to sufficient application of diagrammatical presentation and model at the same time. Pay attention to make a comparison and find the distinction between eukaryotic and prokaryotic gene regulatory rule. Chapter 9 Cellular Signal Transduction [Teaching objective and requirement] 1.To master transmembrane-signal transduction is the major way of signal transfer among the cells、 the characters of receptors、the transfer routes of signals . 2.To familiar with major intercellular and intracellular informatic substances .The classes、general structure and functions of receptors. 3.To know inter-connection among different ways. [Teaching contents] 1.Ligands、receptors and the effects one another 2.The routes of intercellular signal transduction. Receptor-cAMP-protein kinase route and Ca+ -calmodulin one Receptor-protein kinase C route, cGMP-protein kinase G route, receptor-tyrosine-protein kinase route. [Teaching key points and difficulties] The teaching importance of the chapter is Transmembrane-singal transduction and relations between the biofunctions of cells. The difficulties are the routes of cell-signal-transduction. Chapter 10 Hepatic Biochemistry [Teaching objective and requirement] 1.To know the functions of hepatic in metabolism of three nutrients、hormones and that of vitamines 2.To master the concepts about non-nutrients and about biotransformation, the characters of biotransformation, the types of biotransformatic reaction includingⅠphase reaction andⅡphase reaction 3.To familiar with representative examples of each biotransformatic reactions including oxidation(the function of the amine oxidase, hydrogenase and oxygenase)、deoxidization、 hydrolyzation; Ⅱphase reaction(combined with sulfate acids, glucuronic acids, acetyls), and the

physiological meanings of these reactions 4.To master the concepts on primary,sencondary,conjugated,free bile acids,the structure of these all bile acids and raw material which turn into them,their producing location in the cells,tissues or organs 5.To familiar with the physiological meanings of bile acids.The concepts and meaings about bile acids'“enterrohepatic circulation” 6.To familiar with the concepts of bilirubin,it's source,the physical and chimical nature of them and last,the production and transportation of it. 7.To master the concepts of conjugated bilirubin and their change in intestines.Bilinogen enterohepatic circulation.The source of bilinogens and bilins in urine. 8.To familiar with the difference between free bilirubins and conjugated ones.To know the relations between bilirubin and jaundice. [Teaching contents] 1.The functions of liver in metabolism of sugar,lipids,proteins,vitamines and hormones. 2.Hepatic biotransformation on non-nutrients. 3.The metabolism of bile acids 4.The metabolism of bilins [Teaching key points and difficulties] 1.How many important transformatic ways and related-enzymes are there in body? 2.The major differences between bile acids and bilins. Chapter 11 The structure and property of nucleic acid [Teaching Objective and Requirementl 1.Master the primary structure of nucleic acid,main points of DNA double coiled spiral structure;be familiar with the abbreviation express of nucleotide chain;comprehend triplex DNA and tertiary structure of DNA 2.Master the concepts of gene,intron and extron;comprehend construction features of eukaryote genome DNA. 3.Master the concepts of DNA degeneration,renaturation and Tm;Master the ultraviolet absorptive character of nucleic acid and its application;comprehend general characters of nucleic acid,concept and principle of molecular hybridization. 4.Master the structural feature of eukaryotic mature mRNA;be familiar with the relationship between inverse L-type tertiary structure of tRNA and conveying amino acids,Comprehend the kinds and function of RNA in biotic cell,the central dogma of genetic information transmission. [Teaching contents] 1.Primary structure of nucleic acid and abbreviation express of nucleotide chain(teaching points). 2.Secondary structure of DNA (teaching points). 3.Tertiary structure of DNA. 4.Construction features of eukaryotic DNA. 5.Several important physico-chemical property of nucleic acid(teaching points). 6.Structure and function of RNA. 7.Central dogma and development of genetic information transmission
