《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 The design principle of jigs and fixtures

Chapter 2 The design principle of jigs and fixturesabstractIn ordertofulfill the machining requirement ofa certain job,a relativelyaccurate position oftheworkpiece in a machine tool in relation to the cuttingtool during themetal cutting movement must beensured.Thefollowing threeconditionsmust besatisfied when fulfilling such a practical functionwhichare(1)theaccuratepositionofabatchofworkpieces in relation to the jigs or fixtures;(2)theaccurate position ofthejigs orfixtures inrelationtothe machine tool; (3)the accurate position ofthecutting tool in relation to the jigs or fixtures. In thischapter, themainattention is directed to theaccuratepositioningofworkpieces in jigsorfixturesThepositioningofworkpieces inmachinetoolsisindirectly achievedthrough jigs orfixtures
Chapter 2 The design principle of jigs and fixtures abstract In order to fulfill the machining requirement of a certain job, a relatively accurate position of the workpiece in a machine tool in relation to the cutting tool during the metal cutting movement must be ensured. The following three conditions must be satisfied when fulfilling such a practical function, which are (1)the accurate position of a batch of workpieces in relation to the jigs or fixtures;(2) the accurate position of the jigs or fixtures in relation to the machine tool;(3)the accurate position of the cutting tool in relation to the jigs or fixtures. In this chapter, the main attention is directed to the accurate positioning of workpieces in jigs or fixtures. The positioning of workpieces in machine tools is indirectly achieved through jigs or fixtures

8abstract2.1Introduction of jigs or fixtures2.2Thelocation of theworkpiece2.3 Clamping of the workpiece2.4 The basic requirement and designsteps for jigs or fixtures
abstract 2.1 Introduction of jigs or fixtures 2.2 The location of the workpiece 2.3 Clamping of the workpiece 2.4 The basic requirement and design steps for jigs or fixtures
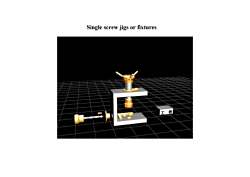
Single screw jigs or fixtures工件
Single screw jigs or fixtures

2.1 Introduction of jigs or fixturesPositioning:in orderto ensurethe accuracy and raisetheefficiency,jigs or fixtures should be used to ensure the accurate position of theworkpieceinrelationtothemachinetool.Clamping :In order to ensure the position of the location underexternalforce,aclampingforcemustbeimposedontheworkpieceSet up :The comprehensive procedure of positioning and clampingJigs or fixtures : The technological equipment to fulfill the procedureofsetup
2.1 Introduction of jigs or fixtures v Positioning : in order to ensure the accuracy and raise the efficiency, jigs or fixtures should be used to ensure the accurate position of the workpiece in relation to the machine tool. v Clamping :In order to ensure the position of the location under external force , a clamping force must be imposed on the workpiece. v Set up :The comprehensive procedure of positioning and clamping v Jigs or fixtures :The technological equipment to fulfill the procedure of set up
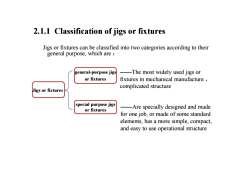
2.1.1 Classification of jigs or fixturesJigsorfixtures canbeclassified intotwocategoriesaccordingtotheirgeneral purpose, which are :-Themostwidelyused jigsorgeneral-purposejigsorfixturesfixtures inmechanical manufacturecomplicated structureJigsorfixturesspecial purpose jigsArespeciallydesignedandmadeorfixturesfor one job, or made of some standardelements,hasamoresimple,compactandeasytouseoperational structure
2.1.1 Classification of jigs or fixtures Jigs or fixtures can be classified into two categories according to their general purpose, which are : general-purpose jigs or fixtures special purpose jigs or fixtures Jigs or fixtures ——Are specially designed and made for one job, or made of some standard elements, has a more simple, compact, and easy to use operational structure ——The most widely used jigs or fixtures in mechanical manufacture , complicated structure
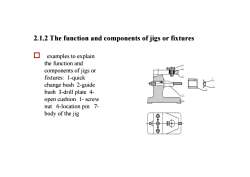
2.1.2 The function and components of jigs or fixturesexamples to explainthe function andcomponents of jigs orfixtures: 1-quickchange bush 2-guidebush 3-drill plate4-opencushion1-screwnut 6-location pin 7-body of the jig
2.1.2 The function and components of jigs or fixtures o examples to explain the function and components of jigs or fixtures: 1-quick change bush 2-guide bush 3-drill plate 4- open cushion 1- screw nut 6-location pin 7- body of the jig

