《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学大纲 A Teaching Outline of Histology and Embryology(留学生)

A Teaching Outline of Histology and Embryology for Foreign Students) Deportment of Histology and Embryology Chongqing medical university 2012-9
1 A Teaching Outline of Histology and Embryology (for Foreign Students) Deportment of Histology and Embryology Chongqing medical university 2012-9

Preface 1.Course Title:Histology and Embryology Credit:2 Teaching hours:36 Text book:Textbook of Histology and Embryology.唐军民,李继承主编, 北京大学医学出版社,2011 2.Course General Description: Histology and Embryology are two courses.They are different but closely correlated. Histology (Microanatomy)is a science which studies the normal microstructure of the human body and the relationship between the microstructure and its functions.Cell is the basic structural and functional units ofhuman body.Cells and extracellular matrix form thetissue. Tissue can be divided into 4 kinds of primary tissue,they are Epithelial tissue,Connective tissue,Muscle tissue and Nervous tissue.Organs are formed by four types oftissue,have their special structure and functions.For example the skin is consisted of epithelium and connective tissue,covered outside of body.The skin can receive the stimulation of environment;secreting metabolite;regulating body temperature,at so on. Several organs which have correlated functions form system.For example: digestive system is consisted of mouth,esophagus,stomach,intestine and anus
2 Preface 1. Course Title : Histology and Embryology Credit: 2 Teaching hours: 36 Text book: Textbook of Histology and Embryology . 唐军民,李继承主编, 北京大学医学出版社,2011 2. Course General Description: Histology and Embryology are two courses. They are different but closely correlated. Histology (Microanatomy) is a science which studies the normal microstructure of the human body and the relationship between the microstructure and its functions. Cell is the basic structural and functional units of human body. Cells and extra cellular matrix form the tissue. Tissue can be divided into 4 kinds of primary tissue, they are Epithelial tissue, Connective tissue, Muscle tissue and Nervous tissue. Organs are formed by four types of tissue, have their special structure and functions. For example: the skin is consisted of epithelium and connective tissue,covered outside of body. The skin can receive the stimulation of environment; secreting metabolite; regulating body temperature, at so on. Several organs which have correlated functions form system. For example: digestive system is consisted of mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestine and anus
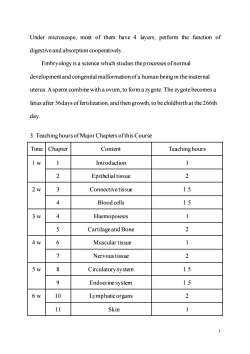
Under microscope,most of them have 4 layers;perform the function of digestive and absorption cooperatively. Embryology is a science which studies the processes ofnormal development and congenital malformation ofa human being in the maternal uterus.Asperm combine with aovum,to form azygote.The zygote becomesa fetus after 56days offertilization,and then growth,to be childbirth at the 266th day 3.Teaching hours of Major Chapters ofthis Course Time Chapter Content Teaching hours lw 1 Introduction 1 2 Epithelial tissue 2 2w Connectivetissue 1.5 4 Blood cells 1.5 3w 4 Haemopoiesis 1 5 Cartilageand Bone 2 4w 6 Muscular tissue 1 Nervoustissue 2 5w 8 Circulatorysystem 1.5 9 Endocrine system 1.5 6w 10 Lymphatic organs 2 11 Skin 3
3 Under microscope, most of them have 4 layers; perform the function of digestive and absorption cooperatively. Embryology is a science which studies the processes of normal development and congenital malformation of a human being in the maternal uterus. A sperm combine with a ovum, to form a zygote. The zygote becomes a fetus after 56days of fertilization, and then growth, to be childbirth at the 266th day. 3. Teaching hours of Major Chapters of this Course Time Chapter Content Teaching hours 1 w 1 Introduction 1 2 Epithelial tissue 2 2 w 3 Connective tissue 1.5 4 Blood cells 1.5 3 w 4 Haemopoiesis 1 5 Cartilage and Bone 2 4 w 6 Muscular tissue 1 7 Nervoustissue 2 5 w 8 Circulatory system 1.5 9 Endocrine system 1.5 6 w 10 Lymphatic organs 2 11 Skin 1
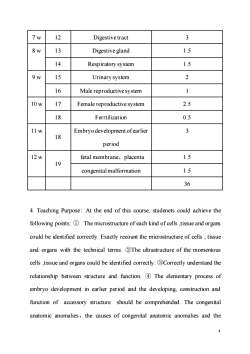
7w 12 Digestivetract 3 8w 13 Digestive gland 1.5 14 Respiratory system 1.5 9w 15 Urinary system 2 16 Male reproductivesystem 1 10w 17 Female reproductive system 2.5 18 Ferrtilization 0.5 11w Embryo development ofearlier 3 18 period 12w fetal membrane,placenta 1.5 19 congenital malformation 1.5 6 4.Teaching Purpose:At the end of this course,studenets could achieve the following points:The microstructure of each kind of cells,tissue and organs could be identified correctly.Exactly recount the microstructure of cells,tissue and organs with the technical terms.2The ultrastructure of the momentous cells,tissue and organs could be identified correctly.Correctly understand the relationship between structure and function.The elementary process of embryo development in earlier period and the developing,construction and function of accessory structure should be comprehended.The congenital anatomic anomalies,the causes of congenital anatomic anomalies and the
4 7 w 12 Digestive tract 3 8 w 13 Digestive gland 1.5 14 Respiratory system 1.5 9 w 15 Urinary system 2 16 Male reproductive system 1 10 w 17 Female reproductive system 2.5 18 Ferrtilization 0.5 11 w 18 Embryo development of earlier period 3 12 w 19 fetal membrane,placenta 1.5 congenital malformation 1.5 36 4. Teaching Purpose: At the end of this course, studenets could achieve the following points: ① The microstructure of each kind of cells ,tissue and organs could be identified correctly. Exactly recount the microstructure of cells , tissue and organs with the technical terms. ②The ultrastructure of the momentous cells ,tissue and organs could be identified correctly. ③Correctly understand the relationship between structure and function. ④ The elementary process of embryo development in earlier period and the developing, construction and function of accessory structure should be comprehended. The congenital anatomic anomalies,the causes of congenital anatomic anomalies and the

