北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 6 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria

Chapter 6 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria X 6.1 Solubility and solubility product x 6.2 Forming and dissolving of precipitates x 6.3 Equilibrium between two precipitates
Chapter 6 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria § 6.3 Equilibrium between two precipitates § 6.2 Forming and dissolving of precipitates § 6.1 Solubility and solubility product

6.1 Solubility and solubility product 6.1.1 Solubility 3一 6.1.2 Solubility product 6.1.3 Relationship between solubility and solubility product
§6.1 Solubility and solubility product 6.1.3 Relationship between solubility and solubility product 6.1.2 Solubility product 6.1.1 Solubility

6.1.1 Solubility Solubility is the maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given quantity of solvent when dynamic equilibrium is established between undissolved solute and the solution at a specific temperature.We usually use the symbol "S"to express it. Solubility usually is expressed in grams of solute per 100g of water(g/100g)for aqueous solution
Solubility is the maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given quantity of solvent when dynamic equilibrium is established between undissolved solute and the solution at a specific temperature. We usually use the symbol ―S‖ to express it. Solubility usually is expressed in grams of solute per 100g of water (g /100g) for aqueous solution. 6.1.1 Solubility

6.1.2 Solubility product The process which involves the dissolution and precipitation of an insoluble electrolyte occurs when it is added to a solvent like water at a certain temperature. NaCl Dissolution of NaCl in Water
The process which involves the dissolution and precipitation of an insoluble electrolyte occurs when it is added to a solvent like water at a certain temperature. 6.1.2 Solubility product NaCl

When the rate of precipitation becomes equal to the rate of dissolving,a condition of dynamic multiphase equilibrium is established. BaSO(s) 溶 沉 -Ba2(aq)+O (aq K(BaSO)=[c(Ba)/cellc(SO )/c] or simply:Ke(BaSO)={c(Ba))(c(SO ) KP一solubility product constant(溶度积常数) For general precipitation reactions: A,B(s)=nAT(aq)+mB"-(ag) Ke(A B)=(A)"(B"))
When the rate of precipitation becomes equal to the rate of dissolving, a condition of dynamic multiphase equilibrium is established. For general precipitation reactions: Ksp — solubility product constant (溶度积常数) A B (s) nA (aq) mB (aq) m n n m + - + m n n m (AnBm) { (A )} { (B )} + - Ksp = c c (BaSO ) { (Ba )}{ (SO )} 2 4 2 4 + - or simply: Ksp = c c (BaSO ) [ (Ba )/ ][ (SO )/ ] 2 4 2 4 + - K = c c c c sp 溶解 BaSO (s) Ba (aq) SO (aq) 2 4 2 4 + - + 沉淀

6.1.3 Relationship between solubility and the solubility product The conversion betweenK and solubility Because concentrations in the Keexpression must be in molarity and the unit of solubility is g solute /100g water,So we need convert the solubility data to molarity(mol-L). A Bm(s)--nAT(aq)+mB"-(aq) Equilibrium /mol.L nS mS K8=(nS)"(mS)" AB type S=
6.1.3 Relationship between solubility and the solubility product 1 Equilibrium /mol L - nS mS m+ n- A Bm (s) nA (aq) + mB (aq) n n m K = (nS) (mS) sp AB type S = Ksp The conversion between and solubility Because concentrations in the expression must be in molarity and the unit of solubility is g solute /100g water, So we need convert the solubility data to molarity(mol·L-1 ). Ksp Ksp