8 physiological meanings of these reactions 4.To master the concepts on primary, sencondary, conjugated, free bile acids, the structure of these all bile acids and raw material which turn into them, their producing location in the cells, tissues or organs. 5.To familiar with the physiological meanings of bile acids. The concepts and meaings about bile acids’ “enterrohepatic circulation”. 6.To familiar with the concepts of bilirubin, it’s source, the physical and chimical nature of them and last, the production and transportation of it. 7.To master the concepts of conjugated bilirubin and their change in intestines. Bilinogen enterohepatic circulation. The source of bilinogens and bilins in urine. 8.To familiar with the difference between free bilirubins and conjugated ones. To know the relations between bilirubin and jaundice. [Teaching contents] 1.The functions of liver in metabolism of sugar, lipids, proteins, vitamines and hormones. 2.Hepatic biotransformation on non-nutrients. 3.The metabolism of bile acids 4.The metabolism of bilins [Teaching key points and difficulties] 1.How many important transformatic ways and related-enzymes are there in body? 2.The major differences between bile acids and bilins. Chapter 11 The structure and property of nucleic acid [Teaching Objective and Requirement] 1.Master the primary structure of nucleic acid, main points of DNA double coiled spiral structure; be familiar with the abbreviation express of nucleotide chain; comprehend triplex DNA and tertiary structure of DNA. 2.Master the concepts of gene, intron and extron; comprehend construction features of eukaryote genome DNA. 3.Master the concepts of DNA degeneration, renaturation and Tm; Master the ultraviolet absorptive character of nucleic acid and its application; comprehend general characters of nucleic acid, concept and principle of molecular hybridization. 4.Master the structural feature of eukaryotic mature mRNA; be familiar with the relationship between inverse L—type tertiary structure of tRNA and conveying amino acids; Comprehend the kinds and function of RNA in biotic cell, the central dogma of genetic information transmission. [Teaching contents] 1.Primary structure of nucleic acid and abbreviation express of nucleotide chain (teaching points). 2.Secondary structure of DNA (teaching points). 3.Tertiary structure of DNA. 4.Construction features of eukaryotic DNA. 5.Several important physico-chemical property of nucleic acid (teaching points). 6.Structure and function of RNA. 7.Central dogma and development of genetic information transmission

[Teaching key points and difficulties] Primary structure of nucleic acid,main points of DNA double coiled spiral structure,ultraviolet absorptive character of nucleic acid and its application are the difficult points of this chapter. Thinking questions: 1.How to make an ultraviolet quantitative concentration of DNA and RNA?What's the key issue that we must pay more attention? 2.Describe the kinds and function of RNA in biotic cell. Chapter 12 Nucleotide Metabolism [Teaching Objective and Requirement] 1.Master the structure and biological function of 5 classes of main nucleotide;be familiar with the important nucleotides:cAMP/cGMP,ADP/ATP;comprehend minor nucleotides 2.Master the material of nucleotide de nove synthesis and synthetic procedure of deoxynucleotide (disoxidation of nucleoside diphosphate level);be familiar with the concept and physiological significance of nucleotide salvage synthesis,the product of purine nucleotide catabolism-the relationship between uric acid and gout;Comprehend the process and regulation of nucleotide de nove synthesis,the process of nucleotide catabolism. [Teaching contents] 1.The structure of basic group ribonucleoside and nucleotide(teaching points). 2.Biological function of nucleotide (teaching points). 3.The similarities and differences of nucleotide composition between DNA and RNA 4.The concepts of minor nucleotide and types of familiar minor nucleotide. 5.The concept material and process of purine nucleotide de nove synthesis(teaching points). 6.The salvage synthesis and physiological significance of Purine nucleotide. 7.Purine nucleotide catabolism,the relationship between uric acid and gout,mechanism of action of gout treatment using allopurinol(teaching points). 8.The concept material and process of pyrimidine nucleotide 9.The salvage synthesis and physiological significance of Pyrimidine nucleotide. 10.The catabolism of Pyrimidine nucleotide. 11.The synthesis of NDP and NTP. 12.The synthetic procedure of deoxynucleotide (teaching points). [Teaching key points and difficulties] Structure and biological function of 5 classes of main nucleotide are the key points of this chapter; difference between nucleotide de nove synthesis and salvage synthesis is the difficult point of this chapter. Chapter 13 Biosynthesis of DNA(replication) Teaching Objective and Requirement 1.Master the concept of DNA semiconservation replication,the template,material,enzymes and other factors that participated in DNA replication;be familiar with the elementary process of DNA replication. 2.Master the concept and key reaction process of reverse transcription
