《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)17_Electrophoresis
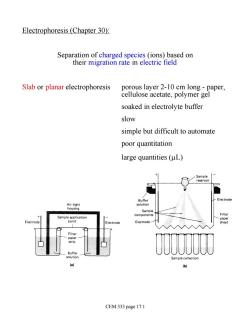
Electrophoresis (Chapter 30): Separation of charged species (ions)based on their migration rate in electric field Slab or planar electrophoresis porous layer 2-10 cm long-paper, cellulose acetate,polymer gel soaked in electrolyte buffer slow simple but difficult to automate poor quantitation large quantities (uL) + Sample Air-tigh housing poliecatio components Electrode uffe ample c 6 CEM 333 page 17.1
Electrophoresis (Chapter 30): Separation of charged species (ions) based on their migration rate in electric field Slab or planar electrophoresis porous layer 2-10 cm long - paper, cellulose acetate, polymer gel soaked in electrolyte buffer slow simple but difficult to automate poor quantitation large quantities (mL) CEM 333 page 17.1
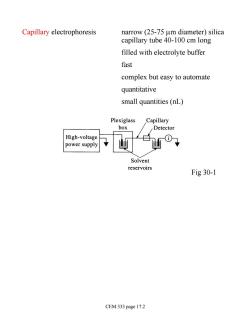
Capillary electrophoresis narrow(25-75 um diameter)silica capillary tube 40-100 cm long filled with electrolyte buffer fast complex but easy to automate quantitative small quantities(nL) Plexiglass Capillary box Detector High-voltage power supply Solvent reservoirs Fig 30-1 CEM 333 page 17.2
Capillary electrophoresis narrow (25-75 mm diameter) silica capillary tube 40-100 cm long filled with electrolyte buffer fast complex but easy to automate quantitative small quantities (nL) Fig 30-1 CEM 333 page 17.2

Migration rate depends on movement in electric field ·molecular weight charge -small/highly-charged species migrate rapidly affected by pH HAH+A affected by ionic strength =(A]ZA2+[B]ZB2) low u,few counter-ions,low charge shielding high u,many counter-ions,high charge shielding CEM 333 page 17.3
Migration rate depends on movement in electric field • molecular weight • charge - small/highly-charged species migrate rapidly - affected by pH HA « H + + A - - affected by ionic strength m = 1 2 [A]×ZA 2 +[B]×ZB 2 ( .) low m, few counter-ions, low charge shielding high m, many counter-ions, high charge shielding CEM 333 page 17.3

Migration Rate: V v=uE=μ migration rate(cm.s1) electric field (V.cm1) electrophoretic mobility (-ve for anions)(cm2.V.s) Electrophoretic mobility depends on net charge and frictional forces (size/molecular weight of analyte) ·Only ions separated Plate Height and Number: N=u.V H=L-2D.L 2D N-HV diffusion coefficient(cm2.s-1) Increase number of plates(better resolution)by increasing V CEM 333 page 17.4
Migration Rate: v = m ×E = m V L migration rate (cm·s-1) electric field (V·cm-1) electrophoretic mobility (-ve for anions) (cm2·V·s) Electrophoretic mobility depends on net charge and frictional forces (size/molecular weight of analyte) • Only ions separated Plate Height and Number: N = m ×V 2D H = L N = 2D×L m× V diffusion coefficient (cm2·s-1) Increase number of plates (better resolution) by increasing V CEM 333 page 17.4

