北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 19 The elements of copper and zinc family

Chapter 19 The elements of copper and zinc family X$19.1 The elements of copper family X 19.2 The elements of zinc family
Chapter 19 The elements of copper and zinc family §19.1 The elements of copper family §19.2 The elements of zinc family

19.1 The elements of copper family >19.1.1 The elemental substances of copper family 319.1.2 The compounds of copper -19.1.3 The copper ions in aqueous solution and the related reactions
§19.1 The elements of copper family 19.1.1 The elemental substances of copper family 19.1.2 The compounds of copper 19.1.3 The copper ions in aqueous solution and the related reactions

19.1.1 The elemental substances of copper family 1.Existence Elemental substance:Cu,Ag,Au Mineral:malachite:Cu2(OH)2CO3(孔雀石) argentite:AgzS(辉银矿) calaverite:AuTe2(碲金矿) 2.Physical properties .Color:Cu(violet red),Ag(white),Au(yellow) .m.p and b.p are lower than that of other transition metals .Good conductor of heat and electricity,the order is Ag>Cu>Au .Good ductibility
19.1.1 The elemental substances of copper family Elemental substance:Cu, Ag, Au Mineral: malachite:Cu2 (OH)2CO3 (孔雀石) argentite:Ag2S (辉银矿) calaverite:AuTe2 (碲金矿) 1.Existence 2.Physical properties •Color:Cu(violet red), Ag(white), Au(yellow) •m.p and b.p are lower than that of other transition metals •Good conductor of heat and electricity, the order is Ag>Cu>Au •Good ductibility

3.Chemical properties ·reacts with oxygen 2Cu+02A→2Cu0(黑) 2Cu+02+H20+C02△→ Cu2(OH)2C0,(绿) 碱式碳酸铜 Au and Ag can't react with oxygen,but the reaction can occur in the presence of precipitating agent or coordinating ligand
3.Chemical properties • reacts with oxygen 2Cu O 2CuO( ) 2 黑 碱式碳酸铜 Au and Ag can’t react with oxygen,but the reaction can occur in the presence of precipitating agent or coordinating ligand Cu (OH) CO ( ) 2Cu O H O CO 2 2 3 2 2 2 绿

M=Cu,Ag,Au 4M+,+2H,O+8CN>4[M(CN)+40H 4Cu+0,+2H,O+8NH3> 4[CuNH3)2](无色)+4OH 02 [CuNH,)4]2+(蓝) Aqueous ammonia can't be shipped in copper containers. 2Ag+2H2S+02->2Ag2S+2H2O 银器年久变黑
M C u, Ag, A u [Cu(N H ) ] ( ) 2 3 4 蓝 Aqueous ammonia can’t be shipped in copper containers. 2Ag 2 H 2 S O 2 2Ag 2 S 2 H 2 O O2 银器年久变黑. 4[Cu(NH ) ] ( ) 4OH 4Cu O 2H O 8NH 3 2 2 2 3 无色 4MO2 2H2 O8CN 4[M(CN)2 ] 4OH

·Reacts with X, Cu+Cl,t>V Ag+Cl2->proceed slowly at r.t. Au+Cl2—→proceed only at high temp Chemical reactivity order CuAg-Au ·reacts with acids DCu,Ag,Au can't displace H+ions in dilute acid (poor reduction ability);
• Reacts with X2 C u C l2 r. t. Chemical reactivity order :Cu>Ag>Au proceed only at high temp. Au Cl2 proceed slowly at r.t. Ag Cl2 • reacts with acids ①Cu, Ag, Au can’t displace H+ ions in dilute acid (poor reduction ability);

2Forming precipitates or complexes can strengthen reduction ability of the elemental substances; 2Ag+H2S->Ag2S(s)+H2(g) 2Ag 2H*+4I->2AgI,+H2 (g) 2Cu+2H*+4CS(NH2)2->2Cu[CS(NH2)2]2+H2(g) 硫脲 HCI 4M+O,+2H,O+8CN->4[M(CN)]+40H M=Cu,Ag,Au
2Cu 2 H 4CS(NH ) 2Cu[CS(NH ) ] H (g) 2Ag 2 H 4 I 2AgI H (g) 2Ag H S Ag S(s) H (g) 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 - 2 2 2 2 HCl 硫脲 ②Forming precipitates or complexes can strengthen reduction ability of the elemental substances; 4MO2 2H2 O8CN 4[M(CN)2 ] 4OH M C u, Ag, A u
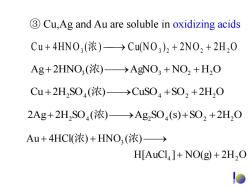
3 Cu,Ag and Au are soluble in oxidizing acids Cu+4HN0,(浓)→CuN0,)2+2N02+2H20 Ag+2HNO,(浓)→AgNO3+NO2+HO Cu+2HS04(浓)→CuS04+S02+2H20 2Ag+2H2S04(浓)→Ag2S04(s)+S02+2H2O Au+4HCI(浓)+HNO3(浓)→ H[AuCl]+NO(g)+2H2O
③ Cu,Ag and Au are soluble in oxidizing acids C u 4HN O3 (浓) Cu(N O 3 ) 2 2N O2 2 H 2 O H[AuCl ] NO(g) 2H O Au 4HCl( ) HNO ( ) 4 2 3 浓 浓 2Ag 2H2 SO4 (浓) Ag2 SO4 (s)SO2 2H2 O Cu 2H2 SO4 (浓) CuSO4 SO2 2H2 O Ag 2HNO3 (浓) AgNO3 NO2 H2 O