Example The solubility of AgCl is found experimentally to be 1.92X 10-3 gL-1 at 25C. Calculate the value of K for AgCl. Answer:We know M(AgCI)=143.3 S=1.92X103 143.3 mol-L=1.34X10mol-L AgCl(s)=Ag(aq)+Cl (aq) Equilibrium/mol.L-1 S S KP(AgC1)={c(Ag)}{c(CI)}=S2=1.80X1010
Example :The solubility of AgCl is found experimentally to be 1.92×10-3 g·L-1 at 25oC. Calculate the value of for AgCl. Equilibrium / mol.L-1 S S Answer:We know Mr (AgCl)= 143.3 1 5 1 3 mol L 1.34 10 mol L 143.3 1.92 10 - - - - S = × = × AgCl(s) Ag (aq) Cl (aq) + - + 2 10 (AgCl) { (Ag )}{ (Cl )} 1.80 10 + - - Ksp = c c = S = × Ksp
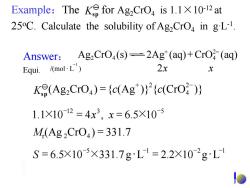
Example:The K for Ag,CrO is 1.1X10-12at 25C.Calculate the solubility of Ag CrO in gL-1. Answer:Ag2 CrO,(s)=2Ag*(aq)+CrO(aq) Equi. /mol·L) 2x X K(Ag2CrO)=(c(Ag))2(c(CrO ) 1.1×1012=4x3,x=6.5×10 M(Ag2Cr04)=331.7 S=6.5×105×331.7gL=2.2×102gL1
/(mol L ) 2 1 x x - Equi. Mr (Ag 2CrO4 ) = 331.7 5 1 2 1 6.5 10 331.7 g L 2.2 10 g L - - - - S = × × = × 12 3 5 1.1 10 4 , 6.5 10 - × - × = x x = Ag CrO (s) 2Ag (aq) CrO (aq) 2 4 4 + 2- + + 2- 4 2 2 4 K (Ag CrO ) ={c(Ag )} {c(CrO )} sp Answer: Example:The for Ag2CrO4 is 1.1×10-12 at 25oC. Calculate the solubility of Ag2CrO4 in g·L-1 . Ksp

Question:Determine the relationship between molar solubility (S,unit:mol.L-)and Ke for Ca3(P04)2 5 K品 S= 108
Question:Determine the relationship between molar solubility (S, unit: mol.L-1 ) and for Ca3 (PO4 )2 . Ksp 5 108 S = Ksp
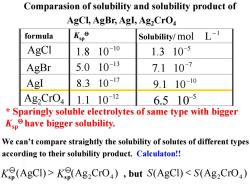
Comparasion of solubility and solubility product of AgCl,AgBr,AgI,Ag,CrO formula Kp° Solubility/mol L-1 AgCI 1.8 10-10 1.310-5 AgBr 5.0 10-13 7.110-7 AgI 8.310-17 9.11010 Ag2CrO4 1.11012 6.5105 Sparingly soluble electrolytes of same type with bigger Kphave bigger solubility. We can't compare straightly the solubility of solutes of different types according to their solubility product.Calculaton!! Ke(AgCI)>Ke(Ag2CrO),but S(AgCI)<S(Ag2CrO)
(AgCl) (Ag CrO ) S S 2 4 sp Ksp Comparasion of solubility and solubility product of AgCl, AgBr, AgI, Ag2CrO4 , but 分子式 溶度积 溶解度/ AgBr AgI AgCl 5 6.5 10- 1 mol L - 10 1.8 10- 13 5.0 10- 17 8.3 10 - 12 1.1 10- 10 9.1 10- 7 7.1 10- 5 1.3 10- Ag2CrO4 formula Ksp Solubility/
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 5 Acid-Base Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 2 Thermochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 16 The d-block elements(Ⅰ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 15 p-block elements(Ⅲ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 14 p-block elements(Ⅱ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 17 The d-block elements(Ⅱ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 09 Molecular Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 07 Redox Reactions and Base of Electrochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 13 The p-block elements(Ⅰ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 08 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 06 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 12 The s-Block Elements.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 11 Coordination Compound Structures.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 10 Solid Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 04 Chemical equilibria, entropy and Gibbs function.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 05 Acid-Base Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 03 Chemical kinetics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 02 Thermochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 01 前言 Preface(负责人:周云山).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十六-十七综合自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 7 Redox Reactions and the Base of Electrochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 8 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 1 Preface.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 2 Thermochemistry.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 5 Acid-Base Equilibrium.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 6 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 4 Chemical equilibria, entropy and Gibbs function.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 4 Chemical equilibria, entropy and Gibbs function.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 10 Solid Structure.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 11 Coordination Compound Structures.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 12 The s-Block Elements.pptx
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 13 The p-block elements(Ⅰ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 14 Chapter 14 The p-block elements(Ⅱ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 15 The p-block elements(Ⅲ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 16 The d-block elements(Ⅰ).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 7 Redox Reactions and the Base of Electrochemistry.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 8 Atomic Structure.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 9 Molecular Structure.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 1 Preface(负责人:周云山).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿,2015)Chapter 2 Basic of thermodynamics.pdf