Slab electrophoresis large cross-sectional area,short length low electrical resistance,high currents Sample heating Vmax=500 V N=100-1000 low resolution Capillary electrophoresis small cross-sectional area,long length high resistance,low currents Vmax=20-100 kV N=100.000-10,000,000 high resolution (HPLC N=1,000-20,000) Zone broadening? Single phase(mobile phase)-no partitioning In chromatography three zone broadening phenomena (1) longitudinal diffusion(ii)transport to/from stationary phase(iii) multipath In planar EP no stationary phase In capillary EP no stationary phase or multipath CEM 333 page 17.5
• Slab electrophoresis large cross-sectional area, short length low electrical resistance, high currents Sample heating Vmax=500 V N=100-1000 low resolution • Capillary electrophoresis small cross-sectional area, long length high resistance, low currents Vmax=20-100 kV N=100,000-10,000,000 high resolution (HPLC N=1,000-20,000) Zone broadening? • Single phase (mobile phase) - no partitioning In chromatography three zone broadening phenomena (i) longitudinal diffusion (ii) transport to/from stationary phase (iii) multipath • In planar EP no stationary phase • In capillary EP no stationary phase or multipath CEM 333 page 17.5

Transport Processes in Electrophoresis: Electromigration ions migrating in electric field cations->cathode (-ve) anions→anode(+ve) Electroosmosis movement of entire fluid near wall of capillary in one direction! anode (+ve)->cathode (-ve) (A)Analyte dissolved in background electrolyte and pH buffer (B)Silica capillary wall coated with silanol (Si-OH)and Si-O- (C)Wall attracts cations-double-layer forms (D)Cations move towards cathode and sweep fluid in one direction Electroosmotic flow proportional to V-usually greater than electrophoretic flow CEM 333 page 17.6
Transport Processes in Electrophoresis: Electromigration ions migrating in electric field cations ® cathode (-ve) anions ® anode (+ve) Electroosmosis movement of entire fluid near wall of capillary in one direction! anode (+ve) ® cathode (-ve) (A) Analyte dissolved in background electrolyte and pH buffer (B) Silica capillary wall coated with silanol (Si-OH) and Si-O- (C) Wall attracts cations - double-layer forms (D) Cations move towards cathode and sweep fluid in one direction Electroosmotic flow proportional to V - usually greater than electrophoretic flow CEM 333 page 17.6
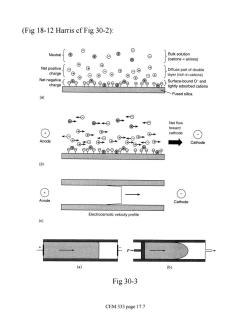
(Fig 18-12 Harris cf Fig 30-2): Neutral{ anions) 0⑧ Diffuse part of double layer(rich in cations) Net negative Surtace. charge Fused silica ⑧ Net flow +) cathode ⊙ Anode ◆ Cathode (+ → Anode Cathode Electroosmotic velocity profile (b) Fig 30-3 CEM 333 page 17.7
(Fig 18-12 Harris cf Fig 30-2): Fig 30-3 CEM 333 page 17.7