9 [Teaching key points and difficulties] Primary structure of nucleic acid, main points of DNA double coiled spiral structure, ultraviolet absorptive character of nucleic acid and its application are the difficult points of this chapter. Thinking questions: 1.How to make an ultraviolet quantitative concentration of DNA and RNA? What’s the key issue that we must pay more attention? 2.Describe the kinds and function of RNA in biotic cell. Chapter 12 Nucleotide Metabolism [Teaching Objective and Requirement] 1. Master the structure and biological function of 5 classes of main nucleotide; be familiar with the important nucleotides: cAMP/cGMP, ADP/ATP; comprehend minor nucleotides 2. Master the material of nucleotide de nove synthesis and synthetic procedure of deoxynucleotide (disoxidation of nucleoside diphosphate level); be familiar with the concept and physiological significance of nucleotide salvage synthesis, the product of purine nucleotide catabolism—the relationship between uric acid and gout; Comprehend the process and regulation of nucleotide de nove synthesis, the process of nucleotide catabolism. [Teaching contents] 1.The structure of basic group、ribonucleoside and nucleotide (teaching points). 2.Biological function of nucleotide (teaching points). 3.The similarities and differences of nucleotide composition between DNA and RNA. 4.The concepts of minor nucleotide and types of familiar minor nucleotide. 5.The concept 、material and process of purine nucleotide de nove synthesis (teaching points). 6.The salvage synthesis and physiological significance of Purine nucleotide. 7.Purine nucleotide catabolism, the relationship between uric acid and gout, mechanism of action of gout treatment using allopurinol (teaching points). 8.The concept 、material and process of pyrimidine nucleotide. 9.The salvage synthesis and physiological significance of Pyrimidine nucleotide. 10.The catabolism of Pyrimidine nucleotide. 11. The synthesis of NDP and NTP. 12.The synthetic procedure of deoxynucleotide (teaching points). [Teaching key points and difficulties] Structure and biological function of 5 classes of main nucleotide are the key points of this chapter; difference between nucleotide de nove synthesis and salvage synthesis is the difficult point of this chapter. Chapter 13 Biosynthesis of DNA (replication) [Teaching Objective and Requirement] 1.Master the concept of DNA semiconservation replication, the template, material, enzymes and other factors that participated in DNA replication; be familiar with the elementary process of DNA replication. 2.Master the concept and key reaction process of reverse transcription

Master the concept of DNA mutation;be familiar with concepts and types of DNA damage and repair;comprehend the elementary process of DNA damage and repair.Comprehend PCR technology,rudiment and application of nucleic acid sequence analytical technique. [Teaching contents] 1.DNA replication 1.1Semiconservation replication and its experimental evidence 1.2 Enzyme and protein that participated in DNA replication 1.3 Process of DNA replication 2.Concept and type of DNA mutate.DNA damage(mutate)and repair. 3.Concept and elementary process of reverse transcription 4 Special subject-polymerase chain reaction(PCR)and nucleic acid sequence analysis [Teaching key points and difficulties] The concept,reaction system and process of replication are the key points of this chapter.The reaction system and process of replication are the difficult points of this chapter. Chapter 14 Transcription [Teaching Objective and Requirement] Master the concept and reaction system of transcription (template,material,enzymes,other correlation factors and its chemical reaction);be familiar with subunits and core enzyme of E.coli RNA polymerase and the function of initiation factors.Be familiar with the classification and function of eukaryotic RNA polymerase.Be familiar with the concept and function of promoter; comprehend the process of transcription.Be familiar with the modification of transcript,concept of intron,extron and ribozyme.Comprehend mode of action of ribozyme. [Teaching contents] 1.Concept and reaction system of transcription 2.Process of transcription 3.Elaboration and modification after transcription [Teaching key points and difficulties] The concept,reaction system and process of transcription are the teaching key points of this chapter. The reaction system and process of transcription are the teaching difficulties of this chapter Chapter 15 Translation-Biosynthesis of protein [Teaching Objective and Requirement] Be familiar with every moity and correlated function of protein biosynthesis system(RNA, amino acids,correlated enzymes,protein factors,dynamophore and so on).Master construction features of mRNA,tRNA and rRNA and its important function in protein synthesis.Be familiar with the process of protein biosynthesis,concepts of ribosome cycle and polyribosome. Comprehend the elaboration and modification ways after polypeptide chain synthesis.Comprehend 10
