北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 2 Basic of thermodynamics

Chapter 2 Basic of thermodynamics To study chemistry using the theories and methods of thermodynamics 1)heat exchange in chemical reactions 2)directions and extent of reaction processes x 2.1 the First law of thermodynamics §2.2 Thermochemistry x 2.3 Direction of a chemical reaction
Chapter 2 Basic of thermodynamics §2.2 Thermochemistry §2.3 Direction of a chemical reaction To study chemistry using the theories and methods of thermodynamics 1) heat exchange in chemical reactions 2) directions and extent of reaction processes §2.1 the First law of thermodynamics

2.1 the First law of thermodynamics 2.1.1 Basic terms in thermodynamics 1.System and surroundings 2.State and state functions 3.Process and path 4.Volume work 5.Thermodynamic energy 2.1.2 the First law of thermodynamics 1.the Content of the First law of thermodynamics 2.Work and heat
2.1.1 Basic terms in thermodynamics 1. System and surroundings 5. Thermodynamic energy 4. Volume work 3. Process and path 2. State and state functions §2.1 the First law of thermodynamics 2.1.2 the First law of thermodynamics 1. the Content of the First law of thermodynamics 2. Work and heat

2.1 the First law of thermodynamics 2.1.1 Basic terms in thermodynamics 1.System and surroundings 2.State and state functions 3.Process and path 4.Volume work 5.Thermodynamic energy 2.1.2 the First law of thermodynamics 1.the Content of the First law of thermodynamics 2.Work and heat
2.1.1 Basic terms in thermodynamics 1. System and surroundings 5. Thermodynamic energy 4. Volume work 3. Process and path 2. State and state functions §2.1 the First law of thermodynamics 2.1.2 the First law of thermodynamics 1. the Content of the First law of thermodynamics 2. Work and heat

2.1.1 Basic terms in thermodynamics l.System(系统)and surroundings(环境) System:the specific part of the universe we are studying Surroundings:the rest of the universe outside the System,normally referring to the closely related moiety Open system:a system can exchange mass and energy with its surroundings Closed system:a system exchanges energy but not matter with its surroundings Isolated system:a system exchange neither mass nor energy with its surroundings
System:the specific part of the universe we are studying Surroundings:the rest of the universe outside the System, normally referring to the closely related moiety Open system: a system can exchange mass and energy with its surroundings Closed system: a system exchanges energy but not matter with its surroundings Isolated system: a system exchange neither mass nor energy with its surroundings 2.1.1 Basic terms in thermodynamics 1. System (系统) and surroundings (环境)

Three systems represented by water in a flask (a) (b) (c)
Three systems represented by water in a flask (a) (b) (c)

2.State(状态)and state function(状态函数) State:the comprehensive condition of a system. State function:physical quantities depicting the property of a system.(e.g.,p,V'T,M...) 3.Process(过程)and Path(途径): Process:A sequence of interdependent and linked procedures which,at every stage,consume one or more resources to convert inputs into outputs.These outputs then serve as inputs for the next stage until a known goal or end results is reached.. Path(途径):the sum of the processes for the system from an initial state to a final state
2. State (状态) and state function(状态函数) State:the comprehensive condition of a system. State function:physical quantities depicting the property of a system. (e.g., p,V,T,M…) 3. Process(过程) and Path(途径): Process: A sequence of interdependent and linked procedures which, at every stage, consume one or more resources to convert inputs into outputs. These outputs then serve as inputs for the next stage until a known goal or end results is reached.. Path(途径) : the sum of the processes for the system from an initial state to a final state

