北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 11 Basic of Coordination Chemistry

Chapter 11 Basic of Coordination Chemistry 11.1 Basic concepts of coordination compounds 11.2 The valence bond theory of coordination compounds 11.3 Crystal Field Theoryof coordination compound 11.4 Stability of coordination compounds $*11.5 Further discussion on coordination compounds
Chapter 11 Basic of Coordination Chemistry §11.2 The valence bond theory of coordination compounds §11.3 Crystal Field Theoryof coordination compound §11.1 Basic concepts of coordination compounds §*11.5 Further discussion on coordination compounds §11.4 Stability of coordination compounds

S 11.1 Basic concepts of coordination compounds 11.1.1 Coordination compounds Defination: A complex is a typical acid-base adduct of a Lewis acid and a lewis base.E.g,[AgNH3)2]+是Lewisi酸Ag+和NH3 的加合物。 A coordination compound or metal complex,has a structure consisting of a central atom or ion (usually metallic),bonded to a surrounding array of molecules or anions (ligands,complexing agents)
11.1.1 Coordination compounds Defination: A complex is a typical acid-base adduct of a Lewis acid and a lewis base. E.g., [Ag(NH3)2]+是Lewis酸Ag+和NH3 的加合物。 §11.1 Basic concepts of coordination compounds A coordination compound or metal complex, has a structure consisting of a central atom or ion (usually metallic), bonded to a surrounding array of molecules or anions (ligands, complexing agents)

Composition of a coordination A Lewis acid,.called形成体(eg,central metal ion): A Lewis base,.called配位体(ligand). Central metal ion(形成体)usually are metals and metal ions,also have few nonmelal .Such as Cu2+,Agt,Fe3+, Fe,Ni,Bm,PV.… Ligand(配位体)in classical coordination chemistry bind to metals,almost exclusively,via their "lone pairs"of electrons residing on the main group atoms of the ligand. Typical ligands are:F-,CI,Br,I,OH-,CN-,H2O, NH3,:C0,H2C=CH2.…
Central metal ion(形成体) usually are metals and metal ions,also have few nonmelal .Such as :Cu2+,Ag+ ,Fe3+, Fe,Ni,BⅢ,PⅤ …… Ligand(配位体) in classical coordination chemistry bind to metals, almost exclusively, via their “lone pairs” of electrons residing on the main group atoms of the ligand. Typical ligands are:F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, OH-, CN- , H2O, NH3 , :CO, H2C=CH2…… A Lewis acid, called形成体(e.g., central metal ion); A Lewis base, called 配位体 (ligand). Composition of a coordination

coordinating atom:The atom having bond with the central metal ion. monodentate ligand:There is only one coordination atom in the ligand. Polydentate ligand:The ligand have two or more coordination atoms
coordinating atom:The atom having bond with the central metal ion. monodentate ligand:There is only one coordination atom in the ligand. Polydentate ligand:The ligand have two or more coordination atoms
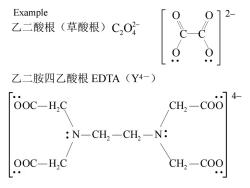
Example 乙二酸根(草酸根)C,O 乙二胺四乙酸根EDTA(Y4-) OOC-HC CH-co] N-CH,-CH,-N: OOC-H,C CH,-COO
乙二胺四乙酸根 EDTA(Y4-) 乙二酸根(草酸根) 2 C2O4 O O C C O O 2– • • • • COO H C CH OOC N CH CH N COO H C CH OOC 2 2 2 2 2 2 4– • • • • • • • • • • • • Example

从溶液中析出配合物时,配离子常与带有相反电 荷的其它离子结合成盐,这类盐称为配盐(complex salt)。配盐的组成可以划分为内层(inner sphere)和外 层(outer sphere)。配离子属于内层,配离子以外的其 他离子属于外层。外层离子所带电荷总数等于配离子 的电荷数。 out sphere inner sphere K3[Fe(CN)6] ↑ 形成体 配配配 位体位 原子
从溶液中析出配合物时,配离子常与带有相反电 荷的其它离子结合成盐,这类盐称为配盐(complex salt)。配盐的组成可以划分为内层(inner sphere)和外 层(outer sphere)。配离子属于内层,配离子以外的其 他离子属于外层。外层离子所带电荷总数等于配离子 的电荷数。 形 成 体 配 位 原 子 配 体 配 位 数 K3[ Fe ( C N ) 6 ] out sphere inner sphere