10 Master the concept of DNA mutation; be familiar with concepts and types of DNA damage and repair; comprehend the elementary process of DNA damage and repair. Comprehend PCR technology, rudiment and application of nucleic acid sequence analytical technique. [Teaching contents] 1.DNA replication 1.1Semiconservation replication and its experimental evidence 1.2 Enzyme and protein that participated in DNA replication 1.3 Process of DNA replication 2.Concept and type of DNA mutate. DNA damage (mutate) and repair. 3.Concept and elementary process of reverse transcription 4 Special subject—polymerase chain reaction(PCR) and nucleic acid sequence analysis [Teaching key points and difficulties] The concept, reaction system and process of replication are the key points of this chapter. The reaction system and process of replication are the difficult points of this chapter. Chapter 14 Transcription [Teaching Objective and Requirement] Master the concept and reaction system of transcription (template, material, enzymes, other correlation factors and its chemical reaction); be familiar with subunits and core enzyme of E. coli RNA polymerase and the function of initiation factors. Be familiar with the classification and function of eukaryotic RNA polymerase. Be familiar with the concept and function of promoter; comprehend the process of transcription. Be familiar with the modification of transcript, concept of intron, extron and ribozyme. Comprehend mode of action of ribozyme. [Teaching contents] 1.Concept and reaction system of transcription 2.Process of transcription 3.Elaboration and modification after transcription [Teaching key points and difficulties] The concept, reaction system and process of transcription are the teaching key points of this chapter. The reaction system and process of transcription are the teaching difficulties of this chapter. Chapter 15 Translation—Biosynthesis of protein [Teaching Objective and Requirement] Be familiar with every moity and correlated function of protein biosynthesis system (RNA, amino acids, correlated enzymes, protein factors, dynamophore and so on). Master construction features of mRNA、tRNA and rRNA and its important function in protein synthesis. Be familiar with the process of protein biosynthesis, concepts of ribosome cycle and polyribosome. Comprehend the elaboration and modification ways after polypeptide chain synthesis. Comprehend
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 重庆医科大学:《生物化学》课程教学大纲(供五年制临床医学、预防专业用).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《生物化学》课程教学大纲(供七年制临床医学专业用).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《生物化学》课程教学大纲(生物化学实验大纲).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《生物化学》课程各章作业习题集(选择判断题含答案).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《生物化学》课程教学实验指导书(生物化学与分子生物学).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《生物化学》课程教学授课教案(负责人:王继红).doc
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第九章 羧酸及其衍生物和取代酸 9.1 羧酸.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第九章 羧酸及其衍生物和取代酸 9.2 羧酸衍生物.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第九章 羧酸及其衍生物和取代酸 9.3 取代酸.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)醇重要化合物.doc
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)酚重要化合物.doc
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)醚重要化合物.doc
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第七章 醇 酚 醚 7.1 醇.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第七章 醇 酚 醚 7.2 酚.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第七章 醇 酚 醚 7.3 醚.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二章 烷烃和环烷烃 2.1 烷烃.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二章 烷烃和环烷烃 2.2 环烷烃.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二章 烷烃和环烷烃 2.1 烷烃的重要化合物.pdf
- 《无机化学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(习题解答)第20章 毛细管电泳法.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第1章 蛋白质的结构与功能(protein structure and function).ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第2章 核酸的结构和功能 Structure and Function of Nucleic Acid.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第4章 糖代谢.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第7章 氨基酸的代谢 Amino Acid Metabolism.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第5章 脂代谢.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第8章 核苷酸代谢 Metabolism of nucleotide.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第3章 酶(enzyme).ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第6章 生物氧化.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第9章 物质代谢的联系与调节.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第10章 DNA的生物合成.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第18章 维生素(vitamin).ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第11章 RNA的生物合成.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第12章 蛋白质生物合成 Protein biosynthesis.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第17章 肝胆生化 biochemistry of liver.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《无机化学》实验课教学大纲(医学及相关专业)医用无机化学实验 Medical inorganic chemistry experiments.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《无机化学》理论课程大纲(医学及相关专业)医用无机化学教学大纲.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《无机化学》实验课程教学大纲(药学专业).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《无机化学》理论课程教学大纲(药学专业).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《无机化学》理论课程授课教案(医学及相关专业).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《无机化学》实验课程授课教案(药学专业).doc
