北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 03 Chemical kinetics

Chapter 3 Chemical kinetics 3.1 Brief introduction of chemical reaction rates 3.2 Brief introduction of effect of concentration of reactants on reaction rate-the rate expression 3.3 Brief introduction of effect of temperature on reaction rate-Arrhenius equation 3.4 Brief introduction of theory of reaction rate and reaction mechanisms 3.5 Brief introduction of catalyst and catalysis
Chapter 3 Chemical kinetics 3.1 Brief introduction of chemical reaction rates 3.2 Brief introduction of effect of concentration of reactants on reaction rate —the rate expression 3.3 Brief introduction of effect of temperature on reaction rate—Arrhenius equation 3.4 Brief introduction of theory of reaction rate and reaction mechanisms 3.5 Brief introduction of catalyst and catalysis

3.1 Brief Introduction of chemical reaction rates 3.1.1 Average rates and instantaneous rates of chemical reactions
§3.1 Brief Introduction of chemical reaction rates 3.1.1 Average rates and instantaneous rates of chemical reactions

3.1.1 Average rates and instantaneous rates of chemical reactions 1.Average rate the change in concentration of a reagent over a certain time period A t 1 AcB 名△t
3.1.1 Average rates and instantaneous rates of chemical reactions 1. Average rate the change in concentration of a reagent over a certain time period Δ t 1 B B Δ Δ = t c ν υ
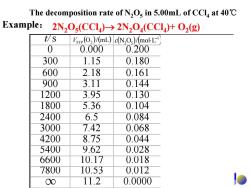
The decomposition rate of N,Os in 5.00mL of CCla at 40C Example:2N,O(CCI)>2N2O(CCI)+O2(g) t/S Vsrp(O2)/(mL)dN,O)/molL 0 0.000 0.200 300 1.15 0.180 600 2.18 0.161 900 3.11 0.144 1200 3.95 0.130 1800 5.36 0.104 2400 6.5 0.084 3000 7.42 0.068 4200 8.75 0.044 5400 9.62 0.028 6600 10.17 0.018 7800 10.53 0.012 00 11.2 0.0000
t/s 0 0.000 0.200 300 1.15 0.180 600 2.18 0.161 900 3.11 0.144 1200 3.95 0.130 1800 5.36 0.104 2400 6.5 0.084 3000 7.42 0.068 4200 8.75 0.044 5400 9.62 0.028 6600 10.17 0.018 7800 10.53 0.012 11.2 0.0000 ( ) (mL/O ) V 2STP ( ) ( )1 52 Lmol/ON − c ⋅ ( )11 sLmol/ −− υ ⋅⋅ 5 1029.7 − × 5 1046.6 − × 5 1080.5 − × 5 1021.5 − × 5 1069.4 − × 5 1079.3 − × 5 1004.3 − × 5 1003.1 − × 5 1044.2 − × 5 1059.1 − × ∞ The decomposition rate of N2O5 in 5.00mL of CCl4 at 40℃ 2N2O5(CCl4)→ 2N2O4(CCl4)+ O2 Example: (g)

2N205(CC14)2N204(CC14)+O2(g) t1=0s c1N205)=0.200molL1 t2=300s c2N20s)=0.180molL1 D=-(0.1800,200mol-L=33×109mol-L2-s 2×300s 2.Instantaneous rate The instantaneous rate of a reaction is the limit of the average reaction rate
t1= 0 s c1(N2O5) = 0.200 mol·L-1 t2=300 s c2(N2O5) = 0.180 mol·L-1 5 1-1- -1 sLmol103.3 s3002 Lmol ⋅⋅×= × (0.180− − 0.200) ⋅ = − υ 2. Instantaneous rate The instantaneous rate of a reaction is the limit of the average reaction rate. 2N2O4 (CCl4) + O2 2N (g) 2O5(CCl4)

