同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 5 The Normal Distribution and Sampling Distributions

Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chapter 5 Some Important Discrete Probability Distributions Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 5-1
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 5-1 Chapter 5 Some Important Discrete Probability Distributions Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft® Excel

Chapter Goals After completing this chapter,you should be able to: Interpret the mean and standard deviation for a discrete probability distribution ■ Explain covariance and its application in finance Use the binomial probability distribution to find probabilities Describe when to apply the binomial distribution Discuss the Hypergeometric distribution Review the Poisson distribution Chap 5-2 Tongji University School of Economics&Management Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 5-2 Tongji University School of Economics & Management Chapter Goals After completing this chapter, you should be able to: ▪ Interpret the mean and standard deviation for a discrete probability distribution ▪ Explain covariance and its application in finance ▪ Use the binomial probability distribution to find probabilities ▪ Describe when to apply the binomial distribution ▪ Discuss the Hypergeometric distribution ▪ Review the Poisson distribution

Introduction to Probability Distributions Random Variable Represents a possible numerical value from an uncertain event Discrete random variables produce outcomes that come from a counting process (e.g. number of classes you are taking). Continuous random variables produce outcomes that come from a measurement (e.g. your annual salary,or your weight). Chap 5-3 Tongji University School of Economics Management Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 5-3 Tongji University School of Economics & Management Introduction to Probability Distributions ▪ Random Variable ▪ Represents a possible numerical value from an uncertain event ▪ Discrete random variables produce outcomes that come from a counting process (e.g. number of classes you are taking). ▪ Continuous random variables produce outcomes that come from a measurement (e.g. your annual salary, or your weight)
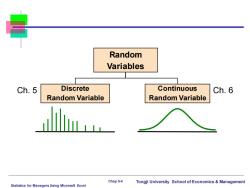
Random Variables Ch.5 Discrete Continuous Ch.6 Random Variable Random Variable Chap 5-4 Tongji University School of Economics Management Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 5-4 Tongji University School of Economics & Management Random Variables Discrete Random Variable Continuous Random Variable Ch. 5 Ch. 6

Discrete Random Variables Can only assume a countable number of values Examples: ■Roll a die twice Let X be the number of times 4 comes up (then X could be 0,1,or 2 times) Toss a coin 5 times. Let X be the number of heads (then X=0,1,2,3,4,or5) Chap 5-5 Tongji University School of Economics Management Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 5-5 Tongji University School of Economics & Management Discrete Random Variables ▪ Can only assume a countable number of values Examples: ▪ Roll a die twice Let X be the number of times 4 comes up (then X could be 0, 1, or 2 times) ▪ Toss a coin 5 times. Let X be the number of heads (then X = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5)
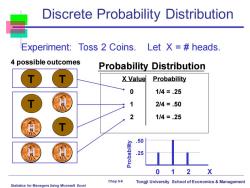
Discrete Probability Distribution Experiment:Toss 2 Coins.Let X =heads. 4 possible outcomes Probability Distribution X Value Probability 0 114=.25 2/4=.50 2 114=.25 50 2 0 1 2 X Chap 5-6 Tongji University School of Economics Management Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 5-6 Tongji University School of Economics & Management Probability Distribution 0 1 2 X X Value Probability 0 1/4 = .25 1 2/4 = .50 2 1/4 = .25 .50 .25 Probability Experiment: Toss 2 Coins. Let X = # heads. T T Discrete Probability Distribution 4 possible outcomes T T H H H H