+ ④→ -⊙ ④ ④ ○ ⊙ e migration rate electrophoretic mobility v=(μ+ueo)E electric field electroosmotic mobility CEM 333 page 17.8
migration rate electrophoretic mobility v = (m + meo )E electric field electroosmotic mobility CEM 333 page 17.8
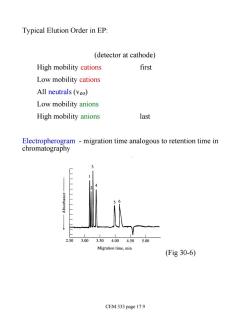
Typical Elution Order in EP: (detector at cathode) High mobility cations first Low mobility cations All neutrals (veo) Low mobility anions High mobility anions last Electropherogram -migration time analogous to retention time in chromatography 2.503.003.504.00 4.50 5.00 Migration time,min (Fig30-6) CEM 333 page 17.9
Typical Elution Order in EP: (detector at cathode) High mobility cations first Low mobility cations All neutrals (veo) Low mobility anions High mobility anions last Electropherogram - migration time analogous to retention time in chromatography (Fig 30-6) CEM 333 page 17.9
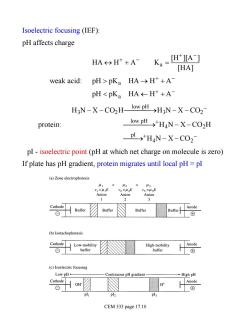
Isoelectric focusing (IEF): pH affects charge HA>H++A- Ka=[HA-] [HA] weak acid:pH>pKa HA>H+A- pHH3N-X-CO2- protein: low pH→+H4N-X-CO2H PI>HaN-X-CO2 pI-isoelectric point(pH at which net charge on molecule is zero) If plate has pH gradient,protein migrates until local pH=pI (a)Zone electrophoresis =41E Anion Anion Anion Cathode 么Buer Buffer (b)Isotachophoresis Cathode Low-mobility High-mobility Anode ⊙1 buffer buffer (c)Isoelectric focusing Low pH- -Continuous pH gradient- →High pH Cathode CEM 333 page 17.10
Isoelectric focusing (IEF): pH affects charge weak acid: HA « H + + A - Ka = [H+ ][A- ] [HA] pH > pKa HA ® H + + A - pH < pKa HA ¬ H + + A - protein: H3N - X - CO2H low pH ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ ® H3N - X - CO2 - low pH ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾ ® +H4N - X - CO2H pI ¾ ¾ ® +H4N - X - CO2 - pI - isoelectric point (pH at which net charge on molecule is zero) If plate has pH gradient, protein migrates until local pH = pI CEM 333 page 17.10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)16_Liquid Chromatography.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)15_Gas Chromatography.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)14 Introduction to Chromatographic Separations.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)13 Flow Injection Analysis.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)12 Voltammetry.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)11 Potentiometry.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)10 Introduction to Electrochemistry.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)09 Atomic Absorption Spectrometry.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)08 Atomic Emission Spectroscopy.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)07 Introduction to Atomic Optical Spectroscopy.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)06 Infrared Spectrometry.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)05 Luminescence Spectroscopy.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)04 UV-Vis(Absorption)Spectrometry.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)03 Optical Spectroscopy and Instrumentation.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)02 Introduction to Spectroscopy.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)01 Instrumental Analysis.pdf
- 山东农业大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十五章 糖类化合物 Saccharides.pdf
- 山东农业大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十三章 杂环化合物和生物碱 Heterocyclic compounds and alkaloids.pdf
- 山东农业大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十二章 含氮和含磷有机化合物 Nitrogenous and phosphorous compounds.pdf
- 山东农业大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十一章 取代酸 Substituted acids.pdf
- 《仪器分析 Instrumental Analysis》课程教学资源(教材讲义)18_Mass Spectrometry.pdf
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十一章 高效毛细管电泳分析 第1节概述.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十一章 高效毛细管电泳分析 第2节高效毛细管电泳的理论基础.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十一章 高效毛细管电泳分析 第3节高效毛细管电泳仪.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十一章 高效毛细管电泳分析 第4节高效毛细管电泳分离模式.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十一章 高效毛细管电泳分析 第5节应用与进展.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十二章 光分析法导论 第1节光分析基础与分类.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十二章 光分析法导论 第2节原子光谱与分子光谱.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十二章 光分析法导论 第3节光谱法仪器与光学器件.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十四章 原子吸收分光光 第1节原子发射光谱分析基本原理.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十三章 原子发射光谱分析法 第2节发射光谱分析装置与仪器.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十三章 原子发射光谱分析法 第3节等离子体发射光谱仪.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十三章 原子发射光谱分析法 第4节定性、定量分析方法.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十四章 原子吸收分光光 第2节原子吸收分光光度仪.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十四章 原子吸收分光光 第3节干扰的类型与抑制.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十四章 原子吸收分光光 第4节操作条件选择与应用.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第十四章 原子吸收分光光 第5节原子荧光光谱分析法.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第二十一章 电子衍射.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第二十二章 透射电子显微分析.ppt
- 《仪器分析》课程教学讲义(PPT课件)第二十三章 扫描电子显微分析与电子探针.ppt