19.1.2 The compounds of copper 1.The compounds of copper Cu:3d104s1 Cu(D):d10,Compounds of Cu(I)are white or colorless, no d-d transition Cu(ID:d9,Compounds of Cu(ID)have colors, d-d transition Cu(IID):ds,K3CuF(light green),strong oxidizing agent d-d transition
1.The compounds of copper 19.1.2 The compounds of copper Cu(I): d 10, Compounds of Cu(I) are white or colorless, no d-d transition Cu(II): d9 , Compounds of Cu(II) have colors, d-d transition Cu(III): d8 , K3CuF6 (light green), strong oxidizing agent d-d transition Cu: 3d104s1
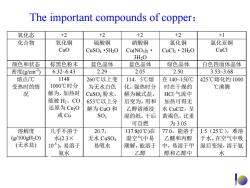
The important compounds of copper: 氧化态 +2 +2 +2 +2 +1 化合物 氧化铜 硫酸铜 硝酸铜 氯化铜 氯化亚铜 Cuo CuSO4·5H20 CuNO3)2· CuCl2·2H2O CuCl 3H20 颜色和状态 棕黑色粉末 蓝色晶体 蓝色晶体 绿色晶体 白色四面体晶体 密度(g/cm2) 6.32-6.43 2.29 2.05 2.50 3.533.68 熔点/℃ 1148 260℃以上变 114.5℃熔 在140~150℃ 425℃熔化约1000 受热时的情 1000℃时分 为无水白色 化,强热时分 时在干燥的 ℃沸腾 况 解为,加热时 CuSO4粉末, 解为碱式盐。 HCI气流中 能被H、CO 653℃以上分 后变为。用和 加热可得无 还原为Cu20 解为CuO和 乙醇溶液浸 水CuC2,呈 或Cu S03 湿的纸,干后 黄褐色,比重 可自燃 为3.05 溶解度 几乎不溶于 20.7, 137.8(0℃)在 77.0,能溶于 1.5(25℃),难溶 (g100gH20) 水(2.3× 无水CuSO4 湿空气中易 乙醚和丙醇 于水。在空气中吸 (无水盐) 105),易溶于 易吸水 潮解,能溶于 中,易溶于甲 湿后变绿,溶于氨 氨水 乙醇 醇和乙醇中 水
The important compounds of copper: 氧化态 +2 +2 +2 +2 +1 化合物 氧化铜 CuO 硫酸铜 CuSO4·5H2O 硝酸铜 Cu(NO3)2· 3H2O 氯化铜 CuCl2·2H2O 氯化亚铜 CuCl 颜色和状态 棕黑色粉末 蓝色晶体 蓝色晶体 绿色晶体 白色四面体晶体 密度(g/cm-2 ) 6.32~6.43 2.29 2.05 2.50 3.53~3.68 熔点/℃ 受热时的情 况 1148 1000℃时分 解为,加热时 能被 H2、CO 还原为 Cu2O 或 Cu 260℃以上变 为无水白色 CuSO4 粉末, 653℃以上分 解为 CuO 和 SO3 114.5℃熔 化,强热时分 解为碱式盐。 后变为。用和 乙醇溶液浸 湿的纸,干后 可自燃 在 140~150℃ 时在干燥的 HCl 气流中 加热可得无 水 CuCl2,呈 黄褐色,比重 为 3.05 425℃熔化约 1000 ℃沸腾 溶解度 (g/100gH2O) (无水盐) 几乎不溶于 水(2.3× 10-5 ),易溶于 氨水 20.7, 无水 CuSO4 易吸水 137.8(0℃)在 湿空气中易 潮解,能溶于 乙醇 77.0,能溶于 乙醚和丙醇 中,易溶于甲 醇和乙醇中 1.5(25℃),难溶 于水。在空气中吸 湿后变绿,溶于氨 水
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 18 Hydrogen and the rare gases.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 17 The halogens.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 16 The elements of oxygen family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 15 The elements of nitrogen family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 14 The elements of carbon family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 13 The elements of boron family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 12 The alkali and alkaline earth metal.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 11 Basic of Coordination Chemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 10 Reduction - oxidization Reactions.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 9 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 8 Acid-Base Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 7 Crystal Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 6 Molecular Structure and covalent bond theory.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 5 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 4 Chemical equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 2 Basic of thermodynamics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 1 Preface(负责人:周云山).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 9 Molecular Structure.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 8 Atomic Structure.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 7 Redox Reactions and the Base of Electrochemistry.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 21 The elements of chromium and Manganese family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 22 The elements of iron and platinium families.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)有机化学教学大纲(药学专业)Organic Chemistry.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第一章 绪论 Organic Chemistry(负责人:杨雪梅).pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第三章 烯烃 Alkenes.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第二章 烷烃和环烷烃 Alkane and Cycloalkane.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第四章 炔烃和二烯烃 Alkynes and Dienes.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第五章 二烯烃 CnH2n-2.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第六章 立体化学基础.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第七章 芳香烃.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第九章 醛和酮 aldehyde and ketone.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十章 羧酸和取代羧酸.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十二章 羧酸衍生物 Carboxylic acid derivatives.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十三章 碳负离子的反应.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十五章 杂环化合物.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第七章 卤代烃.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第八章 醇、酚和醚.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十五章 糖类 saccharide.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十四章 有机含氮化合物.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(专题讲稿)全面解读有机反应类型.pdf
