《病理生理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Dysfunction Of Cell Signaling In Diseases

Signal Transduction and theRelated DisordersPathophysiology DepartmentShiHeZi Medical College
Signal Transduction and the Related Disorders Pathophysiology Department ShiHeZi Medical College

Basic Concept of Cell Signaling(trans-membranous signaling)The process in which cellsthe extracellular stimuli throughsensemembranous orintracellularreceptors,transduce the signals via intracellular molecules,and thus regulate the biological function of thecells
The process in which cells sense the extracellular stimuli through membranous or intracellular receptors, transduce the signals via intracellular molecules, and thus regulate the biological function of the cells Basic Concept of Cell Signaling (trans-membranous signaling)

Major pathways for cell signalingG-protein-mediated pathwayAdenylate cyclase mediatedpathwayPhospholipasemediated pathwaySmall G-protein-mediated pathwayNon-G-protein-mediated pathwayReceptor tyrosine kinase mediated pathwayReceptor serine/threoninekinase mediated pathwayReceptor guanilate cyclase mediated pathwayIntracellular (unclear)receptor mediatedpathway
G-protein-mediated pathway Adenylate cyclase mediated pathway Phospholipase mediated pathway Small G-protein-mediated pathway Non-G-protein-mediated pathway Receptor tyrosine kinase mediated pathway Receptor serine/threonine kinase mediated pathway Receptor guanilate cyclase mediated pathway Intracellular (unclear) receptor mediated pathway Major pathways for cell signaling

Aberrant Cell Signaling andthe Related Disorders
Aberrant Cell Signaling and the Related Disorders
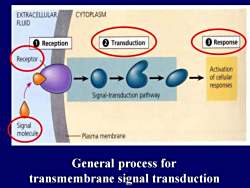
CYTOPLASMEXTRACELLULARFLUID3Response21TransductionReceptionReceptorActivationofcellularresponsesSignal-transductionpathwaySignalmoleculePlasmamembraneGeneral process fortransmembrane signal transduction
General process for transmembrane signal transduction

1. Aberrant Signal
1. Aberrant Signal

Types of cellular signals(1)Physical signalsLight, electronic, mechanic, UV, heat,volume or osmotic, etc(2)ChemicalsignalsHormones,neurotransmitters,GFs.cytokines; odor molecules; ATP, activeoxygen; drugs, toxins, etc
Types of cellular signals (1) Physical signals Light, electronic, mechanic, UV, heat, volume or osmotic, etc (2) Chemical signals Hormones, neurotransmitters, GFs, cytokines; odor molecules; ATP, active oxygen; drugs, toxins, etc

Modes for the function of endogenous signalsEndocrine Act on a far away organ via bloodcirculation, seen in most hormonesParacrine Act on a nearby target, seen in GFs, PG, NOAutocrineActonitself after secreted,seen in GFs.especiallyintumortissuesIntricrineAct on itself before secreted, seenin nuclearreceptorsSynaptic:Presynaptic to postsynaptic,seen in neurotransmitters
Modes for the function of endogenous signals Endocrine Act on a far away organ via blood circulation, seen in most hormones Paracrine Act on a nearby target, seen in GFs, PG, NO Autocrine Act on itself after secreted, seen in GFs, especially in tumor tissues Intricrine Act on itself before secreted, seen in nuclear receptors Synaptic: Presynaptic to postsynaptic, seen in neurotransmitters

Aberrant Signal (SignalExcess)ischemia, epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseasesextracellular glutamate/aspartic acid tNMDARactivationtCa2+influx t[Ca2+li,activation of enzymes excitatoryintoxication
ischemia, epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases extracellular glutamate/aspartic acid NMDAR activation Ca2+ influx [Ca2+]i , activation of enzymes excitatory intoxication Aberrant Signal (Signal Excess)

Aberrant Signal (SignalInsufficiency)Lesions in pancreatic β-cellDecreased insulin productionhyperglycemiaDiabetess (Type I)
Lesions in pancreatic -cell Decreased insulin production hyperglycemia Diabetes (Type I) Aberrant Signal (Signal Insufficiency)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《病理生理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 Fever.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Acid-Base Balance And Disturbances.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 Hypoxia.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Disorders Of Water And Electrolyte Metabolism(2/3).ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Disorders Of Water And Electrolyte Metabolism(3/3).ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Disorders Of Water And Electrolyte Metabolism(1/3).ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Conspectus Of Disease.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验性心肌缺血-再灌注损伤.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)失血性休克及其抢救.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)酸碱平衡紊乱.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验性急性心力衰竭.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)急性心肌梗塞.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)急性肾功能衰竭及肾功对药物作用的影响.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)呼吸功能不全.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)缺氧.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)家兔实验性肺水肿.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)高血钾症.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)哺乳类实验动物基本手术操佣?.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)氨在肝性脑病发病机制中的作用.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程作业习题(无答案)酸碱平衡紊乱.doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 7 Cell Proliferation, Differentiation, Apoptosis And the Related Diseases.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 8 Stress And Stress-Related Diseases.ppt
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)护理学理论基础教学大纲.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)健康评估与诊断教学大纲.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)基础护理技术操作学教学大纲 The Basic Skill of Nursing.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)健康评估与诊断教学大纲 Health Assessment and Diagnosis.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)基础护理技术操作学实验大纲 The Basic Skill of Nursing.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)健康评估与诊断实验大纲 Health Assessment and Diagnosis.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)护理技术操作实验大纲.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)护理学理论基础本科教学大纲 The Fundamental theory of nursing.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)基础护理技术操作学教学大纲 the Basic Skill of Nursing.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)健康评估与诊断教案.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)护理技术操作学教案.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学资源(大纲教案)护理学理论基础教案.doc
- 《护理学基础》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 医学模式与护理思想的转变.ppt
- 《护理学基础》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)心理社会评估(共六章).ppt
- 《护理学基础》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)临床基本护理技术操作学(静脉输液与输血).ppt
- 《护理学基础》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 舒适与安全(Comfort and Safety).ppt
- 《护理学基础》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 健康、疾病与保健.ppt
- 《护理学基础》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 护理学的定义、性质和任务.ppt
