北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 10 Solid Structure

Chapter 10 Solid Structure X$10.1 The Structures and Types of Crystals X 10.2 Metallic Crystals ☒§10.3 Ionic Crystals ☒§10.4 Molecular Crystals ☒§10.5 Network Crystals
§10.1 The Structures and Types of Crystals Chapter 10 Solid Structure §10.5 Network Crystals §10.4 Molecular Crystals §10.3 Ionic Crystals §10.2 Metallic Crystals

10.1 The Structures and Types of Crystals s10.1.1 Crystal Structures 10.1.2 Crystal Defects,Amorphous Soilds 10.1.3 Types of Crystals
10.1.1 Crystal Structures §10.1 The Structures and Types of Crystals 10.1.3 Types of Crystals 10.1.2 Crystal Defects, Amorphous Soilds

10.1.1 Crystal Structures Crystallove 水晶之恋 alibaba.com钟
10.1.1 Crystal Structures

A stage when the Ruby(红宝石) production process comes to end
A stage when the production process comes to end Ruby (红宝石 )
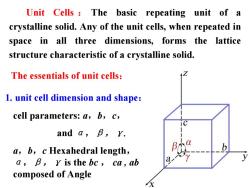
Unit Cells The basic repeating unit of a crystalline solid.Any of the unit cells,when repeated in space in all three dimensions,forms the lattice structure characteristic of a crystalline solid. The essentials of unit cells: 1.unit cell dimension and shape: cell parameters:a,b,c, and a,B,Y. a,b,c Hexahedral length, a,B,y is the be,ca,ab a composed of Angle
Unit Cells : The basic repeating unit of a crystalline solid. Any of the unit cells, when repeated in space in all three dimensions, forms the lattice structure characteristic of a crystalline solid. cell parameters: a,b,c, and α,β,γ. a,b,c Hexahedral length, α,β,γ is the bc , ca , ab composed of Angle The essentials of unit cells: 1. unit cell dimension and shape:
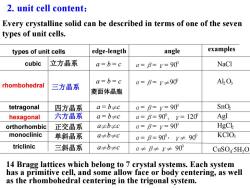
2.unit cell content: Every crystalline solid can be described in terms of one of the seven types of unit cells. types of unit cells edge-length angle examples cubic 立方晶系 a=b=c a=B=y=90 NaCl a=b=c rhombohedral 三方晶系 a=B=y≠90 AbO; 菱面体晶胞 tetragonal 四方晶系 a=b≠c a=B=y=90 SnO hexagonal 六方晶系 a=b≠c a=B=90°,y=120 AgI orthorhombic 正交晶系 a≠b≠c a=B=y=90 HgCk monoclinic 单斜晶系 a≠b≠c a=B=90°,y≠90° KCIO3 triclinic 三斜晶系 a≠b≠c a≠B≠y≠90 CuSO5H2O 14 Bragg lattices which belong to 7 crystal systems.Each system has a primitive cell,and some allow face or body centering,as well as the rhombohedral centering in the trigonal system
2. unit cell content: 14 Bragg lattices which belong to 7 crystal systems. Each system has a primitive cell, and some allow face or body centering, as well as the rhombohedral centering in the trigonal system. Every crystalline solid can be described in terms of one of the seven types of unit cells. cubic rhombohedral tetragonal hexagonal orthorhombic monoclinic triclinic edge-length angle examples 立方晶系 a = b = c α=β=γ= 900 NaCl 三方晶系 a = b = c α=β=γ≠900 Al2O3 四方晶系 a = b≠c α=β=γ= 900 SnO2 六方晶系 a = b≠c α=β= 900 , γ= 1200 AgI 正交晶系 a≠b≠c α=β=γ= 900 HgCl2 单斜晶系 a≠b≠c α=β= 900 , γ≠ 900 KClO3 三斜晶系 a≠b≠c α≠β≠γ≠ 900 CuSO4·5H2O types of unit cells 菱面体晶胞
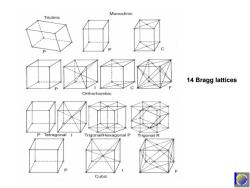
Monoclinic Triclinic 14 Bragg lattices Orthorhombic P Tetragonal Trigonal/Hexagonal P Trigonal R Cubic
14 Bragg lattices

10.1.2 Crystal defects(晶体缺陷) l.Schottky defect(Latent defects,本征缺陷) A Schottky defect consists of an atom or ion vacancy in a crystal lattice,but the stoichiometry of a compound (and thus electrical neutrality)must be retained.In a metal lattice,a vacant atom site may be present.由于晶体中晶格结点上的微粒热涨落所导致的 缺陷
10.1.2 Crystal defects (晶体缺陷 ) 1.Schottky defect (Latent defects,本征缺陷 ) A Schottky defect consists of an atom or ion vacancy in a crystal lattice, but the stoichiometry of a compound (and thus electrical neutrality) must be retained. In a metal lattice, a vacant atom site may be present.由于晶体中晶格结点上的微粒热涨落所导致的 缺陷
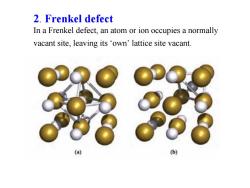
2.Frenkel defect In a Frenkel defect,an atom or ion occupies a normally vacant site,leaving its own'lattice site vacant. 6)
2. Frenkel defect In a Frenkel defect, an atom or ion occupies a normally vacant site, leaving its ‘own’ lattice site vacant
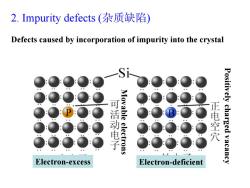
2.Impurity defects(杂质缺陷) Defects caused by incorporation of impurity into the crystal Si 活动电子 Movable electrons 正电空穴 Positively charged vacancy Electron-excess Electron-deficient
2. Impurity defects (杂质缺陷 ) Electron-excess Electron-deficient Positively charged vacancy Movable electrons Defects caused by incorporation of impurity into the crystal
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 04 Chemical equilibria, entropy and Gibbs function.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 05 Acid-Base Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 03 Chemical kinetics.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 02 Thermochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 01 前言 Preface(负责人:周云山).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十六-十七综合自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十六章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十七章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十五章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十三-十四章综合自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十四章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十二章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十三章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十一章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第八章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第九章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第七章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第四章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第六章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 11 Coordination Compound Structures.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 12 The s-Block Elements.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 06 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 08 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 13 The p-block elements(Ⅰ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 07 Redox Reactions and Base of Electrochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 09 Molecular Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 17 The d-block elements(Ⅱ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 14 p-block elements(Ⅱ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 15 p-block elements(Ⅲ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 16 The d-block elements(Ⅰ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 2 Thermochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 5 Acid-Base Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 6 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 7 Redox Reactions and the Base of Electrochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 8 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 1 Preface.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 2 Thermochemistry.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 5 Acid-Base Equilibrium.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 6 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.ppt