3.2 Brief introduction of effect of concentration of reactants on reaction rate -the rate expression -3.2.1 The rate expression
§3.2 Brief introduction of effect of concentration of reactants on reaction rate —the rate expression 3.2.1 The rate expression
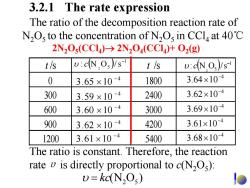
3.2.1 The rate expression The ratio of the decomposition reaction rate of N2Os to the concentration of N2Os in CCla at 40C 2N20s(CC4)-→2N204(CCl4)+O2(g) t/s v:cNOs)/s t/s v:dNO)/s- 0 3.65×10-4 1800 3.64×104 300 3.59×104 2400 3.62×104 600 3.60×10-4 3000 3.69×104 900 3.62×10-4 4200 3.61×104 1200 3.61×10-4 5400 3.68×104 The ratio is constant.Therefore,the reaction rate v is directly proportional to c(N2O): v=kc(N2Os)
The ratio of the decomposition reaction rate of N 2 O5 to the concentration of N 2 O5 in CCl4 at 40 ℃ t /s t /s 0 1800 300 2400 600 3000 900 4200 1200 5400 ( ) 1 5 s/ON: 2 − υ c 4 1065.3 − × 4 1060.3 − × 4 1062.3 − × 4 1061.3 − × 4 1059.3 − × 4 1069.3 − × 4 1062.3 − × 4 1064.3 − × 4 1068.3 − × 4 1061.3 − × ( ) 1 5 s/ON: 2 − υ c 3.2.1 The rate expression The ratio is constant. Therefore, the reaction rate υ is directly proportional to c(N 2 O 5): )ON( 52 υ = kc 2N 2 O 5(CCl 4 ) → 2N 2 O 4(CCl 4)+ O 2(g)
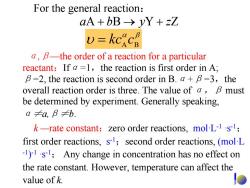
For the general reaction: aA+bB→yY+zZ v=kckc a,B-the order of a reaction for a particular reactant:If a =1,the reaction is first order in A; B=2,the reaction is second order in B.a+B=3,the overall reaction order is three.The value of a,B must be determined by experiment.Generally speaking, a≠a,B≠b. k-rate constant:zero order reactions,mol-L-1's1; first order reactions,s1;second order reactions,(mol L 1)1s;Any change in concentration has no effect on the rate constant.However,temperature can affect the value of k
For the general reaction : α,β—the order of a reaction for a particular reactant:If α = 1 ,the reaction is first order in A; β =2, the reaction is second order in B. α + β = 3 ,the overall reaction order is three. The value of α,β must be determined by experiment. Generally speaking, α≠a,β≠b. k —rate constant:zero order reactions, mol·L-1 ·s-1; first order reactions, s-1;second order reactions, (mol·L -1 )-1 ·s-1; Any change in concentration has no effect on the rate constant. However, temperature can affect the value of k. + ba → y + zZYBA βα υ BA = ckc

3.3 Brief introduction of effect of temperature on reaction rate Arrhenius equation -3.3.1 Arrhenius equation -3.3.2 Application of the Arrhenius equation
3.3.1 Arrhenius equation §3.3 Brief introduction of effect of temperature on reaction rate — Arrhenius equation 3.3.2 Application of the Arrhenius equation
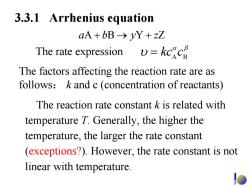
3.3.1 Arrhenius equation aA+bB→yY+zZ The rate expression v=kcacp The factors affecting the reaction rate are as follows:k and c(concentration of reactants) The reaction rate constant k is related with temperature T.Generally,the higher the temperature,the larger the rate constant (exceptions?).However,the rate constant is not linear with temperature
The factors affecting the reaction rate are as follows : k and c (concentration of reactants) The reaction rate constant k is related with temperature T. Generally, the higher the temperature, the larger the rate constant (exceptions?). However, the rate constant is not linear with temperature. The rate expression βα υ BA = ckc 3.3.1 Arrhenius equation + ba y +→ zZYBA
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 02 Thermochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 01 前言 Preface(负责人:周云山).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十六-十七综合自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十六章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十七章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十五章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十三-十四章综合自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十四章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十二章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十三章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十一章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第八章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第九章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第七章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第四章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第六章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第五章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第二章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第三章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 05 Acid-Base Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 04 Chemical equilibria, entropy and Gibbs function.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 10 Solid Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 11 Coordination Compound Structures.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 12 The s-Block Elements.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 06 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 08 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 13 The p-block elements(Ⅰ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 07 Redox Reactions and Base of Electrochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 09 Molecular Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 17 The d-block elements(Ⅱ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 14 p-block elements(Ⅱ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 15 p-block elements(Ⅲ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2011)Chapter 16 The d-block elements(Ⅰ).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 2 Thermochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 5 Acid-Base Equilibrium.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 6 Precipitation-Solubility Equilibria.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 7 Redox Reactions and the Base of Electrochemistry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(教学课件,2012)Chapter 8 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件,2013)Chapter 1 Preface.ppt
