河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(本科双语教学)第八章 蛋白质的生物合成 Enzymes Kinetics
Chapter 8-Enzymes Kinetics Contact to allorteric ite of ofer bni
Chapter 8 – Enzymes Kinetics
Introduction to Enzymes Thousands of biochemical reactions proceed at any given instant within living cells.These reactions are catalyzed by en☑ymes, Enzymes are mostly proteins.But two important enzymes are most certainly to be RNA(ribozymes).One is the ribosome (peptidyl transfer)and the other is the splicesome (splicing of intron); Enzymes are the agents of metabolic function.Enzymes play key functions in controlling rate of reaction,coupling reactions,and sensing the momentary metabolic needs of the cell
Introduction to Enzymes • Thousands of biochemical reactions proceed at any given instant within living cells. These reactions are catalyzed by enzymes; • Enzymes are mostly proteins. But two important enzymes are most certainly to be RNA (ribozymes). One is the ribosome (peptidyl transfer) and the other is the splicesome (splicing of intron); • Enzymes are the agents of metabolic function. Enzymes play key functions in controlling rate of reaction, coupling reactions, and sensing the momentary metabolic needs of the cell

8.1.Enzymes-Catalytic Power, Specificity,and Regulation Enzymes are characterized by three distinctive features: catalytic power, specificity, regulation
8.1 • Enzymes—Catalytic Power, Specificity, and Regulation Enzymes are characterized by three distinctive features: catalytic power, specificity, regulation
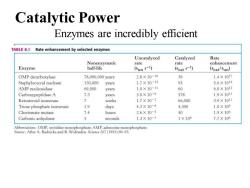
Catalytic Power Enzymes are incredibly efficient TABLE 8.1 Rate enhancement by selected enzymes Uncatalyzed Catalyzed Rate Nonenzymatic rate rate enhancement Enzyme half-life (kun s-1) (kcat s-1) (kcat/kun) OMP decarboxylase 78,000,000 years 2.8×10-16 39 1,4×1017 Staphylococcal nuclease 130.000 years 1.7×10-13 95 5.6×1014 AMP nucleosidase 69,000 years 1.0×10-11 60 6.0×1012 Carboxypeptidase A 7.3 years 3.0×10-9 578 1.9×1010 Ketosteroid isomerase 7 weeks 1.7×10-7 66,000 3.9×10日 Triose phosphate isomerase 1.9 days 4.3×10-6 4,300 1.0×109 Chorismate mutase 7.4 hours 2.6×10-5 50 1.9×106 Carbonic anhydrase seconds 1.3×10-1 1×106 7.7×106 Abbreviations:OMP,orotidine monophosphate:AMP.adenosine monophosphate. Source:After A.Radzicka and R.Wofenden.Science 267 (1995):90-93
Enzymes are incredibly efficient Catalytic Power

Enzyme Specificity The selective qualities of an enzyme are collectively recognized as its specificity. Intimate interaction between an enzyme and its substrates occurs through molecular recognition based on structural complementarity;such mutual recognition is the basis of specificity.The specific site on the enzyme where substrate binds and catalysis occurs is called the active site
Enzyme Specificity The selective qualities of an enzyme are collectively recognized as its specificity. Intimate interaction between an enzyme and its substrates occurs through molecular recognition based on structural complementarity; such mutual recognition is the basis of specificity. The specific site on the enzyme where substrate binds and catalysis occurs is called the active site
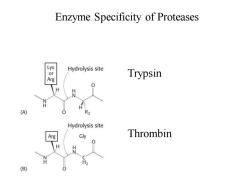
Enzyme Specificity of Proteases Or Hydrolysis site Trypsin Arg H (A) Hydrolysis site Arg Gly Thrombin H (B)
Enzyme Specificity of Proteases Trypsin Thrombin

Regulation Regulation of enzyme activity is achieved in a variety of ways,ranging from controls over the amount of enzyme protein produced by the cell to more rapid,reversible interactions of the enzyme with metabolic inhibitors and activators. Next chapter is devoted to discussions of enzyme regulation.Because most enzymes are proteins, we can anticipate that the functional attributes of enzymes are due to the remarkable versatility found in protein structures
Regulation Regulation of enzyme activity is achieved in a variety of ways, ranging from controls over the amount of enzyme protein produced by the cell to more rapid, reversible interactions of the enzyme with metabolic inhibitors and activators. Next chapter is devoted to discussions of enzyme regulation. Because most enzymes are proteins, we can anticipate that the functional attributes of enzymes are due to the remarkable versatility found in protein structures
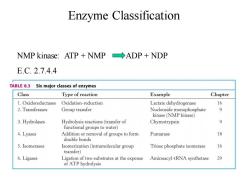
Enzyme Classification NMP kinase:ATP NMP ADP NDP E.C.2.7.4.4 TABLE 8.3 Six major classes of enzymes Class Type of reaction Example Chapter 1.Oxidoreductases Oxidation-reduction Lactate dehydrogenase 16 2.Transferases Group transfer Nucleoside monophosphate kinase(NMP kinase) 3.Hydrolases Hydrolysis reactions(transfer of Chymotrypsin functional groups to water) 4.Lyases Addition or removal of groups to form Fumarase 18 double bonds 5.Isomerases Isomerization(intramolecular group Triose phosphate isomerase 16 transfer) 6.Ligases Ligation of two substrates at the expense Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase 29 of ATP hydrolysis
Enzyme Classification NMP kinase: ATP + NMP ADP + NDP E.C. 2.7.4.4