Path/process (I) Final state Initial state Path/process (II) The characteristics of a state function: (1)the value of a state function is unique when the state of a system is specified. (2)the change in the value of a state function depends only on an initial state and a final state of a system and is independent of the path(途径) /process(过程)between the two states
(2) the change in the value of a state function depends only on an initial state and a final state of a system and is independent of the path (途径) /process(过程) between the two states. Initial state Final state Path/process (II) Path/process (I) The characteristics of a state function: (1) the value of a state function is unique when the state of a system is specified
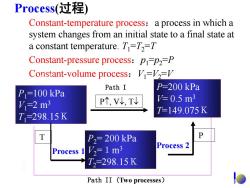
Process(过程 Constant-temperature process:a process in which a system changes from an initial state to a final state at a constant temperature.T=T2=T Constant-pressure process:pi=p2=P Constant-volume process:V=12= Path I P=200 kPa P=100 kPa P个,V,T =0.5m3 V=2m3 T=149.075K T=298.15K P2=200 kPa P V2=1m3 Process 2 Process 1 T2=298.15K Path II (Two processes)
Process(过程) Constant-temperature process:a process in which a system changes from an initial state to a final state at a constant temperature. T1 =T2 =T Constant-pressure process:p1 =p2 =P Constant-volume process:V1 =V2 =V P1=100 kPa V1=2 m3 T1=298.15K P2= 200 kPa V2 =1m3 T2=298.15K P, V, T P=200 kPa V= 0.5 m3 T=149.075K 始态 Path II (Two processes) Path I Process 1 T Process 2 P

4.Thermodynamic energy(热力学能) thermodynamic energy (U):the total of all the forms the kinetic energy due to the motion of particles(translational, rotational,vibrational)and the potential energy associated with the vibrational and electric energy of atoms within molecules or crystals )of energy contained within a system.U is also called the internal energy )U is a state function. Molorined stimer U2-U1=△U hs别n 0,e eatonctarte Change in internal energy aU depend only on initial state and a final state of a system and is independent of the path between the two states
thermodynamic energy (U): the total of all the forms ( ) of energy contained within a system. U is also called the internal energy (内能). U is a state function. U2 U1 U Change in internal energy ΔU depend only on an initial state and a final state of a system and is independent of the path between the two states. the kinetic energy due to the motion of particles (translational, rotational, vibrational) and the potential energy associated with the vibrational and electric energy of atoms within molecules or crystals 4. Thermodynamic energy (热力学能)

2.1.2 the First law of thermodynamics (热力学第一定律) l.Heat(热)and work(功) Heat():Heat is a transfer of energy as a result of temperature difference between a system and its surroundings. Heat is not a state function. Prescript:a system adsorbs heat from its surroundings 2>0; a system releases heat into its surroundings: 2<0
1. Heat (热) and work (功) Heat is a transfer of energy as a result of temperature difference between a system and its surroundings. Heat (Q): Heat is not a state function. Prescript:a system adsorbs heat from its surroundings Q >0; a system releases heat into its surroundings: Q <0。 2.1.2 the First law of thermodynamics (热力学第一定律)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 1 Preface(负责人:周云山).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 9 Molecular Structure.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 8 Atomic Structure.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 7 Redox Reactions and the Base of Electrochemistry.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 16 The d-block elements(Ⅰ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 15 The p-block elements(Ⅲ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 14 Chapter 14 The p-block elements(Ⅱ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 13 The p-block elements(Ⅰ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 12 The s-Block Elements.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 11 Coordination Compound Structures.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 10 Solid Structure.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 4 Chemical equilibria, entropy and Gibbs function.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 4 Chemical equilibria, entropy and Gibbs function.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 6 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 5 Acid-Base Equilibrium.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 2 Thermochemistry.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 1 Preface.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 8 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 7 Redox Reactions and the Base of Electrochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 6 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 4 Chemical equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 5 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 6 Molecular Structure and covalent bond theory.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 7 Crystal Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 8 Acid-Base Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 9 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 10 Reduction - oxidization Reactions.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 11 Basic of Coordination Chemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 12 The alkali and alkaline earth metal.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 13 The elements of boron family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 14 The elements of carbon family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 15 The elements of nitrogen family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 16 The elements of oxygen family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 17 The halogens.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 18 Hydrogen and the rare gases.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 19 The elements of copper and zinc family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 21 The elements of chromium and Manganese family.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 22 The elements of iron and platinium families.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)有机化学教学大纲(药学专业)Organic Chemistry.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《有机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第一章 绪论 Organic Chemistry(负责人:杨雪梅).pdf
