吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Introduction to Pharmacology

Introduction to Pharmacology
Introduction to Pharmacology

Overview The aim of drug therapy ■Drug target tissue Absorption Distribution Metabolism Elimination The route of administration is determined by the properties of the drug and by the therapeutic objectives.Enteral and parenteral
Overview ◼ The aim of drug therapy ◼ Drug target tissue ◼ Absorption Distribution Metabolism Elimination ◼ The route of administration is determined by the properties of the drug and by the therapeutic objectives. Enteral and parenteral

Drug at site of administration Absorption (input) Drug in plasma 2Distribution Drug in tissues Metabolism Metabollte(s)in tissues ④Elimination (output) Drug and/or metabolite(s) in urine,feces,bile Figure 1.1 Schematic representation of drug absorption,distribution,metabolism and elimination

enteral Oral:the most common route Sublingual:allows the drug to diffuse into the capillary network ■ Rectal:Fifty percent of the drainage of the rectal region bypasses portal circulation
enteral ◼ Oral: the most common route ◼ Sublingual: allows the drug to diffuse into the capillary network ◼ Rectal: Fifty percent of the drainage of the rectal region bypasses portal circulation

parenteral Intravascular:IV injection is the most common route used for drugs that are not absorbed orally. Intramuscular:can be aqueous solutions or specialized depot preparations Subcutaneous:slower than the IV route and minimizes the risks associated with IV
parenteral ◼ Intravascular: IV injection is the most common route used for drugs that are not absorbed orally. ◼ Intramuscular: can be aqueous solutions or specialized depot preparations ◼ Subcutaneous: slower than the IV route and minimizes the risks associated with IV

Other Inhalation:provides the rapid delivery across the surface area of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract Intranasal:desmopressin in the treatment of diabetes insipidus. Intrathecal/intraventricular:to introduce drugs directly into the CSF. Topical:the application is used when a local effect of the drug is desired
Other ◼ Inhalation: provides the rapid delivery across the surface area of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. ◼ Intranasal: desmopressin in the treatment of diabetes insipidus. ◼ Intrathecal/intraventricular: to introduce drugs directly into the CSF. ◼ Topical: the application is used when a local effect of the drug is desired
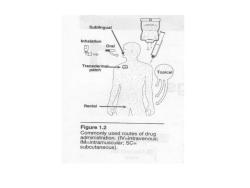
Sublingual Inhalation Oral patch Topica Rectal Figure 1.2 Commonly used routes of drug administration.(IV=intravenous; IM=intramuscular;SC= subcutaneous)

Absorption of drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the blood stream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration
Absorption of drugs ◼ Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the blood stream. The rate and efficiency of absorption depend on the route of administration

Transport of drug from the GI tract Passive diffusion:moves from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration. Active transport:involves specific carrier proteins.Energy-dependent.Against a concentration gradient
Transport of drug from the GI tract ◼ Passive diffusion: moves from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration. ◼ Active transport: involves specific carrier proteins. Energy-dependent. Against a concentration gradient

Effect of pH on drug absorption Weak acids or weak bases HAH++A+ BH B+H+ the effective concentration of the permeable form of each drug at its absorption site is determined by the relative concentrations of the charged and uncharged forms
Effect of pH on drug absorption ◼ Weak acids or weak bases HA H++A + BH B+H+ the effective concentration of the permeable form of each drug at its absorption site is determined by the relative concentrations of the charged and uncharged forms
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Beta-adrenergic blocking agents.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Adrenergic agonists.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第四十五章 抗结核病药及抗麻风病药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第十五章 镇静催眠药 Sedatives and hypnotics.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第十八章 抗精神病药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第二十六章 治疗充血性心力衰竭的药物.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第二十三章 肾素-血管紧张素系统药理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第三十八章 抗菌药物概论.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第十七章 治疗中枢神经系统退行性疾病药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第三十六章 甲状腺激素及抗甲状腺药 Thyroid and Antithyroid drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第四十二章 四环素类及氯霉素类.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第四十三章 人工合成抗菌药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第三十五章 肾上腺皮质激素类药物.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第三十一章 作用于呼吸系统的药物.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第二十七章 抗心绞痛药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第十六章 抗癫痫抗惊厥药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第九章 胆碱受体阻断药 Cholinoceptor blocking drugs(N胆碱受体阻断药,2/2).ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第十章 肾上腺素受体激动药 Adrenoceptor agonists.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第二十九章 影响血液和造血器官的药物.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第四十四章 抗病毒药和抗真菌药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)The autonomic nervous system.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antituberculous drug.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Chemotherapeutic Medicine.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)β-Lactam Antibiotics.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antimicrobial Agents - General Consideration.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antidepressant drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Treatment of Parkinson’s disease.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Neuroleptic drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Anxiolytic and hypnotic drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Anti hypertensive Drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Anticancer Drug.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antianginal Drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Drugs Used to Treat Epilepsy.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Macrolides(Erythromycin).ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Drugs Affecting Blood.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Drugs Affecting the Respiratory System.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Opioid Analgesics and Antagonists.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Diuretic Drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antiarrhythmic drugs.ppt