Enzyme co-factors Apoenzyme cofactor holoenzyme TABLE 8.2 Enzyme cofactors Cofactor Enzyme Coenzyme Thiamine pyrophosphate Pyruvate dehydrogenase Flavin adenine nucleotide Monoamine oxidase Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide Lactate dehydrogenase Pyridoxal phosphate Glycogen phosphorylase Coenzyme A(CoA) Acetyl CoA carboxylase Biotin Pyruvate carboxylase 5'-Deoxyadenosyl cobalamin Methylmalonyl mutase Tetrahydrofolate Thymidylate synthase Metal Zn2+ Carbonic anhydrase Zn2+ Carboxypeptidase Mg2+ EcoRV Mg2+ Hexokinase Ni2+ Urease o Nitrate reductase Glutathione peroxidase Mn2+ Superoxide dismutase K+ Propionyl CoA carboxylase
Enzyme co-factors Apoenzyme + cofactor = holoenzyme

Cofactor (Coenzyme and Prosthetic Group) In most cases,a coenzyme is firmly associated with its enzyme,perhaps even by covalent bonds, and it is difficult to separate the two.Such tightly bound coenzymes are referred to as prosthetic groups of the enzyme.The catalytically active complex of protein and prosthetic group is called the holoenzyme.The protein without the prosthetic group is called the apoenzyme;it is catalytically inactive
Cofactor (Coenzyme and Prosthetic Group) In most cases, a coenzyme is firmly associated with its enzyme, perhaps even by covalent bonds, and it is difficult to separate the two. Such tightly bound coenzymes are referred to as prosthetic groups of the enzyme. The catalytically active complex of protein and prosthetic group is called the holoenzyme. The protein without the prosthetic group is called the apoenzyme; it is catalytically inactive
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(本科双语教学)第七章 核酸的生物合成 Structure of Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(本科双语教学)第六章 含氮化合物代谢 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(本科双语教学)第二章 蛋白质 Amino Acids.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(基础生物化学)第五章 脂类代谢.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 脂类代谢.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 核酸化学.ppt
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第十章 生物膜的结构与功能 Function and structure of bioomembranes.ppt
- 河南师范大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 统计热力学初步.ppt
- 河南师范大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 热力学第二定律.ppt
- 河南师范大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 胶体及大分子溶液.ppt
- 河南师范大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十七章 胺.ppt
- 河南师范大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 卤代烃 haloalkanes.ppt
- 河南师范大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 烷烃 Alkanes.ppt
- 河南师范大学:《无机化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二十四章 周环反应 Pericyclic reaction.ppt
- 河南师范大学:《无机化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二十一章 P区元素.ppt
- 河南师范大学:《无机化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第十一章 电化学基础.ppt
- 济源职业技术学院:《无机及分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 酸碱平衡和酸碱滴定法.pptx
- 济源职业技术学院:《无机及分析化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 原子结构和元素周期表.pptx
- 石家庄职业技术学院:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 卤代烃.pptx
- 石家庄职业技术学院:《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 烷烃.pptx
- 河南农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验八 硝酸还原酶活性测定.doc
- 青岛农业大学(莱阳农学院):《有机化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十五章 氨基酸、蛋白质和核酸.ppt
- 《无机化学》课程教学资源(课堂教学设计)第11章 配位化学基础.pdf
- 《仪器分析》课程教学资源(试卷习题)仪器分析复习题仪器分析复习题1(含参考答案).doc
- 《仪器分析》课程教学资源(试卷习题)仪器分析复习题仪器分析复习题2(含参考答案).doc
- 《仪器分析》课程教学资源(试卷习题)仪器分析复习题仪器分析复习题3(含参考答案).doc
- 《仪器分析》课程教学资源(试卷习题)仪器分析复习题仪器分析复习题4(含参考答案).doc
- 《仪器分析》课程教学资源(试卷习题)仪器分析复习题仪器分析复习题5(含参考答案).doc
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)卫生化学教案(任课教师:杨红兵).pdf
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)药学分析化学教案(任课教师:杨红兵).pdf
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)仪器分析教案(任课教师:洪成林).pdf
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)仪器分析实验教案(授课教师:齐誉).pdf
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)应化仪器分析教案(任课教师:齐誉).pdf
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)仪器分析教案(2008-2009学年第二学期,任课教师:杨红兵).pdf
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)仪器分析教案(2010-2011学年第一学期,任课教师:杨红兵).pdf
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)仪器分析教案(2010-2011学年第二学期,任课教师:杨红兵).pdf
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)仪器分析教学仪器分析教案(任课教师:洪成林).doc
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)仪器分析教案(2010-2011学年第一学期,授课:齐誉).pdf
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)药学分析化学电子教案.doc
- 石河子大学:《仪器分析》课程教学资源(授课教案)仪器分析教案(任课教师:李文娟).pdf
