吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Treatment of Parkinson’s disease

Treatment of Parkinson's disease
Treatment of Parkinson’s disease

Overview of CNS Act presynaptically by influencing the production,storage,or termination of action of neurotransmitters. Other agents may activate or block postsynaptic receptor
Overview of CNS • Act presynaptically by influencing the production, storage, or termination of action of neurotransmitters. • Other agents may activate or block postsynaptic receptor

Neurotransmission in the CNS Similar to autonomic nervous system The circuitry of the CNS is much more complex than the autonomic nervous system Contains powerful networks of inhibitory neurons that are constantly active More than 10 neurotransmitters
Neurotransmission in the CNS • Similar to autonomic nervous system • The circuitry of the CNS is much more complex than the autonomic nervous system • Contains powerful networks of inhibitory neurons that are constantly active • More than 10 neurotransmitters

Synaptic potentials Receptors at most synapses are coupled to ion channels. Depolarization or hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane,depending on the specific ions that move and the direction
Synaptic potentials • Receptors at most synapses are coupled to ion channels. • Depolarization or hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane, depending on the specific ions that move and the direction

Excitatory pathways Excitatory postsynaptic potential(EPSP) are generated by the following 1.stimulation of an excitatory neuron causes the release of neurotransmitter molecules 2.The influx of Na+causes a weak depolarization 3.Pass a threshold,and an all-or-none action potential is generated
Excitatory pathways • Excitatory postsynaptic potential(EPSP) are generated by the following 1. stimulation of an excitatory neuron causes the release of neurotransmitter molecules 2. The influx of Na+ causes a weak depolarization 3. Pass a threshold, and an all-or-none action potential is generated
Inhibitory pathways Results in a hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane.Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP)are 1.releases neurons releases neurotransmitter molecules, such as y-aminobutyric acid (GABA)or glycine.Increase in the permeability of specific ions,such as,potassium and chloride ions 2.the influx of chloride and efflux of potassium cause a weak hyperpolarization or IPSP that moves the postsynaptic potential away from its firing threshold
Inhibitory pathways • Results in a hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane. Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP) are 1. releases neurons releases neurotransmitter molecules, such as γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) or glycine. Increase in the permeability of specific ions, such as, potassium and chloride ions 2. the influx of chloride and efflux of potassium cause a weak hyperpolarization or IPSP that moves the postsynaptic potential away from its firing threshold

Overview of parkinson's disease Parkinson's disease(PD)is a progressive disorder of the nervous system.With an annual incidence of approximately 20 new cases per 100,000 people. PD is generally age-specific;it is estimated that approximately 1%of the population over age 60 has PD
Overview of parkinson’s disease • Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive disorder of the nervous system. With an annual incidence of approximately 20 new cases per 100,000 people. • PD is generally age-specific; it is estimated that approximately 1% of the population over age 60 has PD
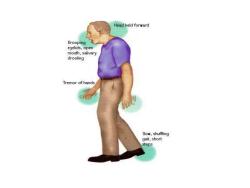
Head held forward Drooping eyelids,open mouth,salivary drooling Tremor of hands Slow,shuffing gait,short steps

Etiology Is correlated with a reduction in the activity of inhibitory dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and corpus striatum
Etiology • Is correlated with a reduction in the activity of inhibitory dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and corpus striatum
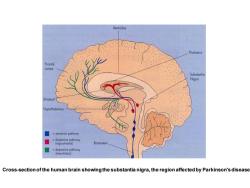
Ventricles Thalamus Fronta cortex Substantia Nigra Striatum Hypothalamu -dopamine pathway Brainstem =dopamine pathway Cross-section of the human brain showing the substantia nigra,the region affected by Parkinson's disease
Cross-section of the human brain showing the substantia nigra, the region affected by Parkinson's disease
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antidepressant drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antimicrobial Agents - General Consideration.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)β-Lactam Antibiotics.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Chemotherapeutic Medicine.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antituberculous drug.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)The autonomic nervous system.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Introduction to Pharmacology.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Beta-adrenergic blocking agents.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Adrenergic agonists.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第四十五章 抗结核病药及抗麻风病药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第十五章 镇静催眠药 Sedatives and hypnotics.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第十八章 抗精神病药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第二十六章 治疗充血性心力衰竭的药物.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第二十三章 肾素-血管紧张素系统药理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第三十八章 抗菌药物概论.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第十七章 治疗中枢神经系统退行性疾病药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第三十六章 甲状腺激素及抗甲状腺药 Thyroid and Antithyroid drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第四十二章 四环素类及氯霉素类.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第四十三章 人工合成抗菌药.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(五年制)第三十五章 肾上腺皮质激素类药物.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Neuroleptic drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Anxiolytic and hypnotic drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Anti hypertensive Drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Anticancer Drug.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antianginal Drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Drugs Used to Treat Epilepsy.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Macrolides(Erythromycin).ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Drugs Affecting Blood.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Drugs Affecting the Respiratory System.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Opioid Analgesics and Antagonists.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Diuretic Drugs.ppt
- 吉林大学:《药理学》课程PPT教学课件(七年制)Antiarrhythmic drugs.ppt
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)药理学步进教程(共四十九章).docx
- 石河子大学:《药理学》课程教学资源(教案,共二十八讲).docx
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第一篇 药理学总论.pdf
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第二篇 传出神经系统药理.pdf
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第三篇 中枢神经系统药理.pdf
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第四篇 心血管药理.pdf
- 《药理学》课程教学资源(讲义)第五篇 内脏药理.pdf