coordination number(CN配位数):配位原子数 monodentente ligand(单齿配体):形成体的配 位数等于配位体的数目; polydentate ligand(多齿配体):形成体的配位 数等于配位体的数目与基数的乘积。 e.g., [Cu(en)2] H.C-NEL.HN CU. Cu H,C-NH,H,N-CH, CN of Cu2+:4
coordination number(CN 配位数):配位原子数 monodentente ligand(单齿配体):形成体的配 位数等于配位体的数目; polydentate ligand(多齿配体):形成体的配位 数等于配位体的数目与基数的乘积。 Cu(en) 2 2 CN of Cu2+: 4。 e.g., H C NH H N CH Cu H C NH H N CH 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2+
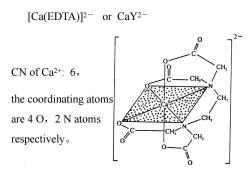
[Ca(EDTA)2 or CaY2- CN of Ca2+:6, CH, the coordinating atoms are 4 O,2 N atoms respectively
[Ca(EDTA)]2- or CaY2- CN of Ca2+: 6, the coordinating atoms are 4 O,2 N atoms respectively

11.1.2.Names of complexes of various types l.The basic procedure for naming a complex(英语命名 法): 1When naming a complex ion,the ligands are named before the metal ion. 2Write the names of the ligands in alphabetical order. i)multiple occurring monodentate ligands receive a prefix according to the number of occurrences:di-,tri-, tetra-,penta-,or hexa.Polydentate ligands (e.g., ethylenediamine,oxalate)receive bis-,tris-,tetrakis-,etc. ii)anions end in o.This replaces the final 'e'when the anion ends with '-ate',e.g.sulfate becomes sulfato.It replaces 'ide':cyanide becomes cyano
11.1.2. Names of complexes of various types 1. The basic procedure for naming a complex (英语命名 法): ①When naming a complex ion, the ligands are named before the metal ion. ②Write the names of the ligands in alphabetical order. ⅰ) multiple occurring monodentate ligands receive a prefix according to the number of occurrences: di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, or hexa. Polydentate ligands (e.g., ethylenediamine, oxalate) receive bis-, tris-, tetrakis-, etc. ⅱ) anions end in o. This replaces the final 'e' when the anion ends with '-ate', e.g. sulfate becomes sulfato. It replaces 'ide': cyanide becomes cyano

iii)neutral ligands are given their usual name,with some exceptions:NH3 becomes ammine;H2O becomes aqua or aquo;CO becomes carbonyl;NO becomes nitrosyl. 3 write the name of the central atom/ion.If the complex is an anion,the central atom's name will end in -ate,and its Latin name will be used if available (except for mercury). 4If the central atom's oxidation state needs to be specified (when it is one of several possible,or zero),write it as a Roman numeral (or 0)in parentheses. 5Name cation then anion as separate words(if applicable,as in last example)
ⅲ) neutral ligands are given their usual name, with some exceptions: NH3 becomes ammine; H2O becomes aqua or aquo; CO becomes carbonyl; NO becomes nitrosyl. ③ write the name of the central atom/ion. If the complex is an anion, the central atom's name will end in -ate, and its Latin name will be used if available (except for mercury). ④If the central atom's oxidation state needs to be specified (when it is one of several possible, or zero), write it as a Roman numeral (or 0) in parentheses. ⑤Name cation then anion as separate words (if applicable, as in last example)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 10 Reduction - oxidization Reactions.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 9 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 8 Acid-Base Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 7 Crystal Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 6 Molecular Structure and covalent bond theory.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 5 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 4 Chemical equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 2 Basic of thermodynamics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 1 Preface(负责人:周云山).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 9 Molecular Structure.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 8 Atomic Structure.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 7 Redox Reactions and the Base of Electrochemistry.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 16 The d-block elements(Ⅰ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 15 The p-block elements(Ⅲ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 14 Chapter 14 The p-block elements(Ⅱ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 13 The p-block elements(Ⅰ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 12 The s-Block Elements.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 11 Coordination Compound Structures.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 10 Solid Structure.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 4 Chemical equilibria, entropy and Gibbs function.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 12 The alkali and alkaline earth metal.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 13 The elements of boron family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 14 The elements of carbon family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 15 The elements of nitrogen family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 16 The elements of oxygen family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 17 The halogens.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 18 Hydrogen and the rare gases.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 19 The elements of copper and zinc family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 21 The elements of chromium and Manganese family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 22 The elements of iron and platinium families.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)有机化学教学大纲(药学专业)Organic Chemistry.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第一章 绪论 Organic Chemistry(负责人:杨雪梅).pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第三章 烯烃 Alkenes.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第二章 烷烃和环烷烃 Alkane and Cycloalkane.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第四章 炔烃和二烯烃 Alkynes and Dienes.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第五章 二烯烃 CnH2n-2.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第六章 立体化学基础.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第七章 芳香烃.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第九章 醛和酮 aldehyde and ketone.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十章 羧酸和取代羧酸.pdf