critical periods in human prenatal development should be grasped 5 Understanding the commonly used technique in Histology and Embryology,as paraffin section,ultrathin section,immunohistochemistry and culture in vitro. 5.Teaching Approach:Instructors should study this outline,and grasp the focal points and difficult points.The new progress could be added in teaching. Instructors should recommend the teaching resources in the network of our university,and pay attention to the students,to conduct their autonomicstudy. 6.Checking Modality:Final theory test of semester.In the process of caurse, check on work attendance and answer question will be considered. 7.Reference (1)William K.Ovalle.Netter's Essential Histology.W.B.Saunders Company, 2008 (2)Keith L.Moor.Before We Are Bore.6th ed.W.B.Saunders Company,2003 (3)Keith L.Moor.The Developing Human 8th ed.W.B.Saunders Company, 2008 (4)Junqueira LC.et al.Basic Histology(9th Ed).Stanford:Appleton&Lange, 1998 (5)SadlerIV.Langman's Medical Embryology(8th ed).Philadelphia: LippincottWilliams Wilkins,2000 (6)William J.Larsen.ofHuman Embryology,PHD.Churchill Livingston,1998 (7)James C.McKenzie Robert M.Klein,Basic concepts in cell biology and histology,.北京大学医学出版社2003 5
5 critical periods in human prenatal development should be grasped ⑤ Understanding the commonly used technique in Histology and Embryology,as paraffin section,ultrathin section,immunohistochemistry and culture in vitro. 5. Teaching Approach: Instructors should study this outline, and grasp the focal points and difficult points. The new progress could be added in teaching. Instructors should recommend the teaching resources in the network of our university, and pay attention to the students,to conduct their autonomic study. 6. Checking Modality: Final theory test of semester. In the process of caurse, check on work attendance and answer question will be considered. 7. Reference (1) William K. Ovalle. Netter`s Essential Histology.W.B.Saunders Company, 2008 (2) Keith L.Moor. Before We Are Bore . 6th ed. W.B.Saunders Company, 2003 (3) Keith L.Moor. The Developing Human 8th ed. W.B.Saunders Company, 2008 (4) Junqueira LC. et al.Basic Histo1ogy(9th Ed).Stanford:Appleton&Lange, 1998 (5) SadlerⅣ . Langman’s Medical Embryology(8th ed) . Philadelphia : LippincottWilliams&Wilkins,2000 (6) William J. Larsen. of Human Embryology ,PHD.Churchill Livingston, 1998 (7) James C. McKenzie Robert M. Klein, Basic concepts in cell biology and histology, 北京大学医学出版社 2003

