华南师范大学:《数值计算方法》课程PPT教学课件(数值分析 Numerical Analysis)Chapter 1 Solution of Nonlinear Equations f(x)=0(主讲:谢骊玲)

Chapter 1.Solution of Nonlinear Equations f(x)=0 华南师范大学数学科学学院谢骊玲
Chapter 1. Solution of Nonlinear Equations f (x)=0 华南师范大学数学科学学院 谢骊玲
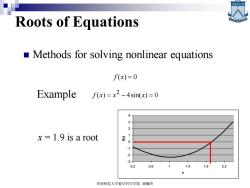
Roots of Equations Methods for solving nonlinear equations f(x)=0 Example f(x)=x2-4sin(x)=0 2 x=1.9 is a root -1 -2 -3 0.2 0.6 2.2 华南师范大学数学科学学院谢骊玲
Roots of Equations ◼ Methods for solving nonlinear equations f (x) = 0 • Example ( ) 4sin( ) 0 2 f x = x − x = -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 0.2 0.6 1 1.4 1.8 2.2 x x = 1.9 is a root f(x) 华南师范大学数学科学学院 谢骊玲
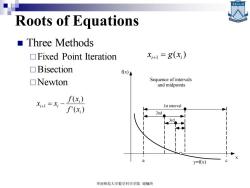
Roots of Equations ■Three Methods Fixed Point Iteration x+1=g(x) ▣Bisection f(x) ▣Newton Sequence of intervals and midpoints f(x,) X+1=X, f'(x) Ist interval 2nd y=f(x) 华南师范大学数学科学学院谢骊玲
Roots of Equations ◼ Three Methods Fixed Point Iteration Bisection Newton ( ) i 1 i x = g x + 华南师范大学数学科学学院 谢骊玲 1st interval 2nd 3rd a c x f(x) Sequence of intervals and midpoints y=f(x) '( ) ( ) 1 i i i i f x f x x + = x −
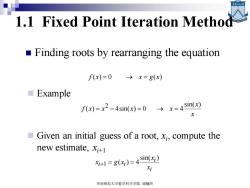
1.1 Fixed Point Iteration Method Finding roots by rearranging the equation f(x)=0 →x=g(x) ■Example f(x)=x2-4sin(x)=0x=4sin(x) Given an initial guess of a root,xi,compute the new estimate,xi+ i+1=8(x)=4sin() x 华南师范大学数学科学学院谢骊玲
1.1 Fixed Point Iteration Method ◼ Finding roots by rearranging the equation f (x) = 0 → x = g(x) x x f x x x x sin( ) ( ) 4sin( ) 0 4 2 = − = → = i i i i x x x g x sin( ) +1 = ( ) = 4 ◼ Example ◼ Given an initial guess of a root, xi , compute the new estimate, xi+1 华南师范大学数学科学学院 谢骊玲
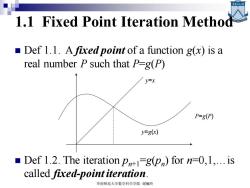
1.1 Fixed Point Iteration Method Def 1.1.A fixed point of a function g(x)is a real number P such that P-g(P) V=x P=gP) y=g(x) Def 1.2.The iteration p(p)for n-0,1,...is called fixed-point iteration. 华南师范大学数学科学学院谢骊玲
1.1 Fixed Point Iteration Method ◼ Def 1.1. A fixed point of a function g(x) is a real number P such that P=g(P) ◼ Def 1.2. The iteration pn+1 =g(pn ) for n=0,1,…is called fixed-point iteration. y=x y=g(x) P=g(P) 华南师范大学数学科学学院 谢骊玲

1.1 Fixed Point Iteration Method An iteration process is repeated until an answer is achieved A rule or function g(x)for computing successive terms is needed,together with a starting value po. A sequence of value p}is obtained using the iterative rule pki=g(p):pk)=po pi-g(po), P2=gP1),…,P=8Pk-1),Pk+1=8Pk…}. If the numbers tend to a limit,something has been achieved. 华南师范大学数学科学学院谢骊玲
1.1 Fixed Point Iteration Method ◼ An iteration process is repeated until an answer is achieved. ◼ A rule or function g(x) for computing successive terms is needed, together with a starting value p0 . ◼ A sequence of value {pk} is obtained using the iterative rule pk+1=g(pk ) : {pk}={p0 , p1=g(p0 ), p2=g(p1 ), …, pk=g(pk-1 ), pk+1=g(pk ),…}. ◼ If the numbers tend to a limit, something has been achieved. 华南师范大学数学科学学院 谢骊玲
1.1 Fixed Point Iteration Method Thm 1.1.Assume that g is a continuous function and that {p,is a sequence generated by fixed-point iteration.If lim,P,then P is a fixed point of g(x).g(x) is an iteration function. Finding roots of equations fx)=0 is equivalent to finding the fixed point of g(x). 华南师范大学数学科学学院谢骊玲
1.1 Fixed Point Iteration Method ◼ Thm 1.1. Assume that g is a continuous function and that is a sequence generated by fixed-point iteration. If limn→∞pn =P, then P is a fixed point of g(x). g(x) is an iteration function. ◼ Finding roots of equations f(x)=0 is equivalent to finding the fixed point of g(x). 0 { }n n p = 华南师范大学数学科学学院 谢骊玲
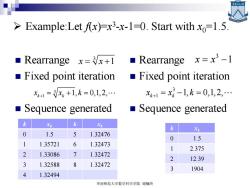
Example:Let fx)-x3-x-1-0.Start with xo-1.5 ■Rearrange x=/x+l ■Rearrange x=x3-l Fixed point iteration Fixed point iteration x+1=x+1,k=0,1,2, Xk+1=x2-1,k=0,1,2,… ■ Sequence generated Sequence generated 玉 X 0 1.5 5 1.32476 0 1.5 1 1.35721 6 1.32473 1 2.375 2 1.33086 7 1.32472 2 12.39 3 1.32588 6 1.32472 3 1904 4 1.32494 华南师范大学数学科学学院谢骊玲
➢ Example:Let f(x)=x 3 -x-1=0. Start with x0=1.5. ◼ Rearrange ◼ Fixed point iteration ◼ Sequence generated ◼ Rearrange ◼ Fixed point iteration ◼ Sequence generated 3 x x = +1 3 1 1, 0,1,2, k k x x k + = + = k xk k xk 0 1.5 5 1.32476 1 1.35721 6 1.32473 2 1.33086 7 1.32472 3 1.32588 8 1.32472 4 1.32494 3 x x = −1 3 1 1, 0,1,2, k k x x k + = − = k xk 0 1.5 1 2.375 2 12.39 3 1904 华南师范大学数学科学学院 谢骊玲

