吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Anti hypertensive Drugs

Anti hypertensive Drugs
Anti hypertensive Drugs

OVERVIEW Hypertension is defined as a sustained diastolic blood pressure greater than 90 mm Hg accompanied by an elevated systolic blood pressure (>140 mm Hg)
OVERVIEW ◼ Hypertension is defined as a sustained diastolic blood pressure greater than 90 mm Hg accompanied by an elevated systolic blood pressure (>140 mm Hg)

Tab.1 Definitions and classifications of blood pressure levels. Category Systolic Diastolic Stroke mortality [mm Hgl (mm Hg] Relative risk Optimal <120 and <80 1.00 Normal <130 and <85 1,73 High normal 130-1390r 85-90 2.14 Hypertension Stage 1(mild) 140-1590r 90-99 3.58 Subgroup:borderline 140-149 90-94 Stage2(moderate) 160-1790r 100-109 6.90 Stage3(severe) 2180 or 2110 9.66 Isolated systolichypertension ≥140and<90 Subgroup:borderline 140-149 and <90 The higher cateory appies if systoliand diastolicblood presurevalues ofa patient fallintoifferentcatris

can lead to congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction,renal damage, and cerebrovascular accidents
◼ can lead to congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, renal damage, and cerebrovascular accidents

ETIOLOGY OF HYPERTENSION more than 90%of patients have essential hypertension,a disorder of unknown origin affecting the blood pressure-regulating mechanism. ■Inheritance factors Environmental factors such as a stressful lifestyle,high dietary intake of sodium,obesity
ETIOLOGY OF HYPERTENSION ◼ more than 90% of patients have essential hypertension, a disorder of unknown origin affecting the blood pressure-regulating mechanism. ◼ Inheritance factors ◼ Environmental factors such as a stressful lifestyle, high dietary intake of sodium, obesity

MECHANISMS FOR CONTROLLING BLOOD PRESSURE In both normal and hypertensive individuals,cardiac output and peripheral resistance are controlled mainly by two overlapping control mechanisms:the baroreflexes mediated by the sym-pathetic nervous system, and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
MECHANISMS FOR CONTROLLING BLOOD PRESSURE ◼ In both normal and hypertensive individuals, cardiac output and peripheral resistance are controlled mainly by two overlapping control mechanisms: the baroreflexes mediated by the sym- pathetic nervous system, and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
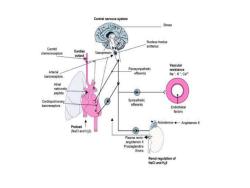
Central nervous systom Stress Nucleus tractus soltarius Carotd chemoreceptors Cardiac output Vascular resistance Arteral efferents Na'K"Ca baroreceptors Atrial natriuretic peptde Cardicpumonary Sympathetic barorecoptors Endothelal factors Preload I (NaCl and H,0) Plasma renin angictensin ll Prostaglandins Kinins Renal regulation of NaCl and H.o

TREATMENT STRATEGIES Mild hypertension can often be controlled with a single drug. More severe hypertension may require treatment with several drugs that are selected to minimize adverse effects of the combined regimen. Treatment is initiated with any of four drugs depending on the individual patient:a diuretic, a [beta-blocker,an ACE inhibitor,or a calcium channel blocker
TREATMENT STRATEGIES ◼ Mild hypertension can often be controlled with a single drug. ◼ More severe hypertension may require treatment with several drugs that are selected to minimize adverse effects of the combined regimen. ◼ Treatment is initiated with any of four drugs depending on the individual patient: a diuretic, a •beta-blocker, an ACE inhibitor, or a calcium channel blocker
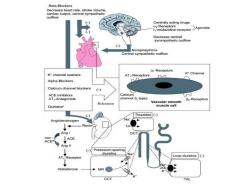
Beta-Blockers Decrease heart rate,stroke volume Centrally acting drugs Receptors 1,-imidazoline-receptorAgorists Decrease central symmpathetic outflow -) Norepinephrine Central sympathetic outfow o,-Receptors K'channel openers AT,-Receptors K'Channel n Alpha-Blockers Calcium channel blockers ACE inhibitors Calciun AT:-Antagonists channel(L-type) B2-Receptors Relaxation Vascular smooth Diuretics" muscle cell Thiazides (- Na non (-) 45a Loop diuretics(-)

DIURETICS Diuretics are currently recommended as the first-line drug therapy for hypertension. Low-dose diuretic therapy is safe and effective in preventing stroke, myocardial infarction,congestive heart failure and total mortality
DIURETICS ◼ Diuretics are currently recommended as the first-line drug therapy for hypertension. ◼ Low-dose diuretic therapy is safe and effective in preventing stroke, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure and total mortality
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Anxiolytic and hypnotic drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Neuroleptic drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Treatment of Parkinson’s disease.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antidepressant drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antimicrobial Agents - General Consideration.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)β-Lactam Antibiotics.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Chemotherapeutic Medicine.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antituberculous drug.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)The autonomic nervous system.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Introduction to Pharmacology.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Beta-adrenergic blocking agents.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Adrenergic agonists.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第四十五章 抗结核病药及抗麻风病药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第十五章 镇静催眠药 Sedatives and hypnotics.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第十八章 抗精神病药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第二十六章 治疗充血性心力衰竭的药物.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第二十三章 肾素-血管紧张素系统药理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第三十八章 抗菌药物概论.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第十七章 治疗中枢神经系统退行性疾病药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第三十六章 甲状腺激素及抗甲状腺药 Thyroid and Antithyroid drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Anticancer Drug.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antianginal Drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Drugs Used to Treat Epilepsy.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Macrolides(Erythromycin).ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Drugs Affecting Blood.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Drugs Affecting the Respiratory System.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Opioid Analgesics and Antagonists.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Diuretic Drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antiarrhythmic drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)药理学步进教程(共四十九章).docx
- 石河子大学:《药理学》课程教学资源(教案,共二十八讲).docx
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第一篇 药理学总论.pdf
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第二篇 传出神经系统药理.pdf
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第三篇 中枢神经系统药理.pdf
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第四篇 心血管药理.pdf
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第五篇 内脏药理.pdf
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第六篇 内分泌药理.pdf
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第七篇 化疗药物.pdf
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验二 常用实验动物的捉拿固定和给药方法.pdf