(8)Cormack D.Clinical Integrated Histology.Philadelphia:Lippincott-Raven 1998 (Weiwei Wang) Catalogue
6 (8) Cormack D.C1inical Integrated Histology.Philadelphia:Lippincott-Raven, 1998 (Weiwei Wang) Catalogue

Chapter 1.Introduction.8 Chapter2.Epithelial tissue.9 Chapter3.Connective tissue. 11 Chapter4.Blood cells and Haemopoiesis.13 Chapter5.Cartilage and Bone.15 Chapter6.Muscular tissue.16 Chapter7.Nervoustissue.18 Chapter8.Circulatory system.20 Chapter9.Endocrinesystem Chapter 10.Lymphatic organs.23 Chapter 11.Skin. .24 Chapter 12.Digestive tract.5 Chapter 13.Digestive gland.27 Chapter 14.Respiratory system. Chapter 15.Urinary system.3 Chapter 16.Male reproductivesystem.32 Chapter 17.Female reproductive system. Chapter18.Embryo development ofearlier period.36 Chapter 19.fetal membrane,placenta,congenital malformation.39 Chapter1.Introduction
7 Chapter 1. Introduction .8 Chapter 2. Epithelial tissue.9 Chapter 3. Connective tissue .11 Chapter 4. Blood cells and Haemopoiesis.13 Chapter 5. Cartilage and Bone.15 Chapter 6. Muscular tissue.16 Chapter 7. Nervous tissue .18 Chapter 8. Circulatory system.20 Chapter 9. Endocrine system.22 Chapter 10. Lymphatic organs.23 Chapter 11. Skin.24 Chapter 12. Digestive tract.25 Chapter 13. Digestive gland .27 Chapter 14. Respiratory system.28 Chapter 15. Urinary system .31 Chapter 16. Male reproductive system .32 Chapter 17. Female reproductive system.34 Chapter 18. Embryo development of earlier period . .36 Chapter 19. fetal membrane,placenta,congenital malformation.39 Chapter1. Introduction

[Teaching aim and requirements] 1.Understanding:what are histology and Embryology. 2.Mastering:what is tissue?what is paraffin sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3.Understanding:electron microscopy and other study methods. [Teaching contents] 1.What are histology and Embryology?Why medical students should study HandE? 2.Histological Methods (1)The paraffin sectionsstained with Hematoxylin and Eosin for LM (2)Other methods for LM(frozen section et al (3)The Ultra-thinsections for the Transmission Electron Microscope (Comparison between LM and EM) Scanning Electron Microscope (4)Histochemistry and cytochemistry (5)Immunocytochemistry (6)Tissueand cell culture Focal and Difficult points] Focal points The paraffinsections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin Difficult points Histochemistry and Cytochemistry,Immunocytochemistry
8 [Teaching aim and requirements] 1. Understanding: what are histology and Embryology. 2. Mastering: what is tissue? what is paraffin sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3. Understanding: electron microscopy and other study methods. [Teaching contents] 1. What are histology and Embryology? Why medical students should study H and E? 2. Histological Methods: (1) The paraffin sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin for LM (2) Other methods for LM ( frozen section et al ) (3) The Ultra-thin sections for the Transmission Electron Microscope (Comparison between LM and EM) Scanning Electron Microscope (4) Histochemistry and cytochemistry (5) Immunocytochemistry (6) Tissue and cell culture [Focal and Difficult points] Focal points The paraffin sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin Difficult points Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, Immunocytochemistry