1.1 Fixed Point Iteration Method The forms of iteration are not unique,and the sequences are also different.Some is convergent while some isn't.Only the convergent process is meaningful. What factors are involved in the convergence of the process? the existence of the fixed point of the iteration function and the convergence of the process the convergence speed of the process(the efficiency of computation) the reliability of the final approximate result(error analysis) 华南师范大学数学科学学院谢骊玲
◼ The forms of iteration are not unique, and the sequences are also different. Some is convergent while some isn’t. Only the convergent process is meaningful. • What factors are involved in the convergence of the process? • the existence of the fixed point of the iteration function and the convergence of the process • the convergence speed of the process(the efficiency of computation) • the reliability of the final approximate result(error analysis) 1.1 Fixed Point Iteration Method 华南师范大学数学科学学院 谢骊玲

Conditions for the existence of a fixed point ■Thm.1.2.Assume that g(x)∈C[a,b], If the range of the mapping y=g(x)satisfies ye[a,b] for all x∈[a,b], then g has a fixed point in [a,b]. Furthermore,suppose that g'(x)is defined over(a,b) and that a positive constant K<1 exists with lg'(x)K<1 for all xE(a,b);then g has a unique fixed point P in [a,b]. 华南师范大学数学科学学院谢骊玲
Conditions for the existence of a fixed point ◼ Thm. 1.2. Assume that g(x)∈C[a, b]. If the range of the mapping y= g(x) satisfies y∈[a, b] for all x∈[a, b], then g has a fixed point in [a, b]. Furthermore, suppose that g’(x) is defined over (a, b) and that a positive constant K<1 exists with |g’(x)|≤K<1 for all x∈(a, b); then g has a unique fixed point P in [a, b]. 华南师范大学数学科学学院 谢骊玲
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验16 常微分方程初值问题的数值解法 习题.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(讲义)实验16 常微分方程初值问题的数值解.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验16 常微分方程初值问题的数值解法 参考答案.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验15 特征值与特征向量 参考答案.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验15 特征值与特征向量 习题.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(讲义)实验15 特征值与特征向量.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验14 数值最优化方法 参考答案.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(讲义)实验14 数值最优化方法.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验14 数值最优化方法 习题.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(讲义)实验13 数值微分和数值积分.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验13 数值微分和数值积分 习题.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验13 数值微分和数值积分 参考答案.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验12 贝塞尔曲线和B样条曲线 参考答案.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(讲义)实验12 贝塞尔曲线和B样条曲线.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验12 贝塞尔曲线和B样条曲线 习题.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(讲义)实验11 最小二乘曲线拟合.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验11 最小二乘曲线拟合 习题.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验11 最小二乘曲线拟合 参考答案.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验10 样条插值 习题.docx
- 华南师范大学:《MATLAB数值分析实验》课程教学资源(作业习题)实验10 样条插值 参考答案.docx
- 华南师范大学:《数值计算方法》课程PPT教学课件(数值分析 Numerical Analysis)Chapter 2 Solution of Linear Systems AX=B.pptx
- 华南师范大学:《数值计算方法》课程PPT教学课件(数值分析 Numerical Analysis)Chapter 3 Interpolation and Polynomial Approximation.pptx
- 华南师范大学:《数值计算方法》课程PPT教学课件(数值分析 Numerical Analysis)Chapter 4 Curve Fitting.pptx
- 华南师范大学:《数值计算方法》课程PPT教学课件(数值分析 Numerical Analysis)Chapter 5 Numerical Integration.pptx
- 华南师范大学:《数值计算方法》课程PPT教学课件(数值分析 Numerical Analysis)Chapter 6 Solution of Differential Equations.ppt
- 华南师范大学:《数值计算方法》课程PPT教学课件(数值分析 Numerical Analysis)Introduction to Numerical Methods.pptx
- 华南师范大学:《数值计算方法》课程PPT教学课件(数值分析 Numerical Analysis)Numerical Differentiation.pptx
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《高等数学选讲》课程教学大纲 Selected Lectures on Advanced Mathematics I.docx
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《应用回归分析》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《统计预测与决策》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《偏微分方程》课程教学大纲.docx
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《程序设计基础(C语言)》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《MATLAB》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《MATLAB》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《常微分方程》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《R程序设计语言》实验课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《R程序设计语言》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《高等数学》课程教学大纲 Higher mathematics I.doc
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《高等数学概论课程》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东财经大学:统计与数学学院《高等代数》课程教学大纲 Advanced Algebra I.doc