Practices in Class -Practice:Let the random variable X represents the number of boys in a family,construct the probability distribution for a family of three children 89 P(X)) 0 1/8 1 3/8 13 2 3/8 3 1/8 Chap 5-7 Tongji University School of Economics Management Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 5-7 Tongji University School of Economics & Management Practices in Class ▪ Practice: Let the random variable X represents the number of boys in a family, construct the probability distribution for a family of three children X P(X) 0 1/8 1 3/8 2 3/8 3 1/8
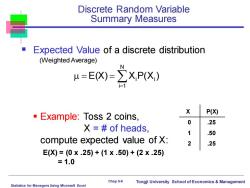
Discrete Random Variable Summary Measures Expected Value of a discrete distribution (Weighted Average) N H=EX)=∑XP(X) X P(X) Example:Toss 2 coins, 0 .25 X=#of heads, .50 compute expected value of X: .25 E(X)=(0x.25)+(1×.50)+(2x.25) =1.0 Chap 5-8 Tongji University School of Economics Management Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 5-8 Tongji University School of Economics & Management Discrete Random Variable Summary Measures ▪ Expected Value of a discrete distribution (Weighted Average) ▪ Example: Toss 2 coins, X = # of heads, compute expected value of X: E(X) = (0 x .25) + (1 x .50) + (2 x .25) = 1.0 X P(X) 0 .25 1 .50 2 .25 = = = N i 1 i i E(X) X P(X )
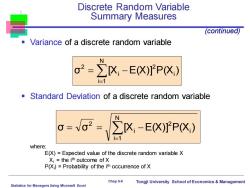
Discrete Random Variable Summary Measures (continued) Variance of a discrete random variable W o2=∑X,-EX)PPX,) i=1 Standard Deviation of a discrete random variable N =V2=∑X-EXPX) where: E(X)=Expected value of the discrete random variable X Xi the ith outcome of X P(Xi)=Probability of the ith occurrence of X Chap 5-9 Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Tongji University School of Economics Management
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 5-9 Tongji University School of Economics & Management ▪ Variance of a discrete random variable ▪ Standard Deviation of a discrete random variable where: E(X) = Expected value of the discrete random variable X Xi = the ith outcome of X P(Xi ) = Probability of the ith occurrence of X Discrete Random Variable Summary Measures = = − N i 1 i 2 i 2 σ [X E(X)] P(X ) (continued) = = = − N i 1 i 2 i 2 σ σ [X E(X)] P(X )
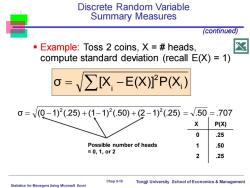
Discrete Random Variable Summary Measures (continued) Example:Toss 2 coins,X =heads, compute standard deviation (recall E(X)=1) V∑X-E(X]P(X) 0=V0-1)2(.25)+(1-1)2(.50)+(2-1)2(.25)=V.50=.707 X P(X) 0 .25 Possible number of heads 1 .50 =0,1,0r2 2 25 Chap 5-10 Tongji University School of Economics Management Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 5-10 Tongji University School of Economics & Management ▪ Example: Toss 2 coins, X = # heads, compute standard deviation (recall E(X) = 1) Discrete Random Variable Summary Measures σ [X E(X)] P(X )i 2 i = − σ (0 1) (.25) (1 1) (.50) (2 1) (.25) .50 .707 2 2 2 = − + − + − = = (continued) X P(X) 0 .25 1 .50 2 .25 Possible number of heads = 0, 1, or 2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 13 Statistical Applications in Quality Management.pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 12 Time series based Demand Management.pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Simple Linear Regression.pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 Analysis of Variance(ANOVA).pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 9 Two-Sample Tests with Numerical Data.pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 8 Fundamentals of Hypothesis Testing(One-Sample Tests).pdf
- Chapter 7 Confidence Interval Estimation.pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution and Other Continuous Distributions.pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 4 Basic Probability(主讲:王世进).pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Numerical Descriptive Measures.pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Presenting Data in Tables and Charts.pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 Introduction and Data Collection(Applied Statistics).pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)考核试卷(B卷)2011-2012学年第2学期(无答案).pdf
- 同济大学:《应用统计学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)考核试卷(A卷)2011-2012学年第2学期(无答案).pdf
- 新乡医学院:《卫生统计学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验五 统计表与统计图.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《卫生统计学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验五 统计表与统计图.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《卫生统计学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验四 卡方检验.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《卫生统计学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验四 卡方检验(教师:晁灵).pdf
- 新乡医学院:《卫生统计学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验三 方差分析实验.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《卫生统计学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验三 方差分析.pdf
- 《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(整理资料)Matlab在统计方面的应用.pdf
- 《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(整理资料)正态分布的前世今生.pdf
- 《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)概率论与数理统计知识点总结.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《随机过程概论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 4 随机过程通过线性系统.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《随机过程概论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 9 检测理论.pdf
- 沈阳航空航天大学:自动化学院《误差理论及数据处理》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 吉林大学:《医学统计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 医学统计中的基本概念、第二章 平均水平(集中趋势)的统计描述(主讲:田迎春).ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学统计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第三章 离散趋势的统计描述、第四章 抽样误差与假设检验.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学统计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第五章 t检验、第六章 方差分析、第七章 相对数及其应用.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学统计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 方差分析、第七章 相对数及其应用.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学统计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 卡方检验、第九章 非参数检验方法.ppt
- 吉林大学:《医学统计学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十章 线性相关与回归.ppt
- 农业院校《试验设计与分析》课程参考资料(多变量分析方法)DUDE - A User-Friendly Crop Information System.pdf
- 农业院校《试验设计与分析》课程参考资料(多变量分析方法)GGE Biplot vs. AMMI Analysis of Genotype-by-Environment Data.pdf
- 农业院校《试验设计与分析》课程参考资料(多变量分析方法)Logistic模型的参数估计.pdf
- 农业院校《试验设计与分析》课程参考资料(多变量分析方法)Logistic模型配合家禽生长资料参数估计方法比较的MonteCarlo研究.pdf
- 农业院校《试验设计与分析》课程参考资料(多变量分析方法)Logistic模型配合家禽生长资料参数估计方法比较的MonteCarlo研究.pdf
- 农业院校《试验设计与分析》课程参考资料(多变量分析方法)Two Types of GGE Biplots for Analyzing Multi-Environment Trial Data.pdf
- 农业院校《试验设计与分析》课程参考资料(多变量分析方法)典范性状的决策分析.pdf
- 农业院校《试验设计与分析》课程参考资料(多变量分析方法)回归分析中的模型偏差及其防止.pdf