[Teaching methods]Class Teaching [Teaching hours]1 hour (Weiwei Wang) Chapter 2.Epithelial Tissue [Teaching aim and requirements] 1.Mastering:the general features and classificationofepithelial tissue 2.Mastering:the structural features,distribution,classification,functions of covering Epithelium 3.Mastering:the structural features,functions ofmicrovilliand cilia 4.Understanding the ultrastructure and functionofcell junction 5.Understanding thestructure and function ofbasement membrane 6.Having the conception of glandular epithelium and glands,structural features of endocrine gland and exocrine [Teaching contents] 1.General description: Composition,distribution,classification,functions oftheepithelium 2.Covering Epithelium (1)Structural Features ofcovering Epithelium (2)Classification-rule (3)The common types of covering epithelium structure,location and
9 [Teaching methods]Class Teaching [Teaching hours] 1 hour (Weiwei Wang) Chapter 2. Epithelial Tissue [Teaching aim and requirements] 1. Mastering: the general features and classification of epithelial tissue 2. Mastering: the structural features, distribution, classification, functions of covering Epithelium 3. Mastering: the structural features, functions of microvilli and cilia 4. Understanding the ultrastructure and function of cell junction 5. Understanding the structure and function of basement membrane 6. Having the conception of glandular epithelium and glands, structural features of endocrine gland and exocrine. [Teaching contents] 1. General description: Composition, distribution, classification, functions of the epithelium 2.Covering Epithelium (1) Structural Features of covering Epithelium (2) Classification-rule (3) The common types of covering epithelium ( structure, location and

functions) Simple squamous epithelium Simple columnar epithelium Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium Stratified squamous epithelium Transitional epithelium 4.Epithelial specialisations (1)Free surface:microvilli and cilia (2)Lateral surface: cell junctions Tight junction,Desmosome,Gap junction,Junctional complex (3)Basal surface:basement membrane 5.Glandular epithelium and glands Focaland Difficult points] Focal points The structure,location and functions ofcoveringepithelium Difficult points Cell junctions [Teaching methods]Class Teaching [Teaching hours]2 hours (Weiwei Wang) Chapter 3.Connective Tissue proper
10 functions) Simple squamous epithelium Simple columnar epithelium Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium Stratified squamous epithelium Transitional epithelium 4. Epithelial specialisations (1) Free surface: microvilli and cilia (2) Lateral surface: cell junctions Tight junction, Desmosome, Gap junction, Junctional complex (3) Basal surface: basement membrane 5. Glandular epithelium and glands [Focal and Difficult points] Focal points The structure, location and functions of covering epithelium Difficult points Cell junctions [Teaching methods] Class Teaching [Teaching hours] 2 hours (Weiwei Wang) Chapter 3. Connective Tissue proper
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学实习指导(共二十个知识点).doc
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十七章 肾功能不全(renal insufficiency).ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十六章 肝功能不全(肝性脑病 hepatic encephalopathy).ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十五章 肺功能不全(呼吸衰竭 respiratory failure).ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十四章 心功能不全(心力衰竭 heart failure).ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十三章 缺血-再灌注损伤 Ischemia -reperfusion injury.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 休克 shock.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 凝血与抗凝血平衡紊乱(disseminated intravascular coagulation DIC).ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 应激 stress.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 细胞凋亡与疾病 Apoptosis and Diseases.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 细胞增殖分化异常与异常 Disorders of Cell Proliferation and Differentitation.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 细胞信号转导异常与疾病 第二节 细胞信号转导障碍与疾病.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 细胞信号转导异常与疾病 第一节 细胞信号转导 cellular signal transduction.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 发热 fever.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 缺氧 hypoxia.ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 酸碱平衡紊乱(acid-base disturbances).ppt
- 《病理生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 水、电解质代谢紊乱.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理生理学》课程教学资源(学习指导,共十五章).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理生理学》课程作业试题集(绪论、疾病概论,含参考答案).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理生理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十七章 肾功能不全.doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学大纲(供七年制临床医学等专业使用).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学大纲(供五年制临床医学等专业使用).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学大纲(人体显微形态学实验教学大纲,30学时).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学大纲(人体显微形态学实验教学大纲,45学时).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程理论授课教案(重庆医科大学:顾恒伟).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第1章 组织学绪论(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第3章 结缔组织(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第4章 血液、淋巴和血细胞发生(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第5章 软骨和骨(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第6章 肌组织(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第7章 神经组织(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第9章 眼与耳(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第10章 循环系统(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第11章 皮肤(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第12章 免疫系统(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第13章 内分泌系统(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第14章 消化管(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第15章 消化腺(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第16章 呼吸系统(含参考答案).doc
- 《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(作业习题)第17章 泌尿系统(含参考答案).doc