Wecanknowfromtheexample:口2.1.2.1The function of jigs or fixtures :(1)Reduce thenonproductivetime, and raise the productionefficiency;(2) maintain the stability of machining accuracy :(3) enlarge the application scope of machine tools(4) release the working stress, and ensure secure production
We can know from the example: o 2.1.2.1The function of jigs or fixtures : (1)Reduce the nonproductive time, and raise the production efficiency; (2)maintain the stability of machining accuracy ; (3)enlarge the application scope of machine tools (4) release the working stress, and ensure secure production
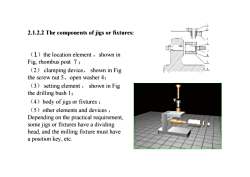
2.1.2.2 The components of jigs or fixtures:(1)thelocationelement,shown inFig, rhombus post 7 ;(2)clampingdevice,showninFigthescrewnut5、openwasher4:(3)settingelement, shown inFigthe drillingbush l;(4)body of jigs or fixtures;(5)otherelementsanddevicesDependingonthepractical requirement.some jigs or fixtures have a dividinghead,andthemillingfixturemusthaveapositionkey,etc
2.1.2.2 The components of jigs or fixtures: (1)the location element ,shown in Fig, rhombus post 7 ; (2) clamping device, shown in Fig the screw nut 5、open washer 4; (3) setting element , shown in Fig the drilling bush 1; (4)body of jigs or fixtures ; (5)other elements and devices , Depending on the practical requirement, some jigs or fixtures have a dividing head, and the milling fixture must have a position key, etc

2.2 The location of the workpiece口2.2.1Theoretical positioningofasolidinspace(isostatismIt is well known that aperfect solid can be positionedinspacebysixparameters,normallythreemoveableparameters and three rotationalparameters.In Fig. 1-2, six degrees offreedom ofa free solidSix degrees of freedom of an object返回
2.2 The location of the workpiece o 2.2.1Theoretical positioning of a solid in space ( isostatism) It is well known that a perfect solid can be positioned in space by six parameters, normally three moveable parameters and three rotational parameters . In Fig.1-2, six degrees of freedom of a free solid Six degrees of freedom of an object
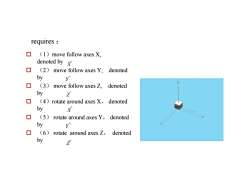
requires :口(1) movefollowaxes X,denoted by x口(2)movefollowaxesY,denotedbyY口(3)denotedmove followaxes Z.byZ口(4)rotatearound axes X, denotedbyx口(5)rotate around axes Y,denotedbyY口(6)rotate aroundaxesZ,denotedbyz
requires : o (1)move follow axes X, denoted by o (2) move follow axes Y, denoted by o (3) move follow axes Z, denoted by o (4)rotate around axes X, denoted by o (5) rotate around axes Y, denoted by o (6) rotate around axes Z, denoted by X v Y v Z v X ) Y ) Z )
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Machining Accuracy.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 the process planning of mechanical manufacturing.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第02章 机床夹具设计原理.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第01章 机械加工工艺规程的制订.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第00章 基本概念(石河子大学:葛云).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第06章 机械制造技术的发展.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第03章 机械加工精度.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第05章 机械装配工艺.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第04章 机械加工表面质量.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Chapter 2 The design principle of jigs and fixtures.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Chapter 1 The Process Planning of mechanical manufacturing.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Chapter 3 Machining Accuracy.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程授课教案(石河子大学:葛云).doc
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程考试大纲.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2 机床夹具设计原理(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)1 工艺规程(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)3 机械加工精度(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(书籍文献)机械制造工艺学习题集(部分有解答).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)4 机械加工质量分析与控制(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 机械制造技术的发展.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 机械加工表面质量.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 机器装配工艺过程设计 Machine Assembling.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 机械加工精度.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 机床夹具设计.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第0章 绪论 Mechanical Manufacturing Technology(石河子大学:葛云).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 机械加工工艺规程设计.pdf
- 《汽车设计》课程教学大纲 Automobile Design.pdf
- 《汽车设计》课程授课教案(文字版).docx
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学大纲 Technology of Machinery Manufacture.pdf
- 《汽车构造》课程授课教案 Brief Introduction of Automobile.pdf
- 《机械原理》课程教学大纲及基本要求(机械原理课程设计).doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学大纲 Theory of Machines and Mechanisms.doc
- 《机械原理》课程实验教学大纲.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)10.1-10.2机械的平衡.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)11.2机械的等效动力学模型和机器运动方程式.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)11.3周期性速度波动及其调节.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)9.1其他常用机构.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)8.1齿轮系分类定轴轮系传动比计算.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)7.4渐开线齿轮的切削加工及变位齿轮.doc
